IANN FileGPS User Manual
1. Introduction:
Pragma Edge FileGPS provides enterprise-wide file/transaction monitoring capabilities, tracks SLA, and provides alerts on events or non-events. FileGPS provides enterprise-wide file/transaction monitoring across any application. Many organizations utilize file transfers as a means of communication between B2B partners or between application-to-application integration; due to various applications involved in handling the end-toend process integration, the end-to-end visibility of the transactions/files are lost, which causes inefficiencies and missed SLA. FileGPS provides the ability to provide enterprise-wide end to end file/transaction monitoring that can track SLA and key events in the processing of the files/transactions.
End to End File monitoring:
FileGPS is can also called as End-to-End file monitoring software that enables organizations to capture, collect, enrich, aggregate, contextualize file events to track and trace files as they move through various disparate IT systems and business applications. FileGPS provides insights for the business to bring situational awareness to the file activities impacting customer business processes and enabling proactive responses to problems or degrading processes.
End to End Transaction Visibility and Reconciliation:
FileGPS provides a simplified business end-user activity dashboard and SLA management interface to allow the business users, most knowledgeable about customer file activity and organizational commitments, to manage, track and get alerts on file activity and SLA noncompliance. Alerts can be personalized and can be received either on the dashboard, by email or SMS or Rest API.
SLA Management:
FileGPS is a single solution that uniquely provides the ability for an organization to perform SLA monitoring and management across disparate IT systems and business applications. It allows for the collection of related events from disparate systems, correlates the events and can apply the business context or nomenclature necessary to make the information presented more meaningful for business users. Business end users can manage and monitor file processes and assign required SLAs because the events can be contextualized in business terms, not IT terms. SLAs can be set at the partner, enterprise, business unit/group and file/transaction levels like Vender SLA’s, Supplier SLA’s, Shipment SLA’s and Healthcare eligibility responses SLA’s, Missed acknowledgements.
Event Correlation:
FileGPS’s sophisticated event correlation engine applies the intelligence to data collected to correlate the various events received from the participating business applications. The engine uniquely identifies files received and links all the events together to trace the lineage and activities of the file as it moves through the enterprise across the various participating applications. It even handles events received out of sequence due to system outages or planned downtime.
Data Security:
FileGPS provides fine-grain access controls for data security and restricting end-user access. The solution allows for end-users and groups to be set up to view and/or manage SLAs for a specific customer or set of customers and can also restrict viewing to a specific file from a specific customer. This enables greater business end-user participation in the solution because they won’t have access to information outside their responsibility. FileGPS provides the ability to create rolebased access to limit the access to the file/transaction.
API Framework:
FileGPS provides an API framework to allow any system to connect to it for real–time file event collection. The framework offers implementation flexibility to accommodate applications with various degrees of openness. The framework allows for event queueing and catchup in the event of systems going off-line.
Data Enrichment:
FileGPS provides a canonical data model for standardizing event data collected from disparate systems within the enterprise. More importantly, FileGPS allows each system in the process to enrich data collected to add more business context to the events being monitored. Business enriched event data provides more meaningful insights for business end user experience and removes the complexity inherent in IT systems with their myriad, disparate identifiers and technical naming conventions.
2. Pragma Edge FileGPS Benefits:
Monitors your Strategic goals, Operational Intelligence, Business Operations and
Process improvements.Monitors Supplier performance, Predictive maintenance.
Manage and react to performance grantee before they are hit.
Manages and guarantees the performance of Business process.
Compare your process performance by industry standards. Integrate any business process except to Specific business users that can resolve a particular business case.
Manages the exception using efficient tracking process.
Send Alerts by email, dashboard and Rest API.
Predicts the KPI based on current and past trends.
Creates ad-hoc business reports, generates multi-dimensional reports as required.
Creates missed sla reports as per entity, transaction volume and error volume reports
Monitors process across wide technology platforms like IBM WebSphere, Microsoft, Oracle Applications, SAP, Mainframe, AS400 and many other technology platforms.
3. Login:
To login into FileGPS Application, we have different roles to access the application which includes super admin, Admin, Data admin, Business User, business admin, business user executive and File Operator.
These are the below input elements that are present in the Login screen.
• Username
• Password
• Show Password
• Login (redirects to Dashboard Screen after successful login).
• Forgot Password
On the Login screen enter the Username and password related to your account for filegps application and then click on login button. It will validate your user credentials and redirect to the home screen of Search file page with user role on the right corner of the header section on top.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | To be filled by the user. |
| Password | Valid Credentials provide access to the application. |
| Show Password | Displays the password, Characters. |
| Sign In | Logs into the application post credential validation. |
Forgot Password:
If you forgot your password, you could easily reset it using the forgotten password link on the login page. All you need is your email address. After entering the details. We can select “Forgot password?” link near the bottom of the login page. After clicking on the forgot password link it will redirect you to the next screen.
On the next screen, enter your email address. Click on the continue button and now check your email which was mentioned we will be sending an OTP (One Time Password) to change your password which will be validated for the next 24 hours. Please enter this one-time password on the next page.
By giving the details in below mentioned screenshot as User ID of the user, New Password to change, Confirm Password of new password given, OTP (one time password) sent.
After providing the details click on the submit button which will successfully change the password to a success message.
File GPS Application provides numerous actions that could be performed on various types of files. We have toggle switch by clicking this, menu will display the modules we have in FileGPS. And we can also collapse the menu which will just display the images of the modules.
By Clicking on toggle switch, below are the different operations modules that are available in the
Dashboard (on the left side of the page).
• Dashboard
• Search Files
• Reports
• Entity
• SLA’s/KPI’s
• Alerts
• Alert Management
• Configure
• Administration
• Access Management
The Home screen of the FileGPS application initially displays the ‘Search Files’ module with ‘Search Files’ sub menu tab of the available operations.
The Layout of the dashboard is categorized into four sections (displayed in all modules)
• Header
• Left Navigation Menu
• Content Area
I) Header:
- The header consists of the Pragma Edge Logo with product name ‘Pragma Edge FileGPS’ on the top left corner.
Toggle Switch: On clicking this, menu will collapse and vice-versa. Welcome message with username of the logged in user is displayed on the top right corner of this section
ii) Left Navigation Menu:
This panel is placed on the left side of the application which displays all operations tabs. where corresponding tabs redirect to their respective pages.
iii) Content Area:
This panel has various fields which fetches the data upon the user search criteria. Based on the input user could perform actions on the data that is fetched or retrieved.
4. Dashboard:
Path:
Login  Dashboard
Dashboard
After logging into the FileGPS Application, users will see FileGPS dashboard. The dashboard provides a comprehensive view of application transaction reports for various FileGPS applications. Users can now access concise information regarding file transaction data across various time intervals, including the number of file transactions that occurred today, this week, this month, this quarter, and this year. On the dashboard, you’ll find a dropdown menu featuring a list of applications integrated with FileGPS. Simply select the desired applications and click the “Retrieve” button to generate a transaction report for the chosen agents.
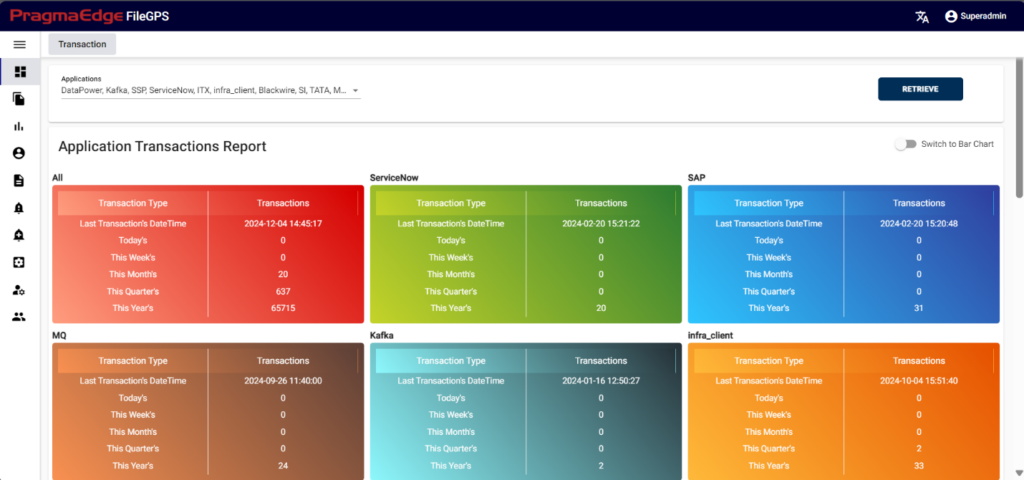
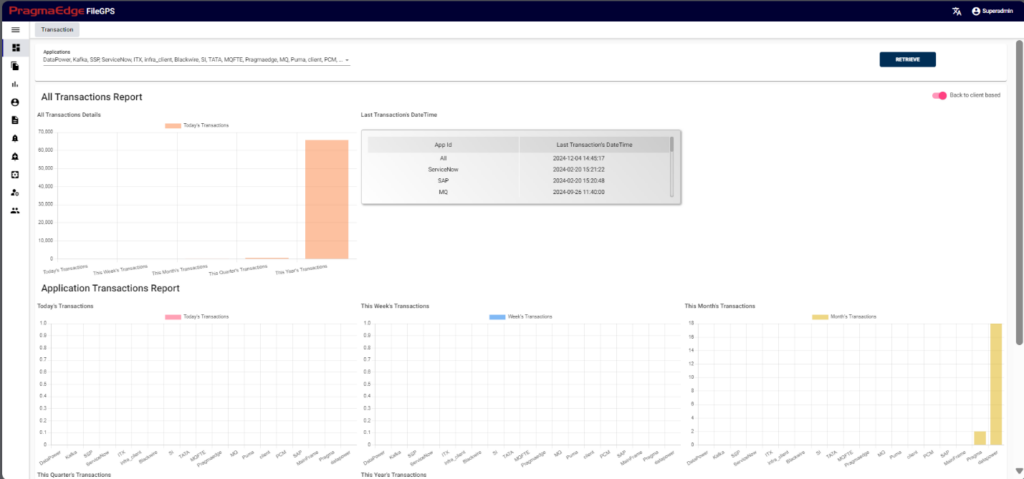
We have a page where users can access graphical representations of file transaction data. To switch between different bar charts for better understanding, simply move the toggle. We’ve organized the file transaction data into bar charts across various time intervals to provide clearer visualization.
5. Search Files:
Search Files provides the entire information regarding a file that was transmitted. There are two sub menu tabs in search files
• Search File
• Queue Depth Search
• File View
• Uncorrelated
• File Search Criteria
5.1. Search Files:
This operation enables the user to search all kinds of Transaction files that were processed
Path:
Login -> Search Files -> Search Files
In this screen, the user can search the entire life cycle of the list of files and their respective status. We can see the file search screen in the below figure
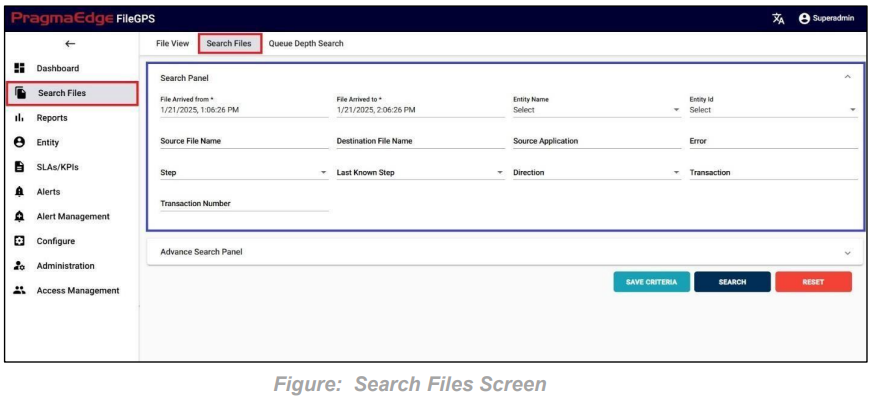
| Property | Description | Format / Rules/ E.g. |
|---|---|---|
| File Arrived Date | The date on which file has arrived from Entity to Application | mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss |
| Entity Name | Name of an entity | IKEA/alpha numeric |
| Entity ID | Unique Identity of entity | IKEA001/alpha numeric |
| Step | State of the file | (Start, process, stop, error) |
| Source File Name | Name of the file that was sent from specific source hub | e.g., FS_Startfile.txt |
| Destination File Name | Name of the file that arrived at destination hub | e.g., FS_Stopfile.txt |
| Error | Error name that occurs in the process of the file | e.g., Transaction Failed |
| Source Application | Node ID/Source application Name | e.g.: FS |
| Last known status | Last status of the file | (Start, Process, Stop, Reprocess, Error) |
| Direction | File direction | (Inbound/Outbound) |
| Transaction | Transaction number of the file (850, 855, 856, 810, 820 etc) | Number |
| Transaction Number | Transaction Id of the file | Number |
| Search (Button) | Used to retrieve/ data based on the input data criteria | |
| Reset (Button) | Used to empty the values of inputs/Clear the existing values/reload the page to build new search |
Note: Here You can use wild card “*” search for better search.
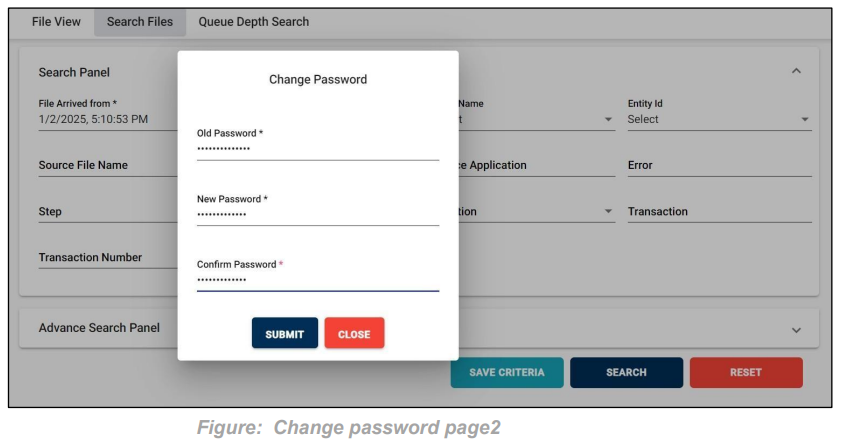
Change Password: To Change FileGPS user password. We can click on user role provided on the right top corner side; it will display “change password”. After clicking on the change password, it will redirect you to the next screen.
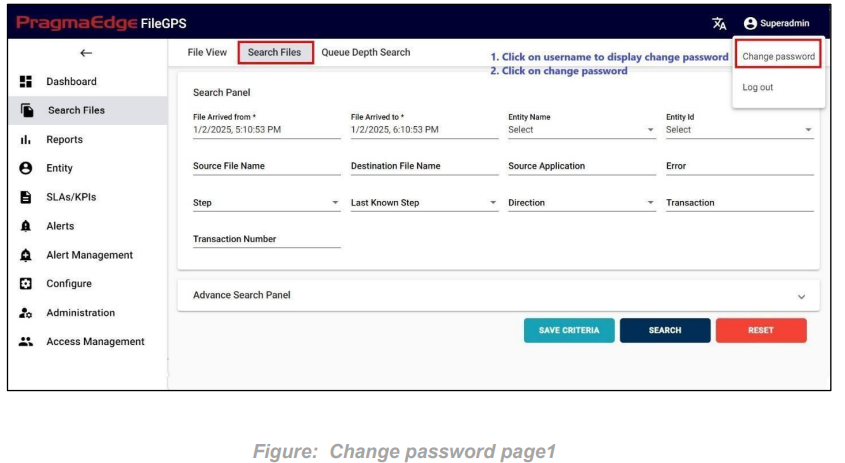
Now please provide the old and new password details and then click on the submit button which will successfully change the password.
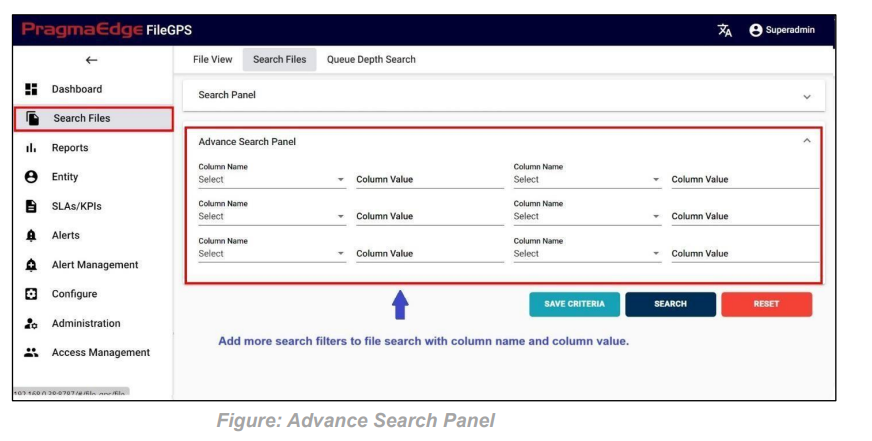
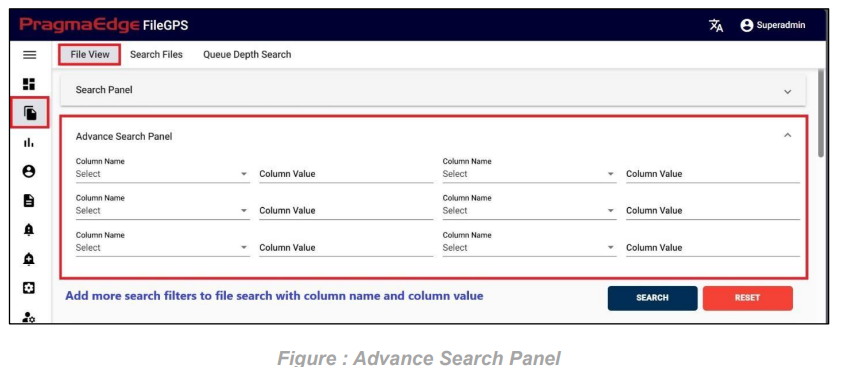
Advance Search Panel:
Advance Search Panel is used as an option to add more search filters to our File Search which gives us six options with column name and column value.
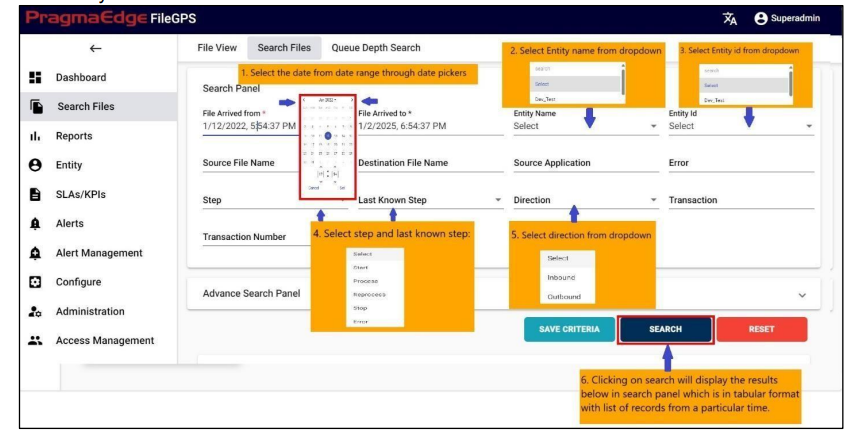
In the below figure steps to be followed by the users to fetch the files with the various option fields are provided.
By entering the required data in any of the below fields that are marked in red would fetch the total life cycle of the files.
After clicking on search, the list of records is displayed in the tabular format as shown in Figure.
Result:
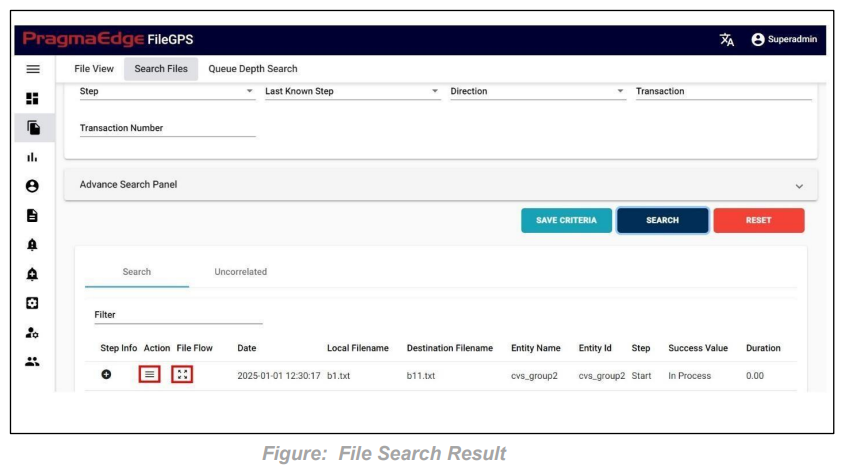
‘Displayed Results’ have been modified for ‘success value’ and ‘duration’ fields for success value ‘100’ it is modified as ‘Processed in Time’ and for ‘0’ it is modified as ‘Not Processed in Time’, Similarly for duration it will display the duration in minutes.
Different features are available in File Life Cycle to ease the process of file tracking.
5.1. a) Action:
Clicking on the action button in displayed page will show you the alerts that we can tie for the files we searched in search page itself as shown in the below figure.
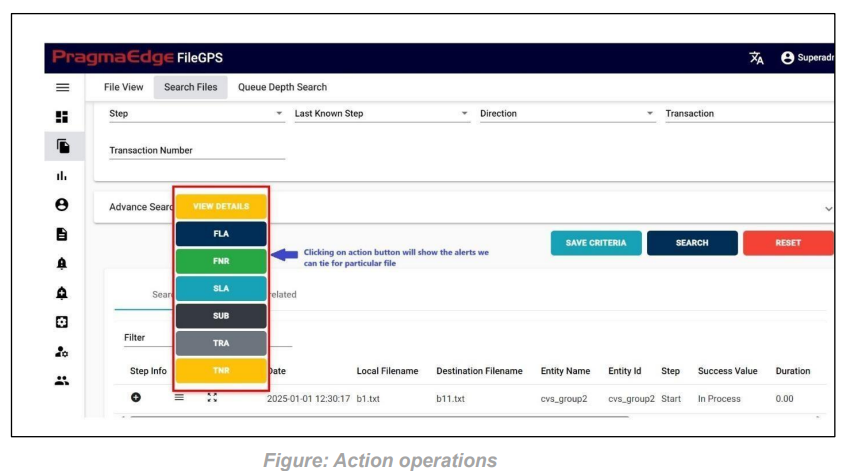
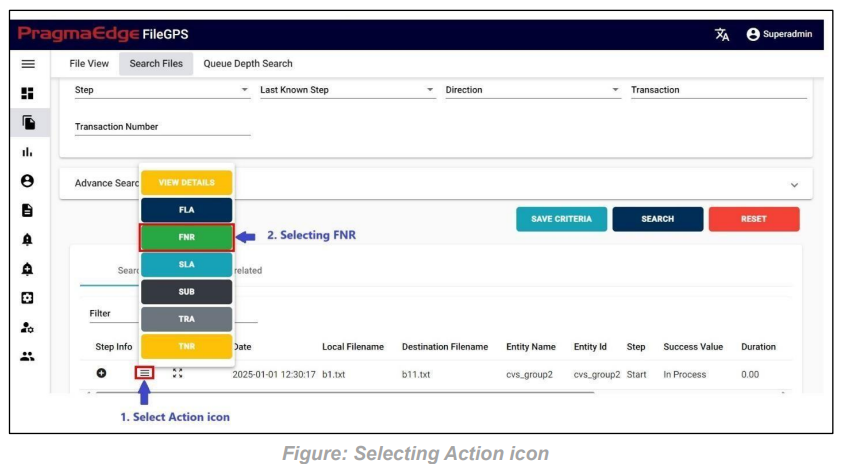
Clicking on the alert button will redirect you to the alert creation page with default suggested alert name which is the combination of entity name + entity id + type of alert + present date and time which can be changeable according to user.
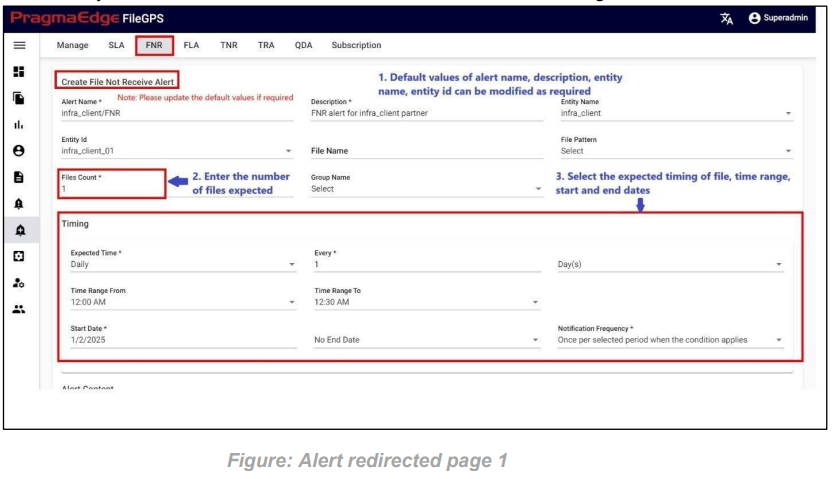
For Example, we have created the FNR alert for the file as shown in the below figure.
While creating alert from a file by default it will provide details like alert name, description, Entity name, entity id and now select the files count to be checked and timing details.
After providing the above details, please update the alert content and enable the email and rest API notification and details required.
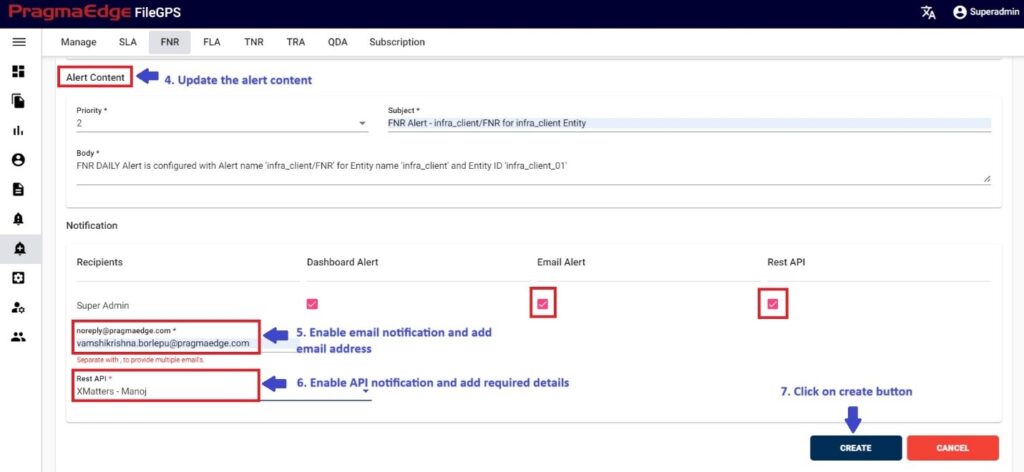
Now click on the create button which will successfully create the FNR alert from the search page file.
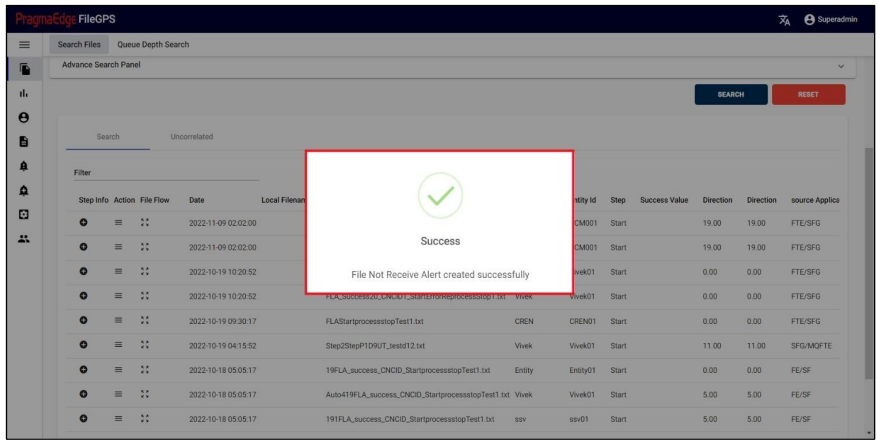
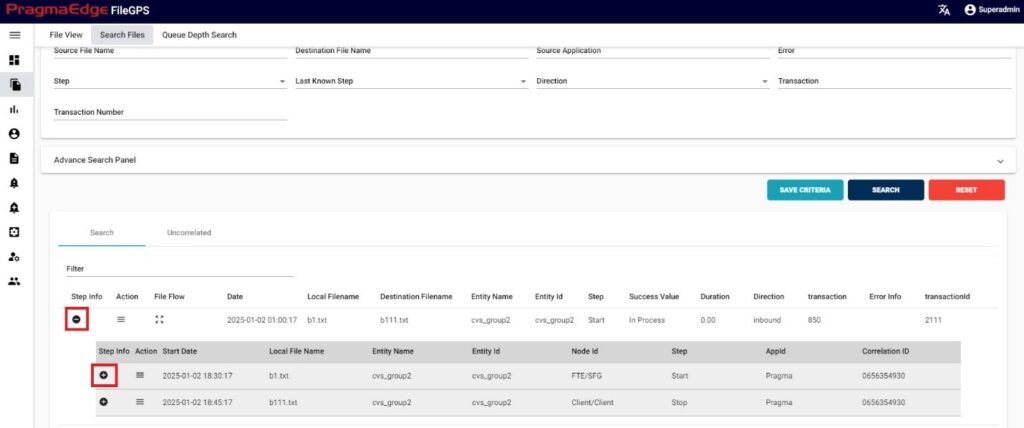
5.1. b) Step Info:
In the records displayed, to check the milestones of a particular record click on the step info button that is available on the left side of the record.
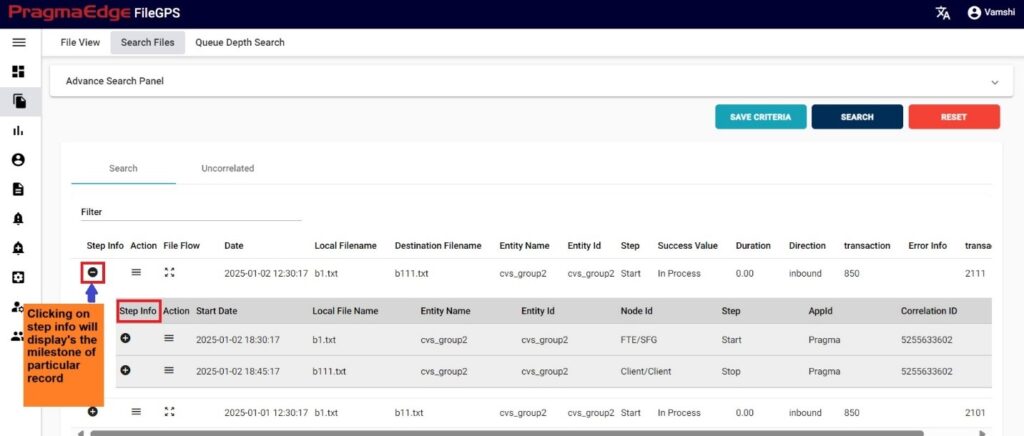
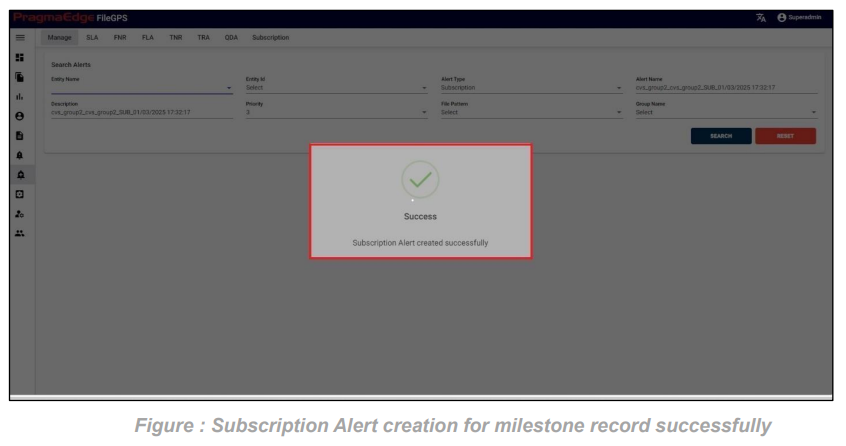
After getting the milestone record, we have an action button to every milestone record displayed. Clicking on the alert button will have ‘SUB’ option where we can create subscription alert for every record.it will redirect to the alert creation page with default suggested alert name which is the combination of entity name + entity id + type of alert + present date and time which can be changeable according to user as shown in below figure.
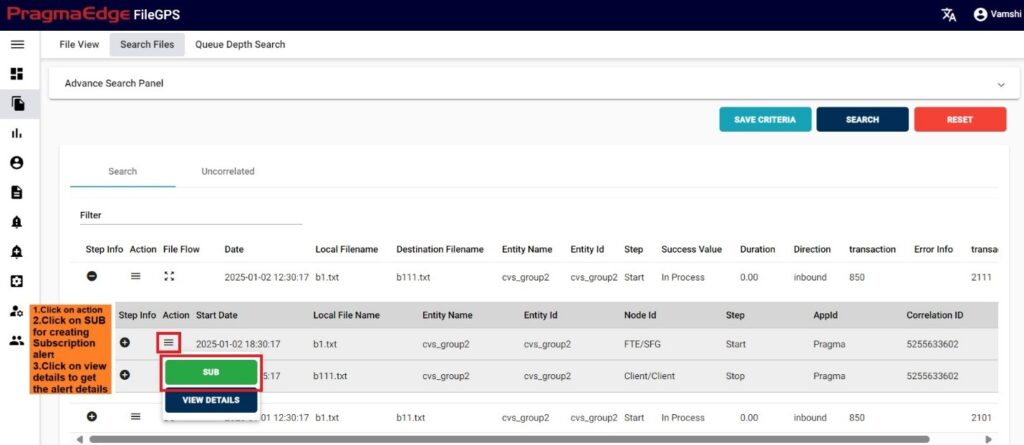
While creating sub alert from a file by default it will provide details like alert name, description, Entity name, entity id and now select the type of event to subscribe.
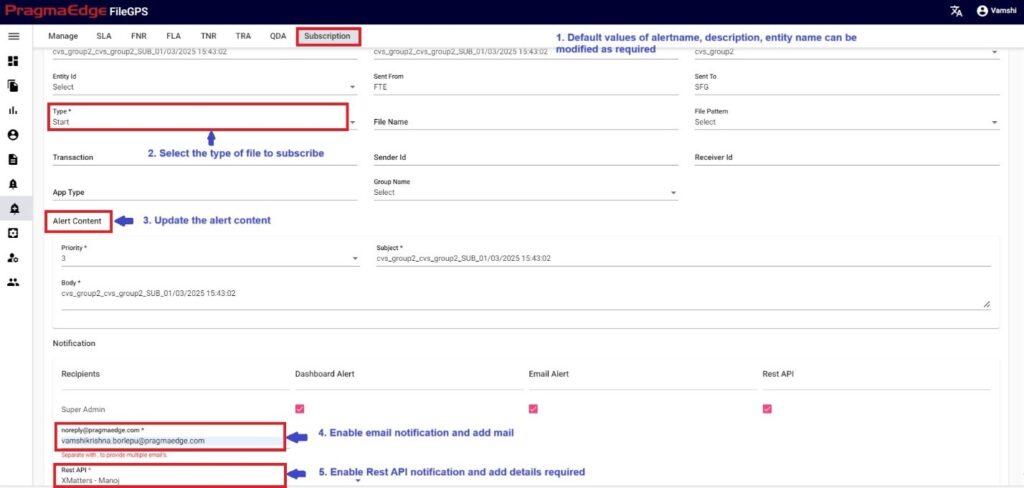
Now click on the create button which will successfully create the subscription alert from search page file.
5.1. c) File Flow:
‘File Flow’ button displays the flow of the file along with file names and file type in graphical representation as shown in Figure.
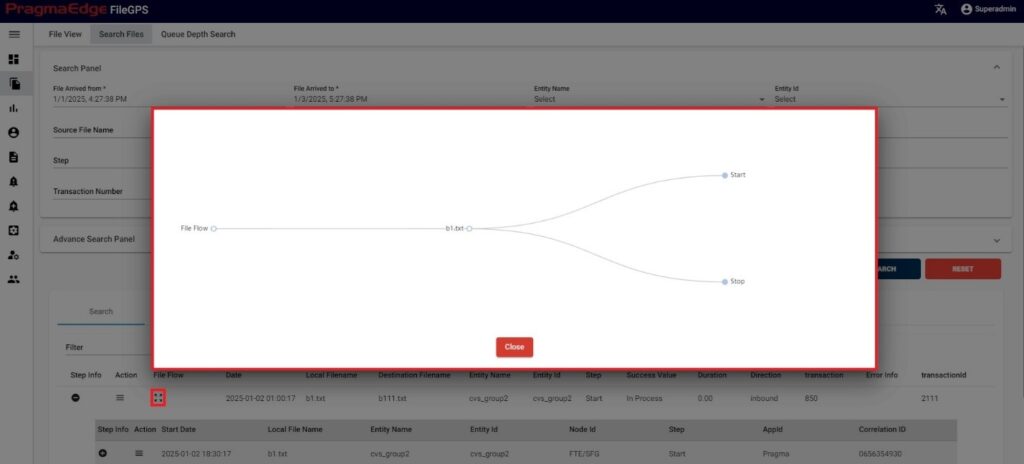
Note: The functionality of Action buttons remains same for all kinds of transactions such as One to One, Many to One and One to Many
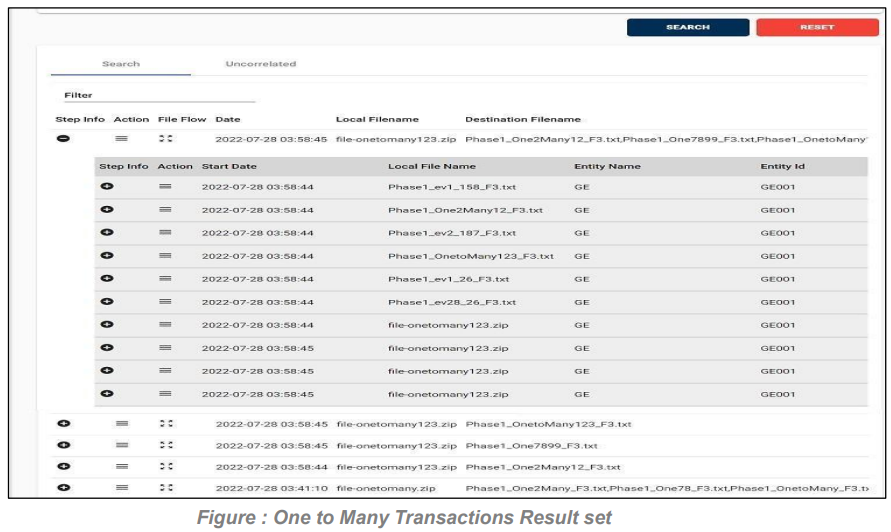
One to Many Transactions:
A Transaction set of files that have a single source and multiple destinations, in other words, a Single start and multiple Processes and stops. Result Structure of One-to-Many Transaction is Shown below Figure 25
Many to One Transaction:
A Transaction set of files that have multiple sources and single destinations, in other words, multiple starts, multiple Processes and a single stop.
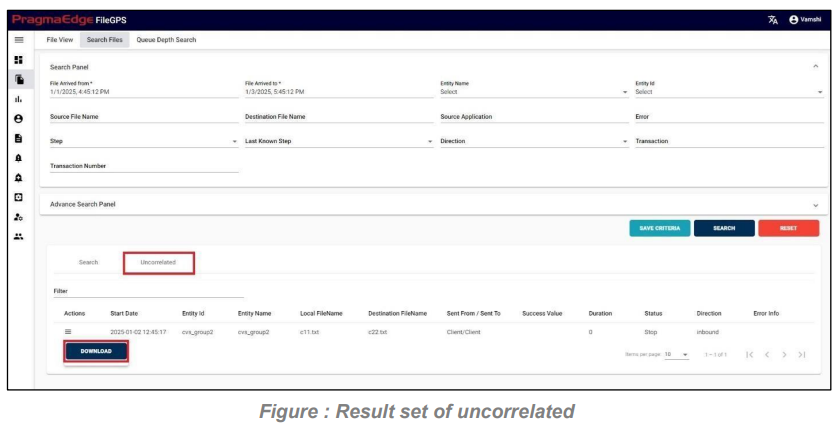
5.2. Uncorrelated:
We have a sub menu tab in the Search file page. This operation enables the user to search all kinds of Transaction files that were not processed.
Path:
Login File Life Cycle
Uncorrelated
When the user searches the files with date ranges and other required fields as filters the resultant records will be displayed on a page where we can check both search and uncorrelated files. By default, we will get records of search which file transmission were completed change to the sub side menu uncorrelated which will display the transaction files which were not processed.
This screen enables the user to view the files that bypassed the ‘START’ stage.
In other words, the files contain only ‘PROCESS’ and ‘STOP’ events.
By navigating to the sub tab of search files we have an uncorrelated tab which would fetch the data of files that were not processed.
The list of records is displayed in the tabular format as shown in the Figure.
5.2 a) Action:
In the records that were displayed in the main page, click on the ‘Action’ button that is available on the left side of the record to download the entire file information which was not processed.
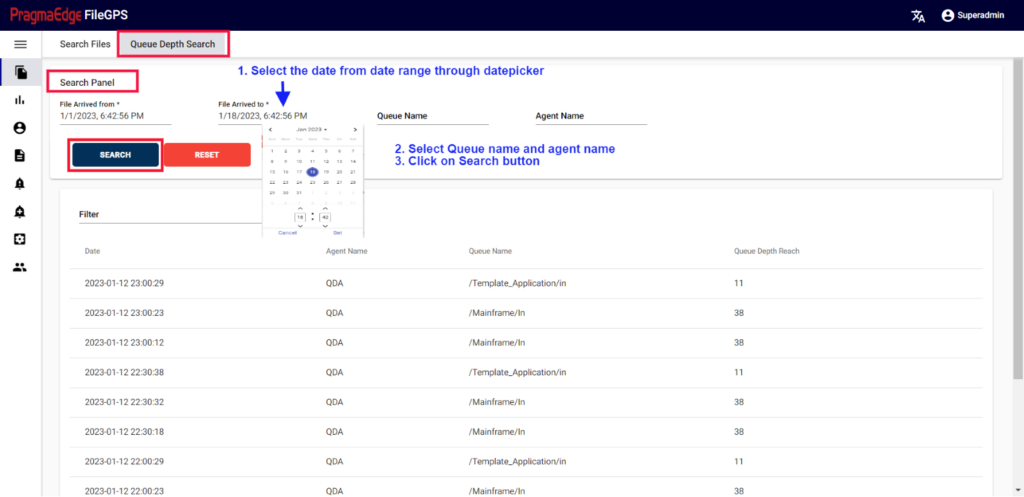
5.3. Queue Depth Search:
Queue Depth Search Provides the information regarding a file that was transmitted with its Queue Name and Depends on Queue Depth Reach and Agent Name
Path:
Login Search Files
Queue Depth Search
In this screen user can search for Queue Depth Search by giving File Arrived From date (The date on which file has arrived from Entity to Application) in the form of (mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss) and File Arrived To date with date pickers provided. And enter with Queue Name and Agent Name.
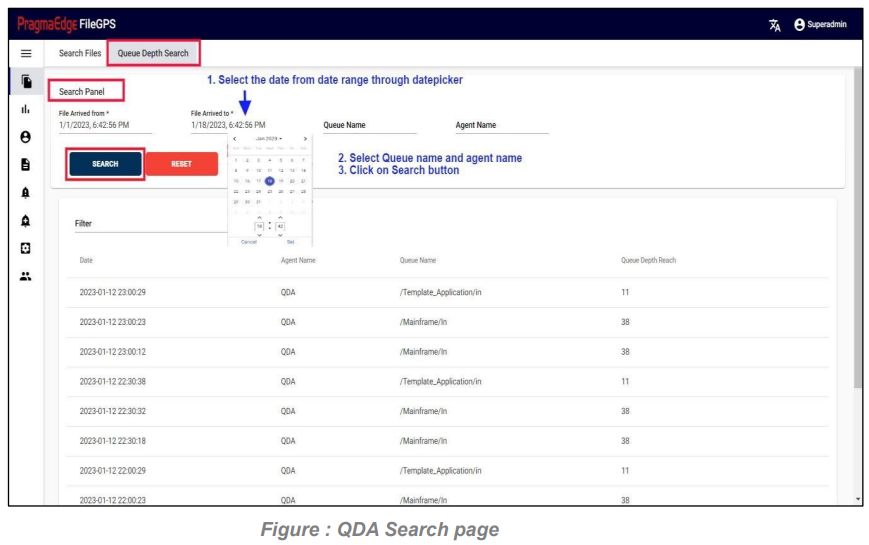
Clicking on the Search button by giving required field details will give the Result of Queue Depth Search.
5.4. File View:
This operation enables the user to search all kinds of Transaction files that were processed.
Path:
Login Search
Files File View
File View is an advanced and visually enhanced version of our file search functionality. With File View, users can search and monitor files, users can view different hops and directions of file transactions in a cleaner way.
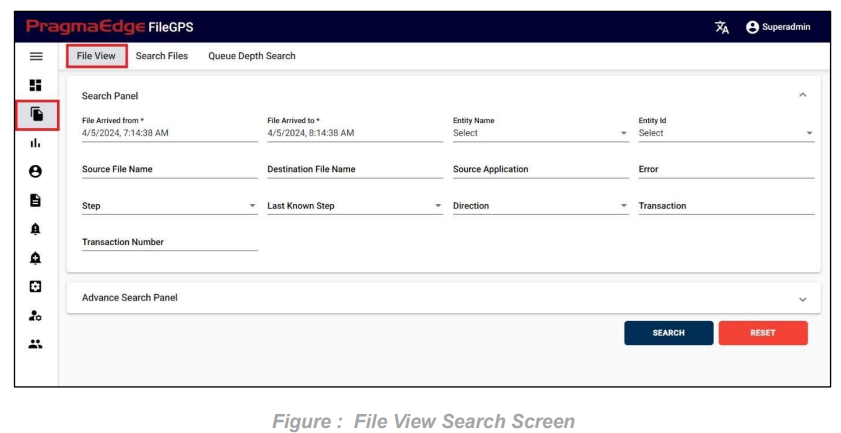
| Property | Description | Format / Rules/ E.g. |
|---|---|---|
| File Arrived Date | The date on which file has arrived from Entity to Application | mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm:ss |
| Entity Name | Name of an entity | IKEA/alpha numeric |
| Entity ID | Unique Identity of entity | IKEA001/alpha numeric |
| Step | State of the file | (Start, process, stop, error) |
| Source File Name | Name of the file that was sent from specific source hub | e.g., FS_Startfile.txt |
| Destination File Name | Name of the file that arrived at destination hub | e.g., FS_Stopfile.txt |
| Error | Error name that occurs in the process of the file | e.g., Transaction Failed |
| Source Application | Node ID/Source application Name | e.g.: FS |
| Last known status | Last status of the file | (Start, Process, Stop, Reprocess, Error) | Direction | File direction | (Inbound/Outbound) |
| Transaction | Transaction number of the file (850, 855, 856, 810, 820 etc) | Number |
| Transaction Number | Transaction Id of the file | Number |
| Search (Button) | Used to retrieve/ data based on the input data criteria | |
| Reset (button) | Used to empty the values of inputs/Clear the existing values/reload the page to build new search |
Note: Here You can use wild card “*” search for better search.
Advance Search Panel:
Advance Search Panel is used as an option to add more search filters to our File Search which gives us six options with column name and column value.
Searching Files in File View:
The figure below outlines the steps users should follow to fetch files, along with various option fields provided.
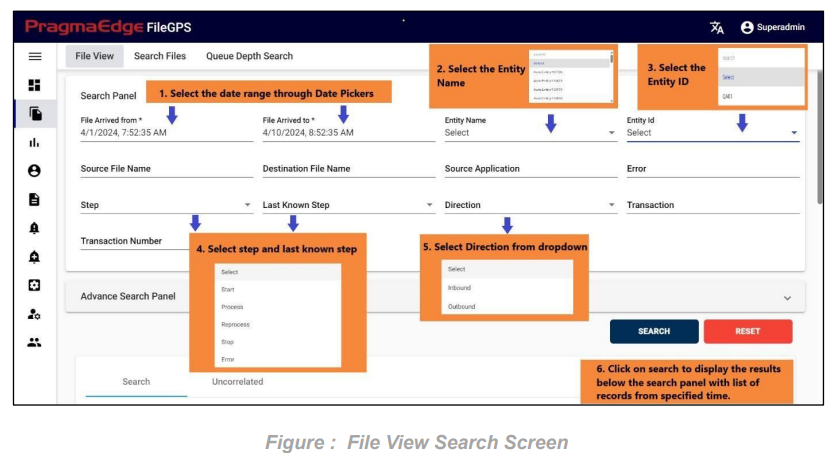
After clicking on search, the list of records is displayed in the tabular format as shown in Figure.
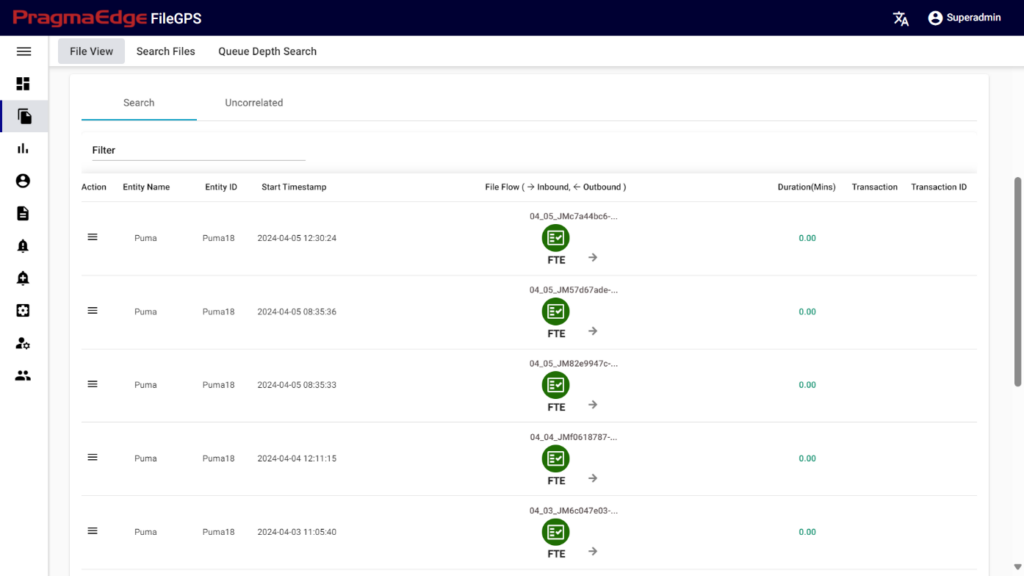
Different features are available in File Life Cycle to ease the process of file tracking.
a)Action:
Clicking on the action button in displayed page will show you the alerts that we can tie for the files we searched in File View search page itself as shown in the below figure, and users have an option to navigate to older File Search page.
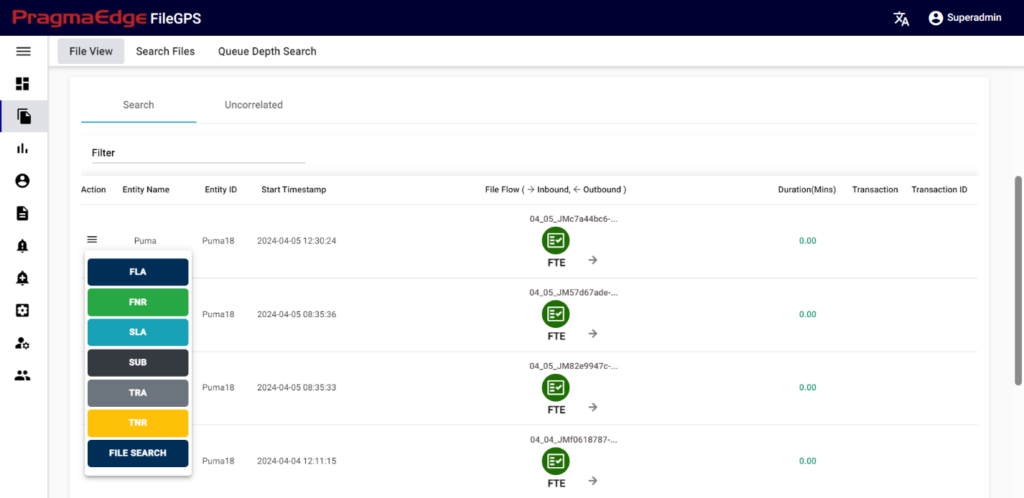
Clicking on the alert button will redirect you to the alert creation page with default suggested alert name which is the combination of entity name + entity id + type of alert + present date and time which can be changeable according to user.
b) File View: Hovering over the icon provides details such as timestamp and status of the file. “–>” indicates inbound, and “<–” indicates outbound direction of file flow as shown in the below figure.
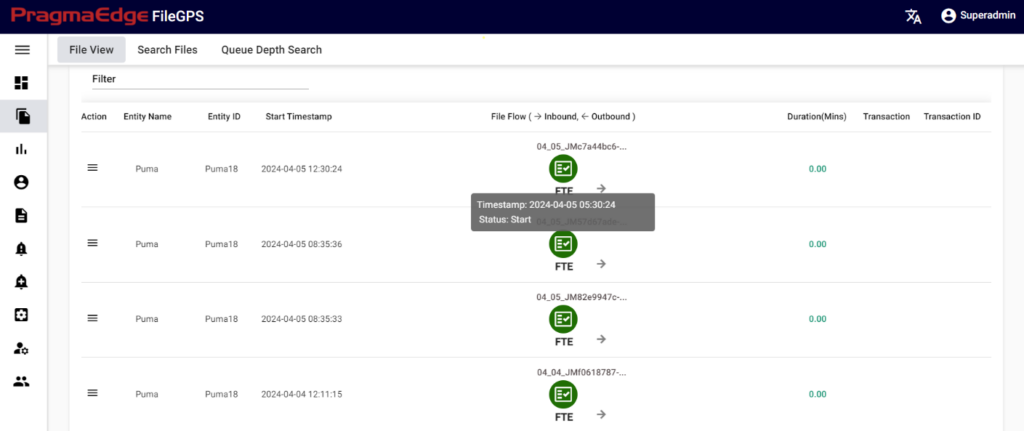
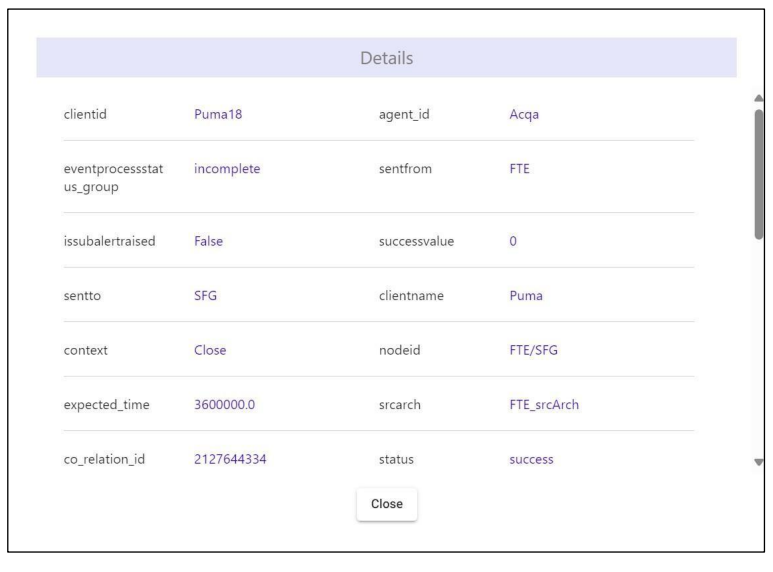
Clicking on the icon opens a dialog box displaying file details such as client name, client ID, sender, receiver, correlation ID, node ID, etc., as shown in the below figure.
5.5. File Search Criteria:
Path:
Login Search Files
Search Files
Users can now save their search criteria, including entity name, entity ID, or step, removing the need to re-enter them for each search. This feature is tailored to individual user preferences, streamlining workflows and simplifying the overall process.
Select the File Arrived from and File Arrived to through date pickers, apply the desired filters and click on save criteria button to save the search criteria.
For example, the entity name has been selected, and the criteria have been saved as shown in
the figure below.
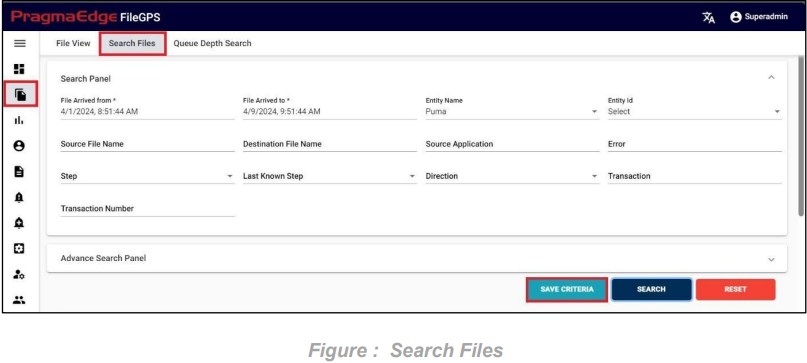
Enter the Criteria name and click on save criteria to save it as shown in below figure.

To access the saved file search criteria, navigate to the configuration module and select “File Search Criteria”. Here, you can view all the saved search criteria.
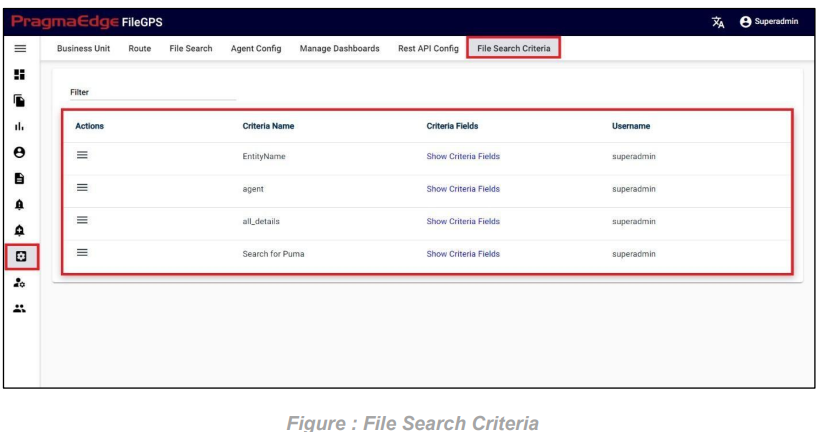
Clicking on “Show Criteria Fields” will display all the saved criteria fields.
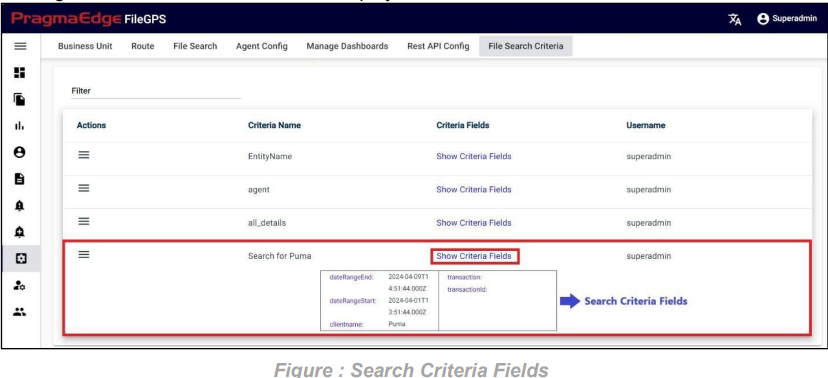
To search for files using the saved criteria, open the Actions menu for the corresponding criteria and select “File Search”.
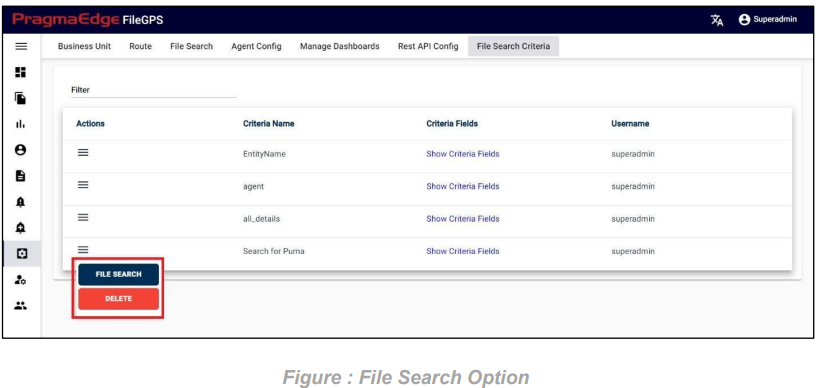
Click the search button to retrieve the files based on the criteria.
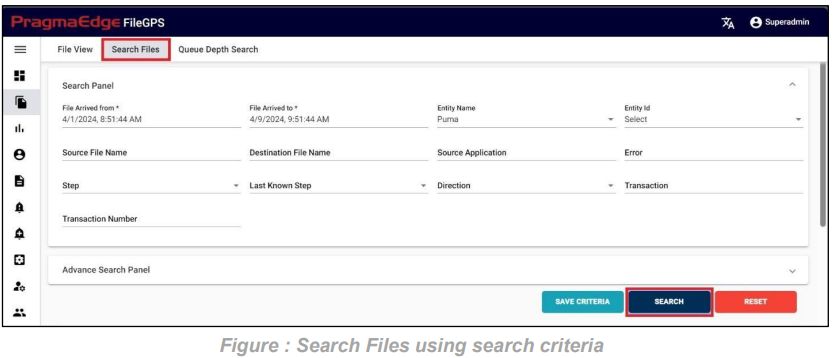
After clicking on search, the list of records is displayed in the tabular format as shown in Figure.
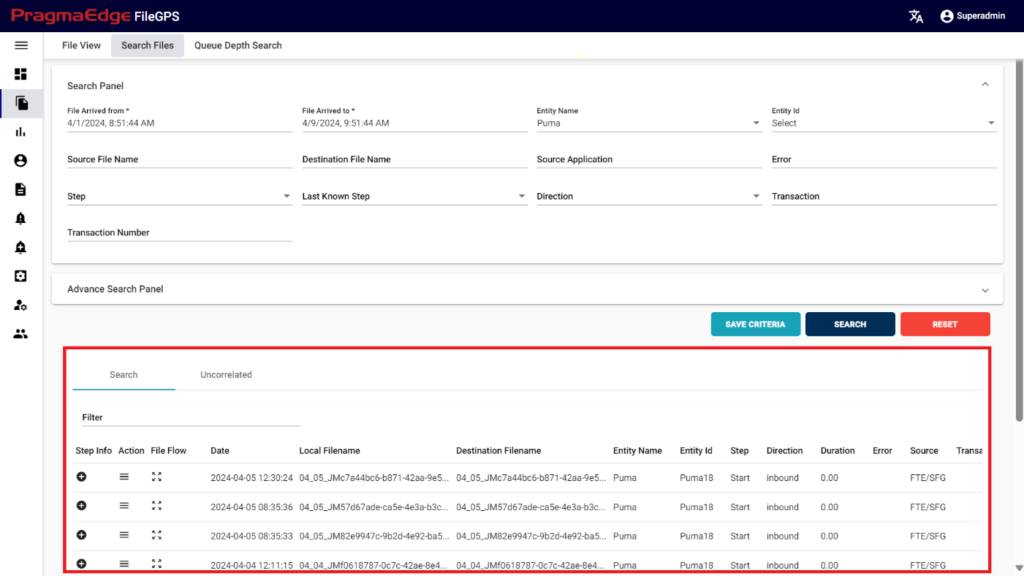
6. Reports:
FileGPS Reports are the Infographics that depict the statistics of the data that was processed between the hubs.
Path:
Login Reports
Reports provide diversified options to view the file statistics
We have multiple graphs in dashboard module, where we can give inputs to generate the reports. This dashboard reports represent different kinds of Line & Bar Graphs regarding information of missed SLA, top missed SLA entity, missed SLA by entity, transactions volume, top transactions volume entity, transactions volume by entity, error volume, error volume by entity.
Top Transactions Volume by Entity: This graph will display the number of transactions that occurred by volume over the Top Entities. We can see in the graph below that, if we don’t select any entity then it will display transaction volume for all the Top Entities.
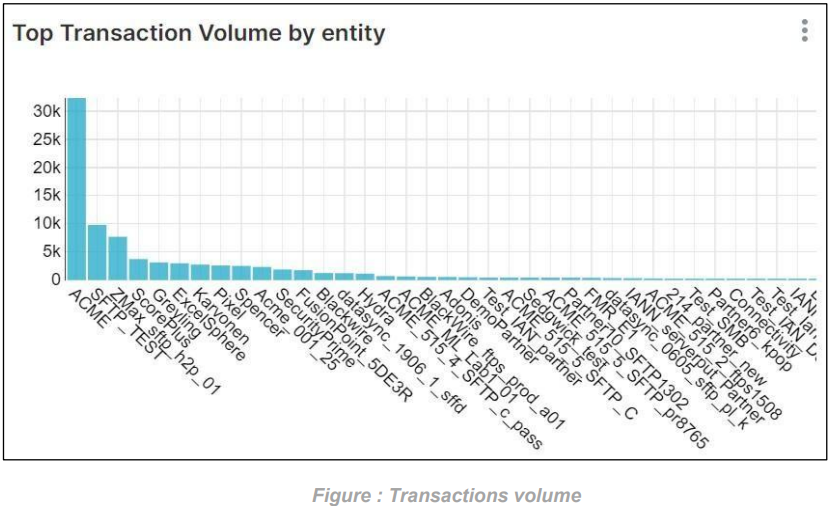
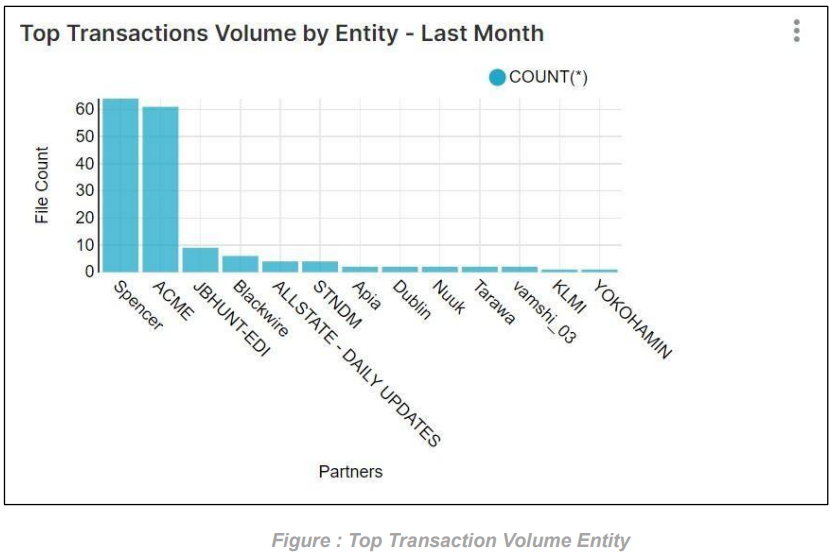
Top Transaction Volume Entity for Last Month: This graph will display the highest number of transactions for a entity over the Last Month. If we don’t select any entity, then it will display the highest number of transactions for all the entities based on the Last Month as shown in the graph below.
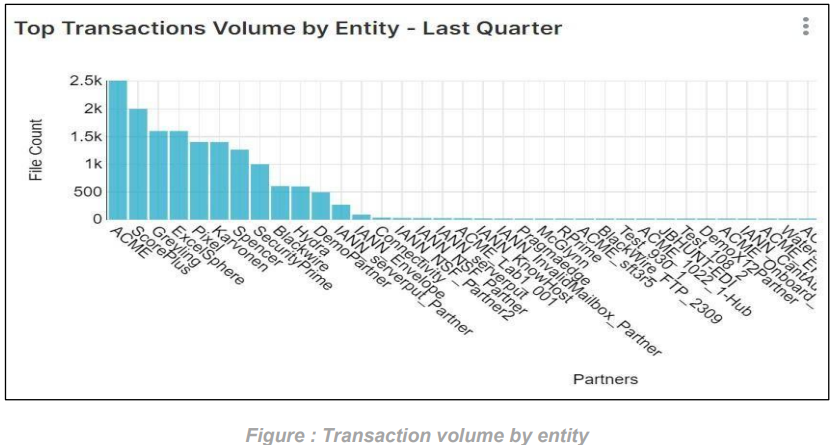
Transaction volume by entity for Last Quarter: This graph will display the number of transactions that occurred to that entity over the Last Quarter. If we don’t select any entity, then it will display the number of transactions for each entity over the Last Quarter as shown in the graph below.
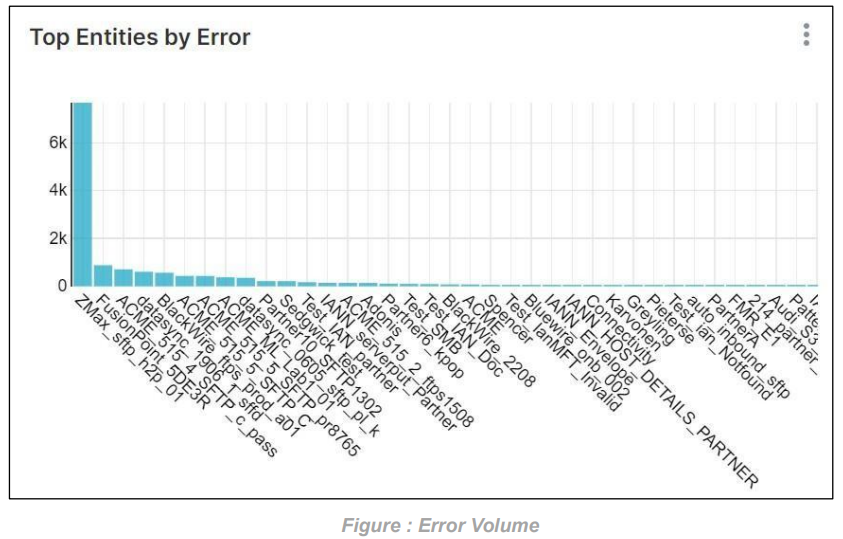
Error For Top Entities: This graph will display the total number of errors that occurred for the selected Top entities. If we don’t select any entity, then it will display the total number of errors for all the entities as shown in the graph below.
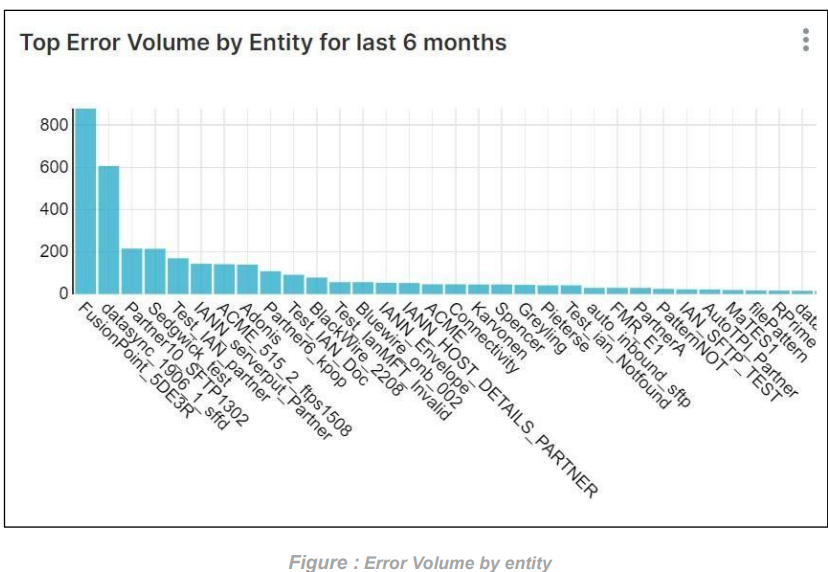
Error Volume by entity for last 6 months: This graph shows if we select entity then it will display the number of errors that occurred for that entity over the last 6 months. If we don’t select any entity, then it will display the number of errors for all the entities over the last 6 months.
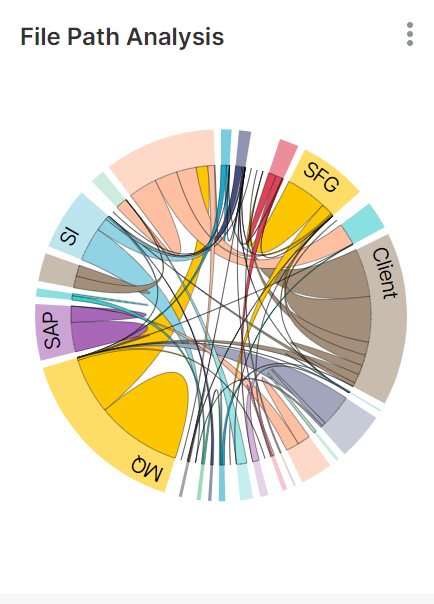
Path Analysis Shows the connection of node paths and number of files transferred in between the applications based on time range.
Path Analysis: By default, all paths are added for report
• It will show the path of the nodes from one application to the other and the amount of space that each application occupies.
• If we hover over an application, then it will display the path and the count of files that are transferred between those applications.
Below graph represents the path analysis report generated based on the date range selected.
7. Entity:
Path: Login Entity
This module of the FileGPS application provides the user with the ability to perform various operations on entity. These are various operations
• Create Entity
• Manage Entity
• Create File Name Pattern
• Manage File Name Pattern
7.1. Create Entity:
Path:
Login Entity
Create Entity
In this screen, to onboard an Entity, the User can create an Entity and Unique ID and assign business Partners and groups to it.
For example, in this scenario ACME Entity details are provided in the ‘Create Entity’ sub tab to create an entity as shown below Figure.
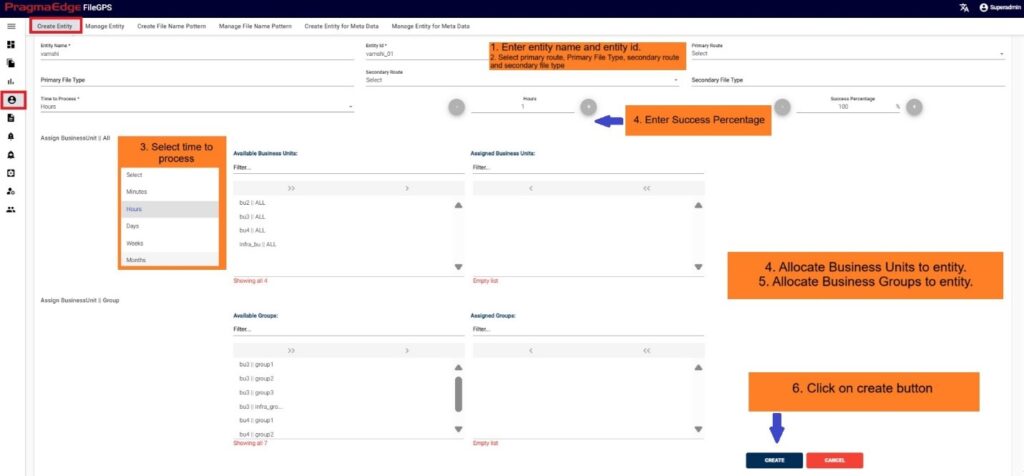
| Property | Description | Format / Rules / E.g. |
|---|---|---|
| Entity Name: * | Name of an Entity, which is generated either by admin/Admin based on the specifications | e.g. – name- ACME |
| Entity ID: * | Unique identification of an Entity | e.g. – name- ACME@12345 |
| Primary Route | Collection of Node IDs to form a Path/route from a start stage to another stage | |
| Primary File Type | Mention the Format of the file / file extension would be the type | e.g. – .doc, .docx, .txt |
| Secondary Route | Collection of Node IDs to form a Path/route from a second level stage to final level of stage | |
| Secondary File Type | Mention the Format of the file / file extension would be the type | |
| Success Percentage: * | Configurable rate given based on SLA (see section SLA) | |
| Time to Process: * | Time taken to process the request may be in minutes, hours from one Node ID to its successor Node ID | |
| Assign Business Unit (ALL) | Allocating business units to Entity | |
| Assign Business Unit (Group) | Allocating business Groups to Entity | |
| Create (button) * | Used to Create a new Entity with required data | |
| Cancel (button) | Used to empty the values of inputs/Clear the existing values/reload the page to build new search |
Those which are marked as “*” are required/mandatory fields After entering all the details of Entity, just click on the create button it will create entity successfully as shown below figure.
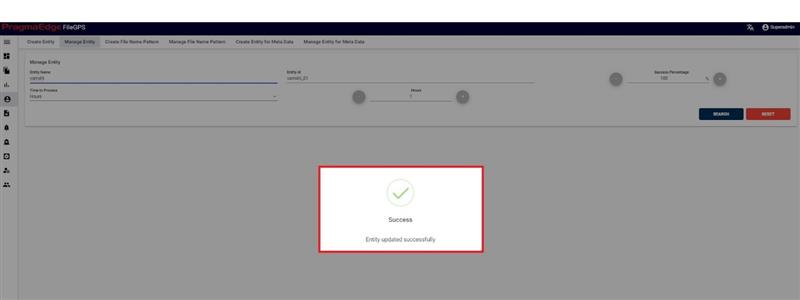
Note: When a client is not assigned to any group or Business Unit, the data of the corresponding client is visible to all the users.
ACME Entity is now successfully created.
7.2. Manage Entity:
In Manage entity, User can search for the entities based on the filters that were provided at the time of entity creation.
Path:
Login Entity
Manage Entity
In this Manage Entity screen, Users have edit/delete/View Activity options to perform on Entity.
All the actions such as edit/delete/View Activity could be performed when user click on the particular record as shown in figure
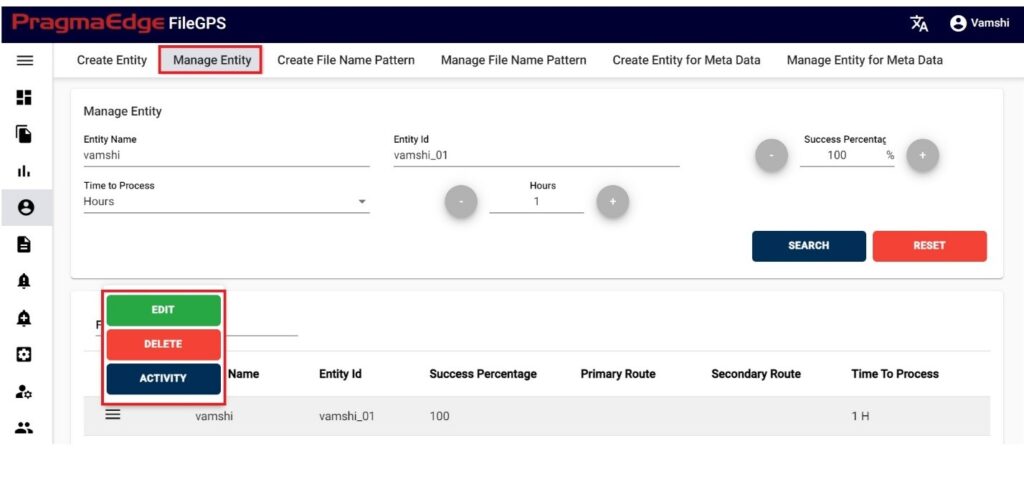
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Entity Name | Name given while creating the Entity |
| Entity ID | Unique Identification alpha numeric code |
| Time to Process | Time taken form one Node to another node |
| Success Percentage | Configurable Success ratio as a standard |
| Search | Search for the result grid based on given criteria |
| Reset Search | Clear the input field values to make a new search |
| Update | Saves the values and updates the records |
| Cancel | Clear all the filled inputs such that user can have search for new records |
Manage Entity have the ‘EDIT’ option where we can edit the Entity details. By clicking on the edit option, it will navigate the page to create a page module where we can change details as per requirement
Note: When an entity is initially created and subsequently undergoes updates with modifications such as renaming the entity, all alerts associated with that specific entity will be automatically adjusted to reflect the corresponding changes.
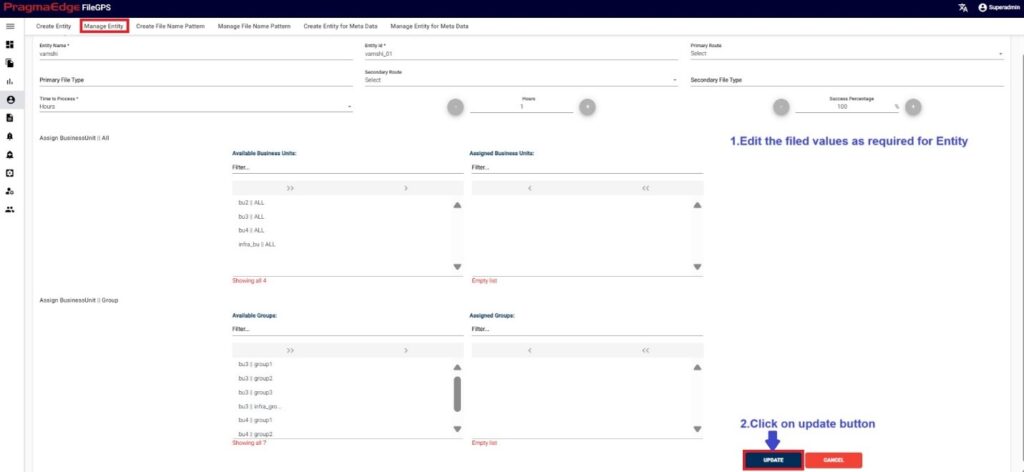
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the entity details as shown in figure.
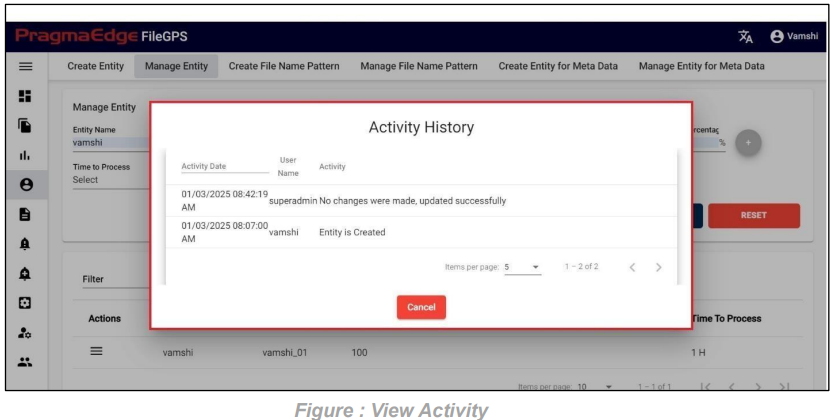
‘Activity’ will have the record of all the actions performed by the users as shown in figure.
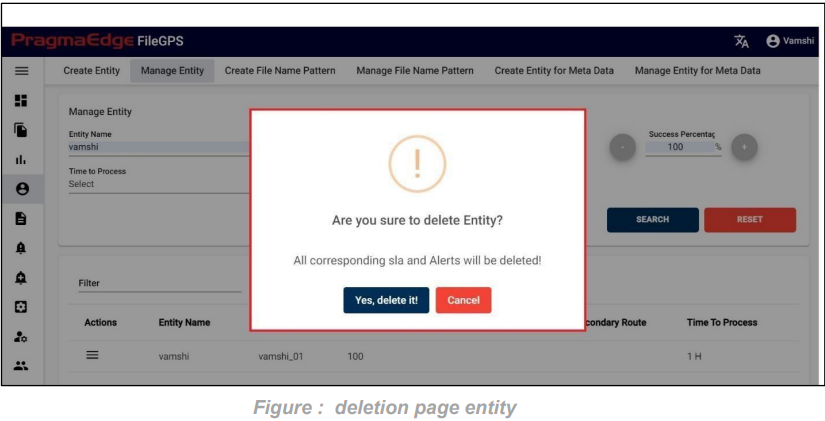
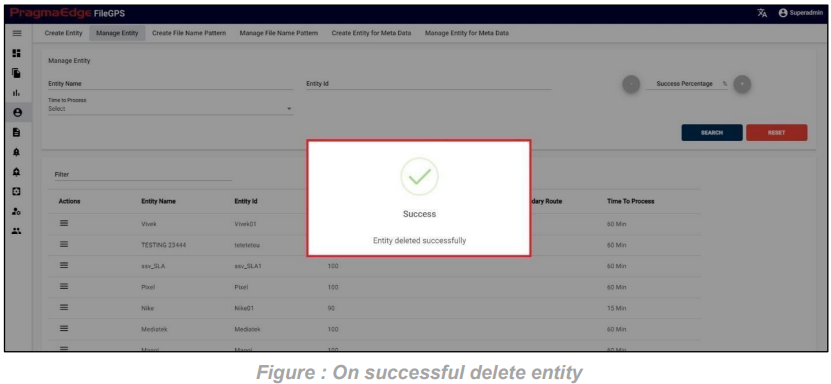
Entity record could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure
Note: If the entity is deleted, all alerts linked to that specific entity will be removed or deleted accordingly.
7.3. Create File Name Pattern:
This is the page in which the File Patterns can be created for Particular Entity
Path: Login Entity
Create File Name Pattern
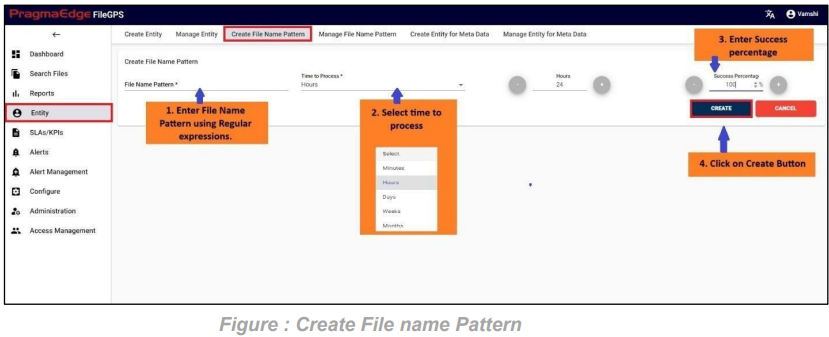
In this screen, admin can create a File Name Pattern.
Any regular expression can be created as File Name Pattern.
For example, in this scenario %ACME File Pattern details are provided in the ‘Create File Name Pattern’ as shown below Figure.
In this screen, admin can create a File Name Pattern.
| Property | Description | Format / Rules/ E.g., |
|---|---|---|
| File Name Pattern: * | Name of an Entity, which is generated either by admin/Admin based on the specifications | e.g. – %ACME |
| Success Percentage: * | The Required Success Percentage for file | |
| Time to Process: * | Time taken to process files with the request may be in minutes, hours from one Node ID to its successor Node ID |
Those which are marked as “*” are required/mandatory fields.
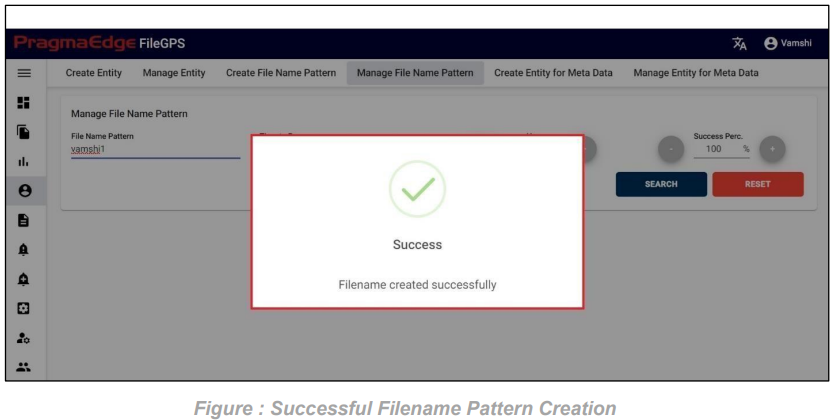
After entering all the details of File Name Pattern, click on create button it will create File Pattern successfully as shown Figure
7.4. Manage File Name Pattern:
In Manage Entity, User can search for the Entity based on the filters that were provided at the time of Entity creation.
Path: Login Entity
Manage File Name Pattern
Users have edit/delete/View Activity options to perform on File Pattern.
All the actions such as edit/delete/View Activity could be performed when user click on the particular record as shown in figure.
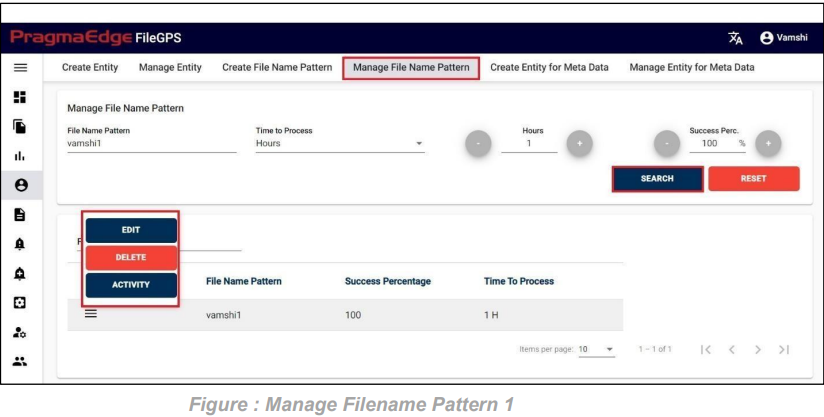
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| File Name Pattern | Name given while creating the Entity |
| Time to Process | Time taken to Process from one Node to another node |
| Success Percentage | Configurable Success ratio as a standard |
| Search | Search for the result grid based on given criteria |
| Reset Search | Clear the input field values to make a new search |
| Update | Saves the values and updates the records |
| Cancel | Clear all the filled inputs such that user can search for new records |
Manage Entity have the ‘EDIT’ option where we can edit the Entity details. By clicking on the edit option, it will navigate the page to create page module where we can change details as per requirement.
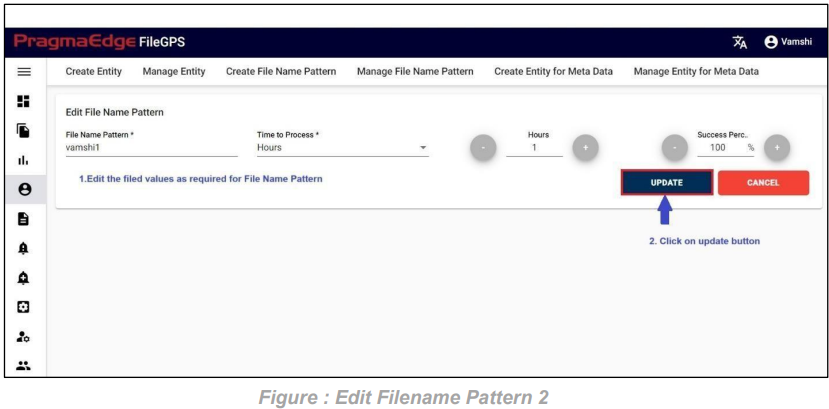
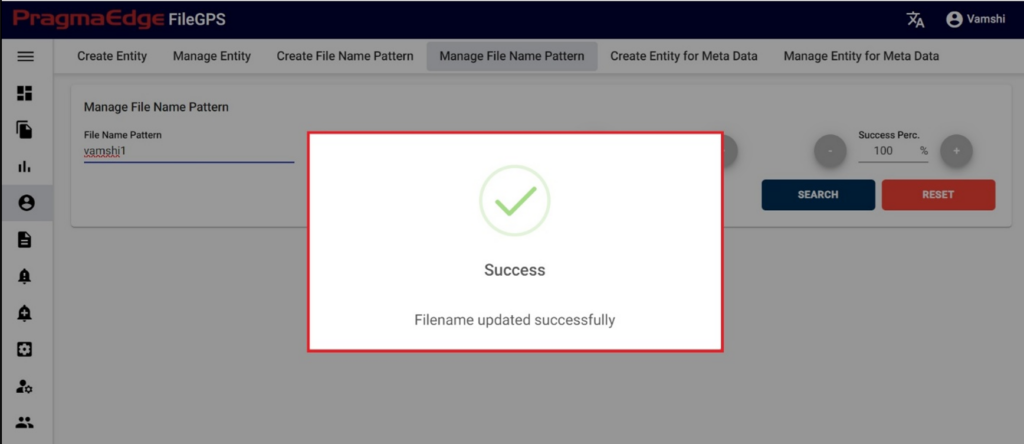
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the File name pattern details as shown in figure.
Note: If a filename pattern is created and then updated with some changes, then all the alerts configured with that filename pattern will also get updated accordingly.
File Pattern record can be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure.
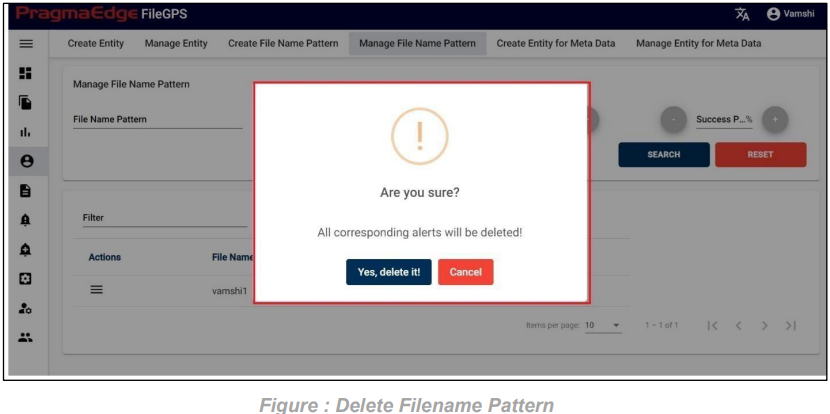
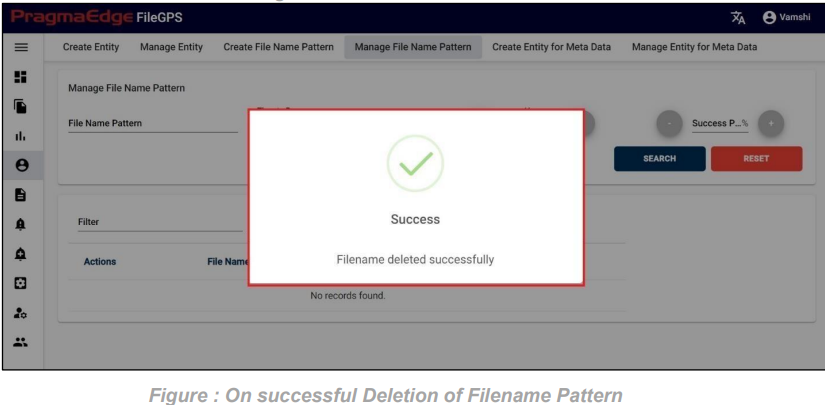
Note: If the filename pattern is deleted, then all the alerts with that filename pattern will be deleted.
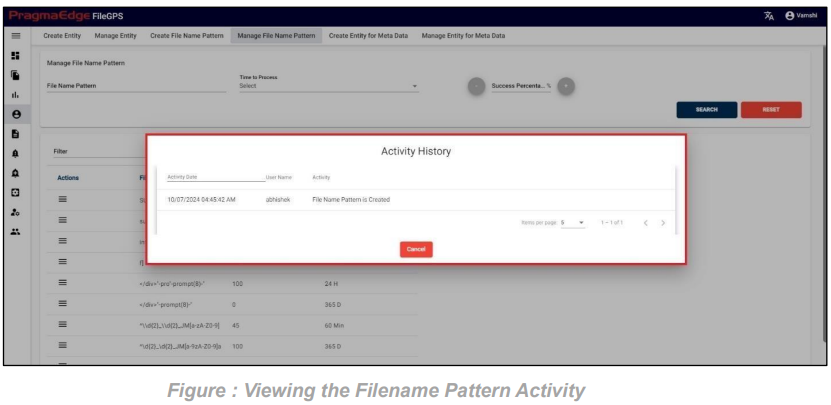
‘Activity’ will have the record of all the actions performed by the users as shown in figure.
7.5. Create Entity for Meta Data:
Path:
Login Entity
Create Entity for Meta Data
Users have the ability to create entities for metadata and oversee the management of these entities for metadata purposes.
7.5.1 Create Entity for Meta Data:
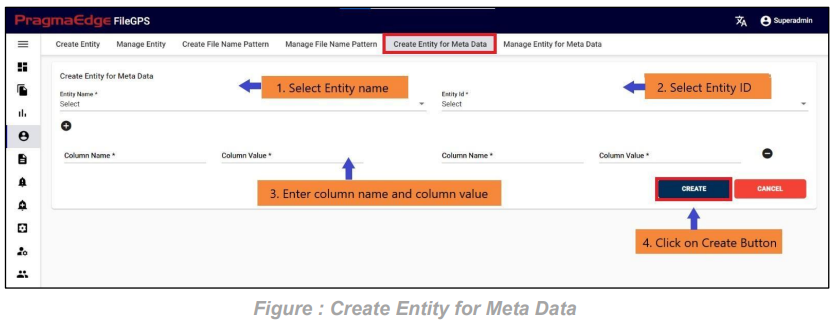
On the “Create Entity for Metadata” screen, users are empowered to generate metadata for different entities. Following the onboarding of the entity, as demonstrated in the 7.1 Create Entity module, kindly choose the Entity name and Entity ID from the provided dropdown menus. Proceed by adding the column name and corresponding default column value, which will be applied in the absence of an actual similar column in a file transaction. Finally, clicking the “Create” button completes the process.
As an example, choose “ACME” as the Entity name and “ACME” as the Entity ID. Introduce a column with the name ‘appid’ and assign its corresponding value as ‘Pragma’. Similarly, add another column with the name ‘origin’ and set its column value to ‘onprem’.
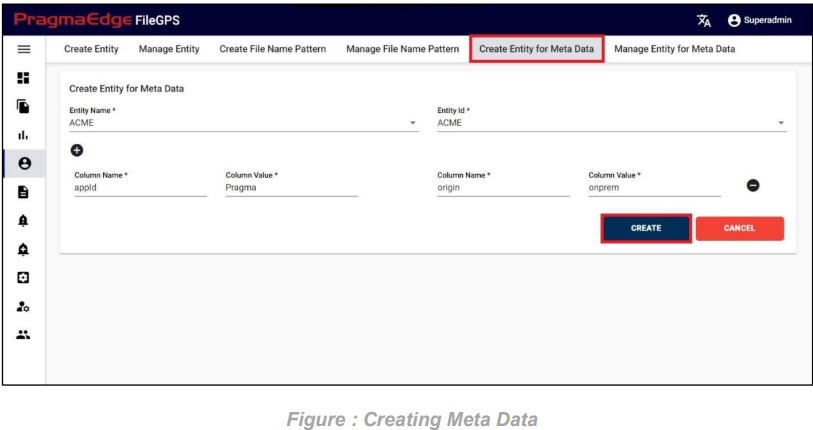
After entering all the details of Entity Meta Data, just click on the create button it will create Entity Meta Data successfully as shown below figure.
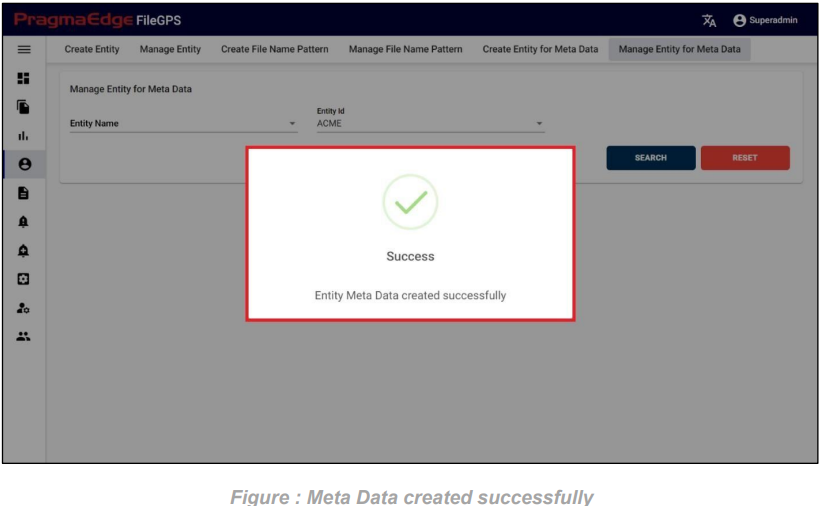
7.5.2 Manage Entity for Meta Data:
In the “Manage Entity for Metadata” section, users have the capability to search for created metadata by selecting specific values from the Entity Name and Entity ID dropdown menus.
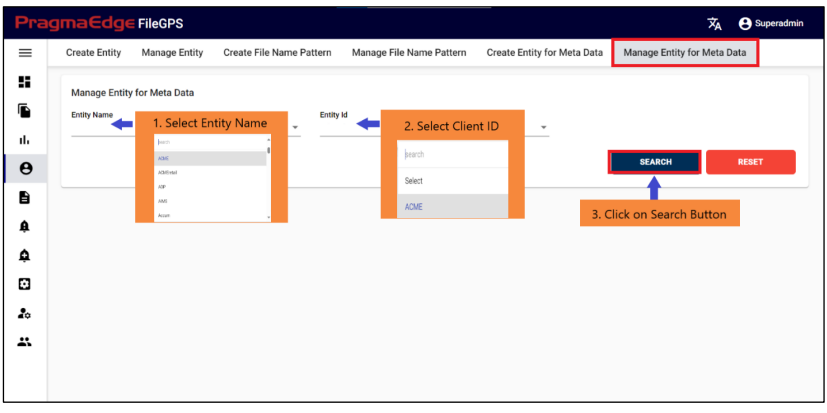
Upon clicking the search button, users can access a comprehensive view of all the configured metadata associated with clients as shown in the below figure.
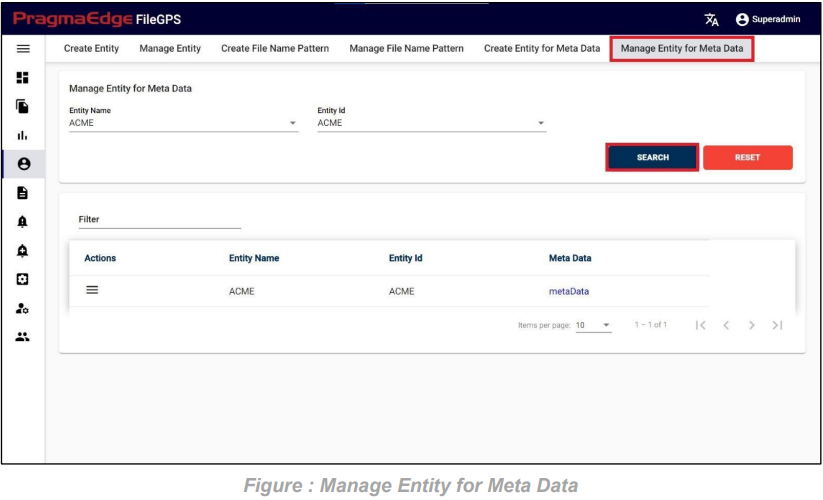
Following the search, users can conveniently access the Action button to either edit or delete the existing metadata.
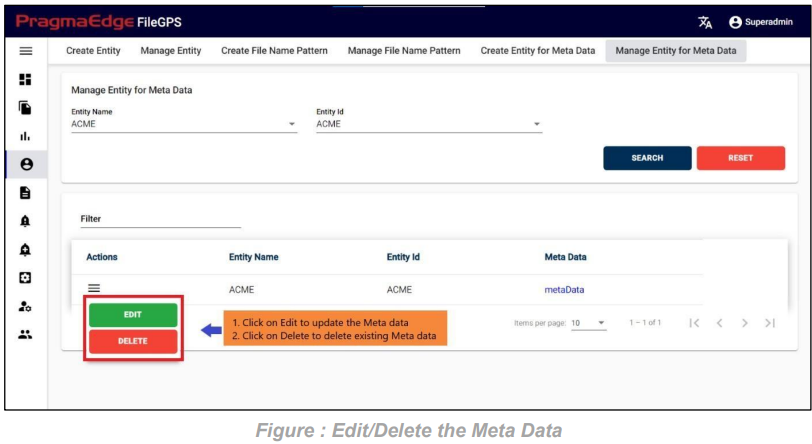
Within the “Manage Entity for Metadata,” the ‘EDIT’ option allows users to add a new column name and column value, delete an existing column name and its corresponding value. Additionally, users can modify the entity and entity ID by selecting different options from the dropdown. Upon clicking the edit option, the system navigates to the “Edit Entity for Metadata” page, facilitating the updating of details based on specific requirements.
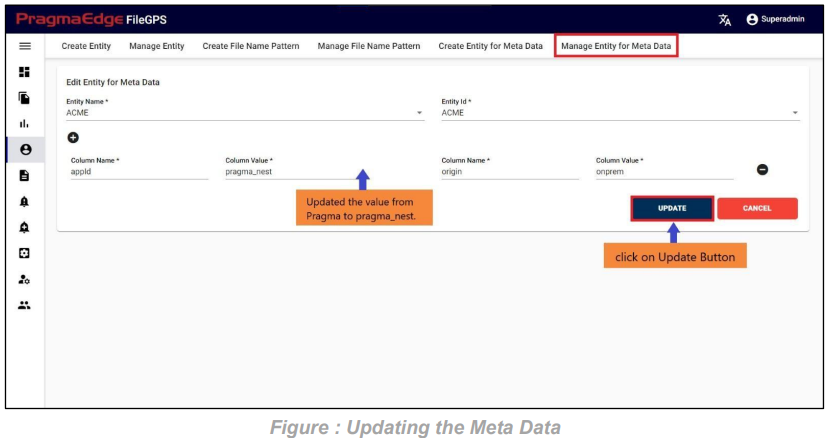
Upon clicking the “Update” button, the Entity Metadata will be successfully updated, as illustrated in the figure below.
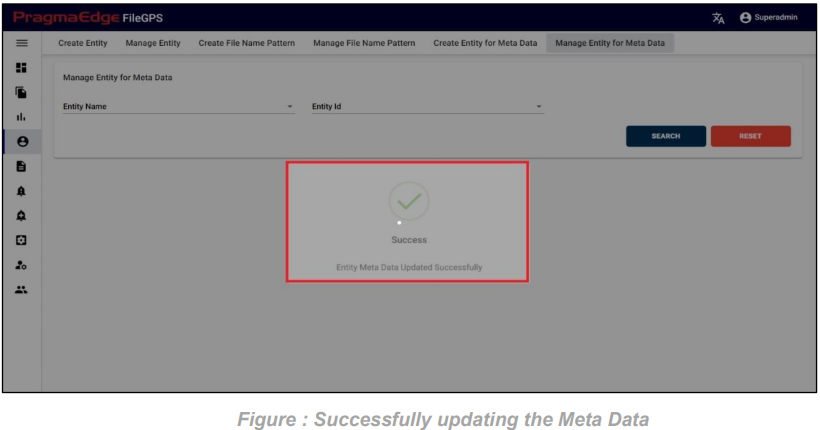
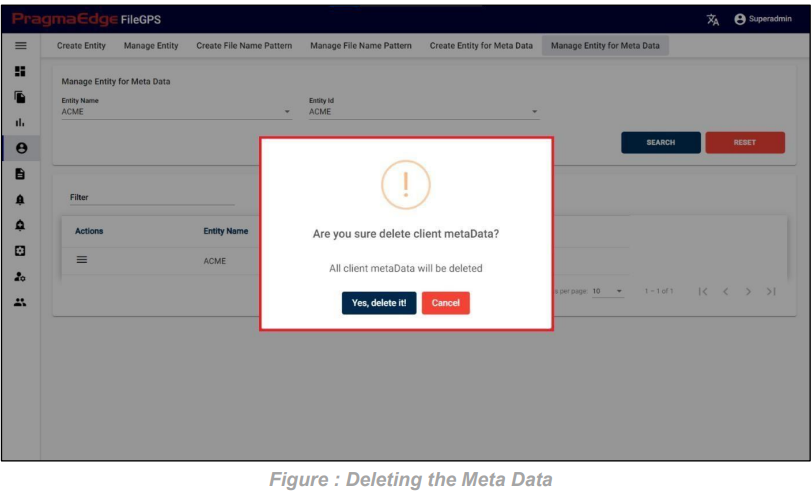
The record of Client Metadata can be permanently deleted using the ‘DELETE’ option, as depicted in the figure below.
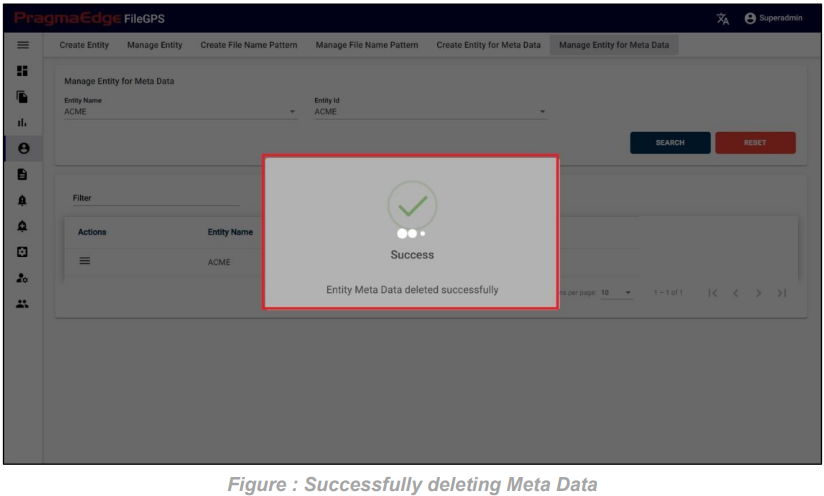
The above Client Meta Data record is successfully deleted.
8. SLA’s/KPI’s:
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and an entity. It is also called Key Performance Indicator (KPI).
Path:
Login SLAs/KPIs
Create File Based SLA
8.1. Create File Based SLA:
Before creating the SLA alert, the user has to create an SLA for the entity with the required processing parameters to model the condition.
There are two types of SLA
• Entity-based SLA
• File-based SLA
Users can Create SLAs/KPIs for the created entities, file patterns and mention the type of SLA’s/KPI’s in two formats
1. Percentage.
2. Duration.
Below is a detailed description of mandatory fields that are present in the SLA.
Configuration:
• It is a mandatory field
• Should select a radio button of Entity Based SLA or File Based SLA based on requirement of SLA
• By selecting Entity Based SLA configuration it displays the Entity name and Entity Id whereas Entity Name is mandatory field and Entity Id is optional field
• By selecting File Based SLA configuration it displays File Name where it is mandatory field
Time Reference:
• It is a mandatory field
• You should select any time period which is mentioned below Last completed period:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the last completed period For example: Last completed Month (As of now: A Last completed Quarter (As of now: Second Quarter) Current period:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the current period For example: Current Month (As of now: May)
Current Quarter (As of now: Second Quarter) Fixed
Interval:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in fixed intervals
For example: From fixed Period to fixed period Type
of SLA:
• It is a mandatory field
• Should select type of SLA which are mentioned below
Percentage:
• In Percentage Range values should not be in decimals
• In Percentage Start Setting percentage range values from red zone
Duration:
• In Duration Start Setting duration range values from green zone
Entity Based SLA:
Users can create entity based or file-based SLA/KPI’s based on the file status. Here users should provide either a range of percentages or durations to raise alerts accordingly. For example, here in this scenario an SLA named ‘ACME Percentage SLA’ is created with required details as shown below Figure.
In the SLA details please enter the SLA name, description and select the configuration type entity based or file based. Here we selected entity-based SLA so given the entity name and entity id details to check the particular files related to that entity in the configured period.
In the Time reference details please enter the time when we are expecting this SLA to tie the files in the time range provided. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Time reference of SLA in detail’.
In type of SLA, we have percentage and duration values to calculate SLA value. Where percentage will be in integer values and duration will be in time range values. Please fill the ranges accordingly.
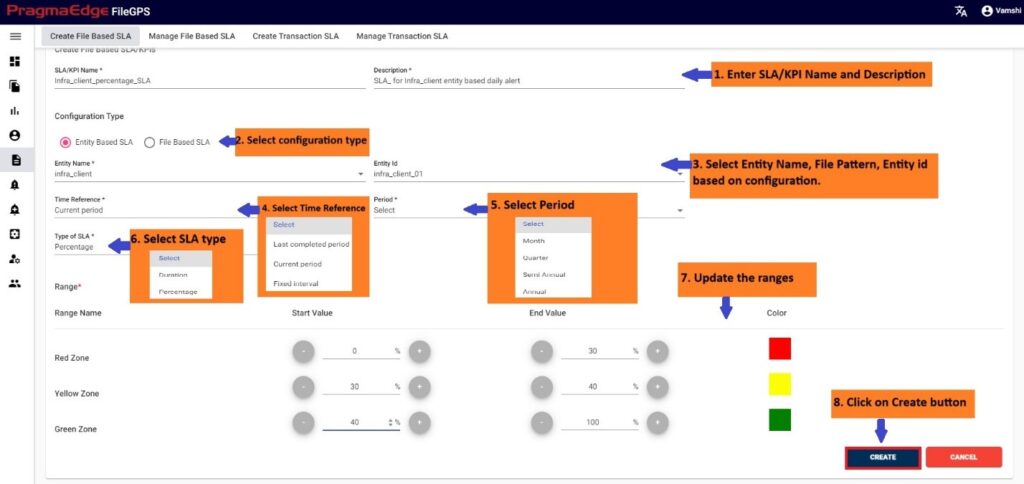
| Property | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
| SLA/KPI Name (Service Level Agreement) | Property is the minimum level of service that a carrier will deliver to you per your agreement | |
| Description | SLA description info | |
| Entity Name | List of entities created | |
| Entity ID | Based on entity name, entity id is generated | |
| Time Reference | List of Time Intervals | |
| Period | Time range | |
| Type of SLA | Duration/Percentage | |
| Start Value | Duration (dd:hrs:min:sec)/Percentage – % | |
| End Value | Duration (dd:hrs:min:sec)/Percentage – % | |
| Color Hexa Code value | Color picked from Color Pickers | |
| Create | Creates New SLA | |
| Cancel | Clear all the input fields to new search |
Time reference of SLA:
SLA Alert Expected time should be selected from the drop down provided so that the alert should check the condition on selected timings. Below are the scenarios we have provided in timing module of the alert under expected time selection so According to this condition SLA alert will check the condition of SLA ranges and raise the notification.
1. SLA Last completed period scenario:
In this scenario we selected the time reference as ‘Last completed period’. After selecting it will ask you to select the period like month, quarter, semiannual and annual So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for last completed period with period we selected.
• Below example: It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the last completed period (month, quarter, semiannual and annual)
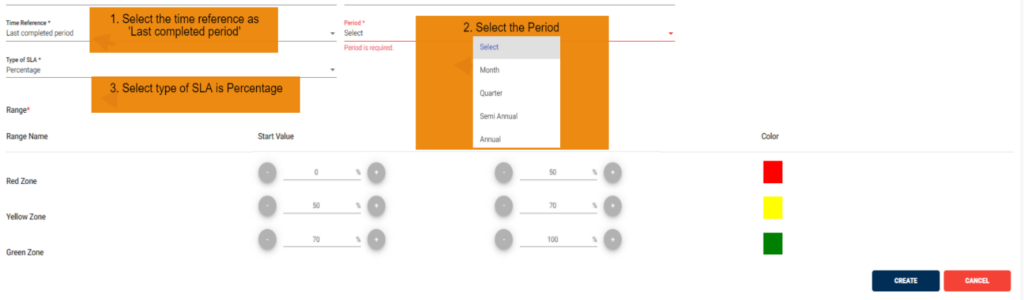
2. SLA Current period scenario:
In this scenario we selected the time reference as ‘Current period’. After selecting it will ask you to select the period like month, quarter, semiannual and annual So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for current period with period we selected.
• Below example: It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the current period (month, quarter, semiannual and annual)
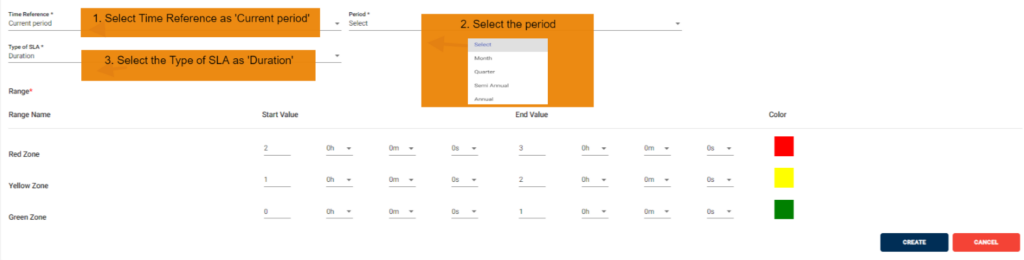
3. SLA Fixed Interval scenario:
In this scenario we selected the time reference as ‘Fixed Interval’. After selecting it will ask you to select the period from date and to date So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for that between date range we selected.
• Below example: It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in from date and end date configured through date pickers.
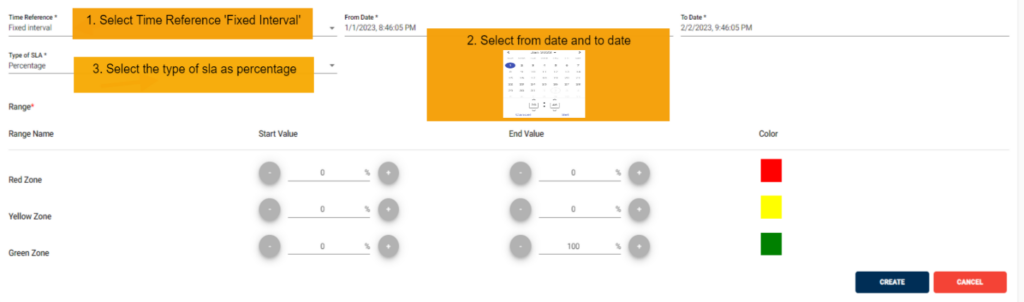
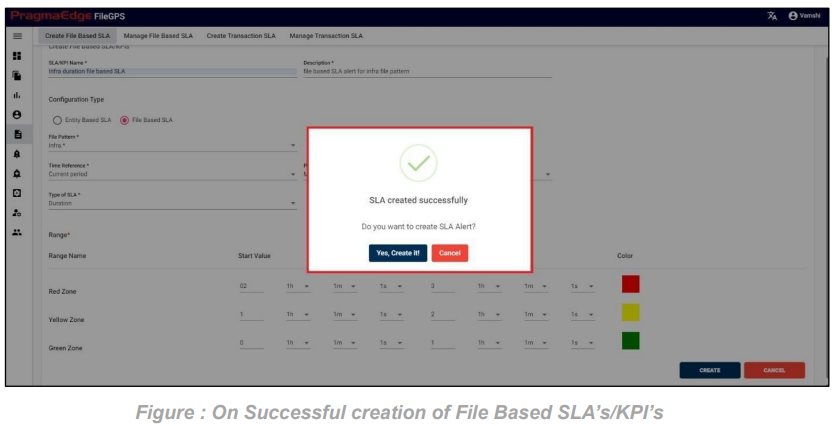
After giving details. Just click on the create button which will create SLA successfully and displays success message as shown below.
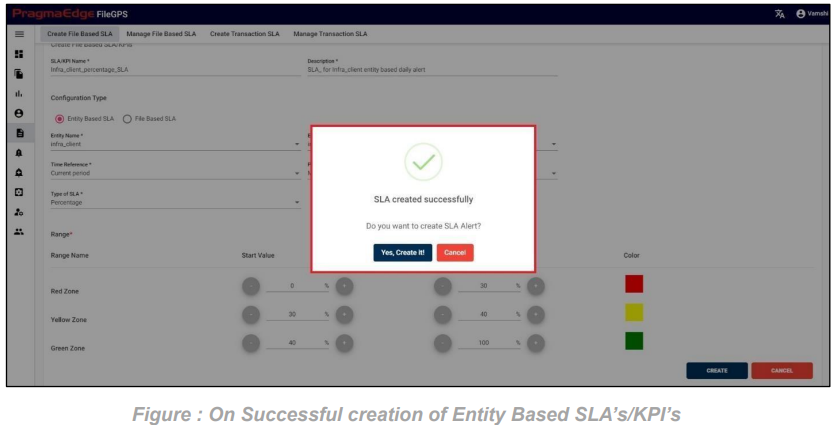
After SLA is successfully created it will ask you to create SLA Alert for that particular SLA created.
If we are required to click on “Yes, create it” if not please click cancel.
Creation of SLA Alert from SLA Page:
If we click on to create SLA alert. It will navigate to the SLA alert creation page with some default values provided in SLA as below please provide the required details and create it.
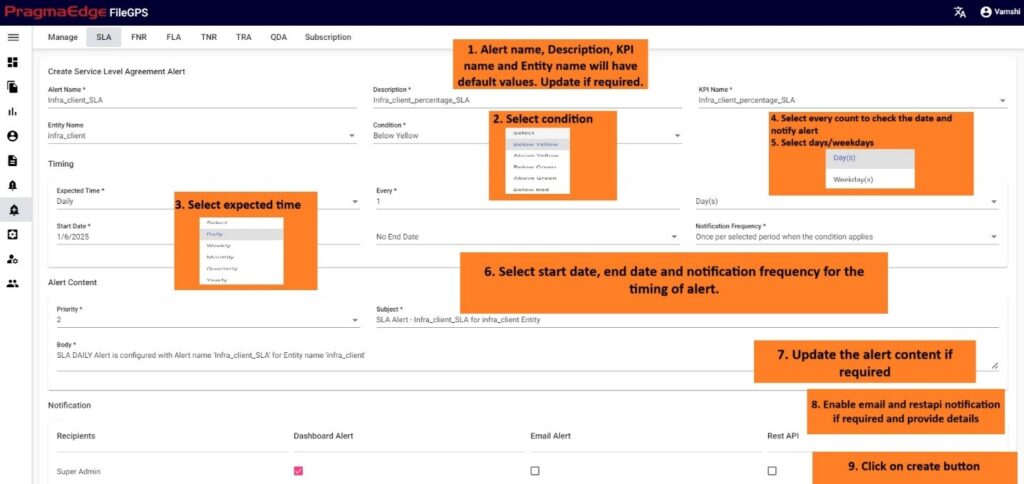
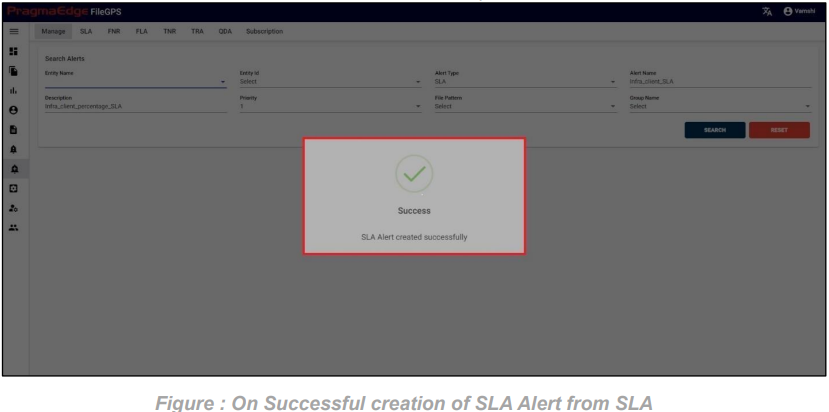
After providing the timing of the alert to be notified. Please enable the email notification by providing email address and rest API notification by providing method, URL and auth type. Now click on the create button to create SLA alert successfully as shown below.
File Based SLA Creation:
Users can create File based SLA/KPI’s based on the file status. Here users should provide time durations to raise alerts.
For example, here in this scenario an SLA named ‘INFRA Duration file-based SLA’ is created with required details as shown below Figure. Please find the description for fields in the table below and fill in the details accordingly.
In the SLA details please enter the SLA name, description and select the configuration type entity based or file based. Here we selected file-based SLA so given the file pattern details to check the particular files related to that pattern in the configured period.
In the Time reference details please enter the time when we are expecting this SLA to tie the files in the time range provided. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Time reference of SLA’ in detail.
In type of SLA, we have percentage and duration values to calculate SLA value. Where percentage will be in integer values and duration will be in time range values. Please fill the ranges accordingly. Here we Select the duration which select the time range from green zone.
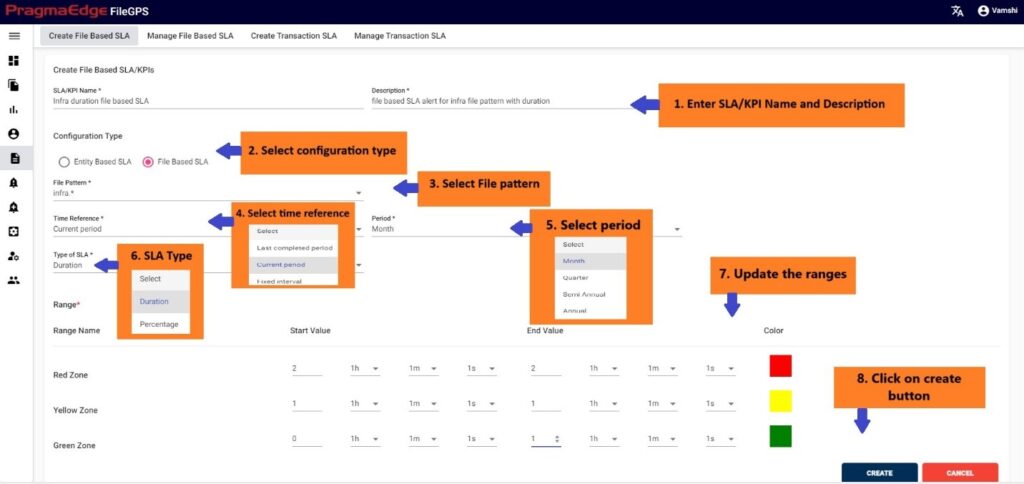
| Property | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
| SLA/ KPI Name | Service Level Agreement the minimum level of service that a carrier will deliver to you per your agreement. | |
| Description | SLA description info | |
| File Pattern | Need to select pattern of the file | |
| Time Reference | Either it may be one month, Year etc. | |
| Type of SLA | Percentage/Duration | |
| Search | Allows user to filter the records based on the inputs | |
| Cancel | Cancels the search |
After giving details. Just click on the create button which will create SLA successfully and displays success message as shown below.
8.2. Manage File Based SLA:
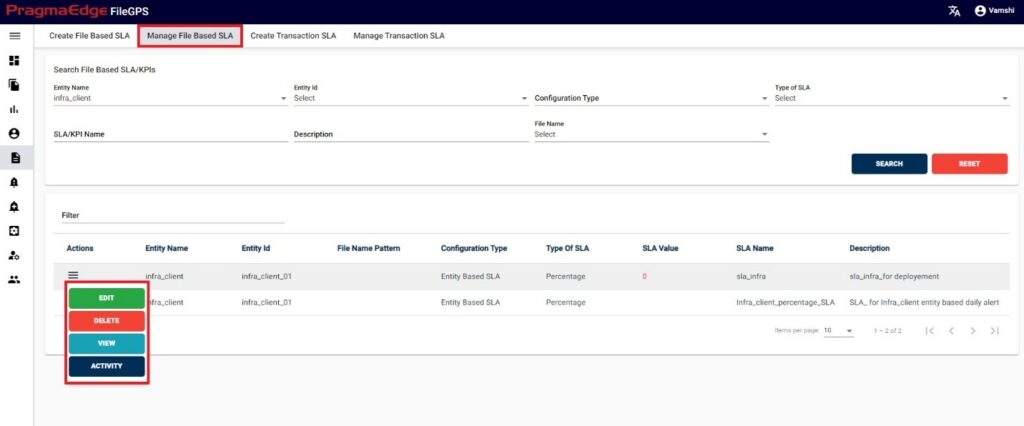
In Manage file-based SLA, User can search for the SLAs based on the filters that were provided at the time of SLA creation.
In screen of Search File Based SLA/KPI’s we can search the SLAs by providing the Entity name, Entity id, Configuration type, type of SLA and SLA name as well.
Path:
Login SLAs/KPIs
Manage File Based SLA
User has privilege to modify the SLA’s/KPI’s for the created entity. User has access to perform below
actions
1. Edit
2. Delete
3. Graph
4. Activity
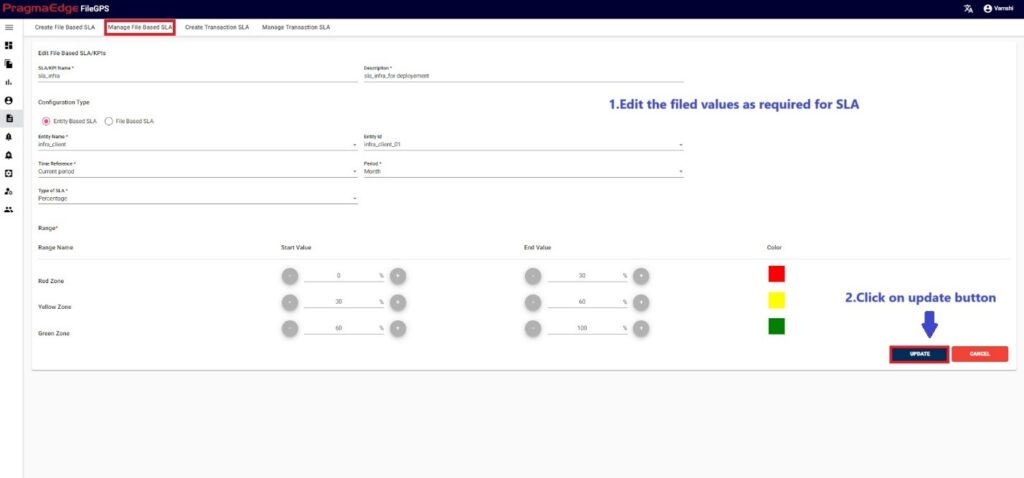
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the SLA details. By clicking on the edit option, the page will be navigated to create a page module where we can change details as per requirement.
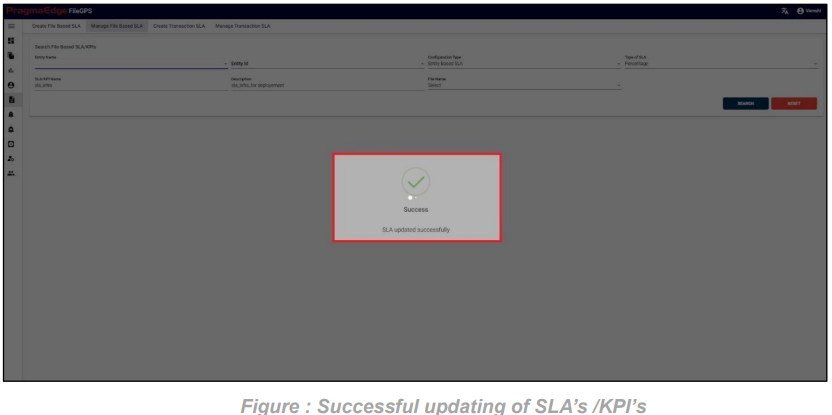
Click on ‘Update’ button; after making the required changes, application will update the SLA details as shown in figure.
Note: Changes or deletions applied to a created SLA/KPI will be automatically propagated across all instances where the SLA/KPI is employed or utilized.
Clicking on ‘Activity’ will have the record of all the actions performed by the users as shown in figure.
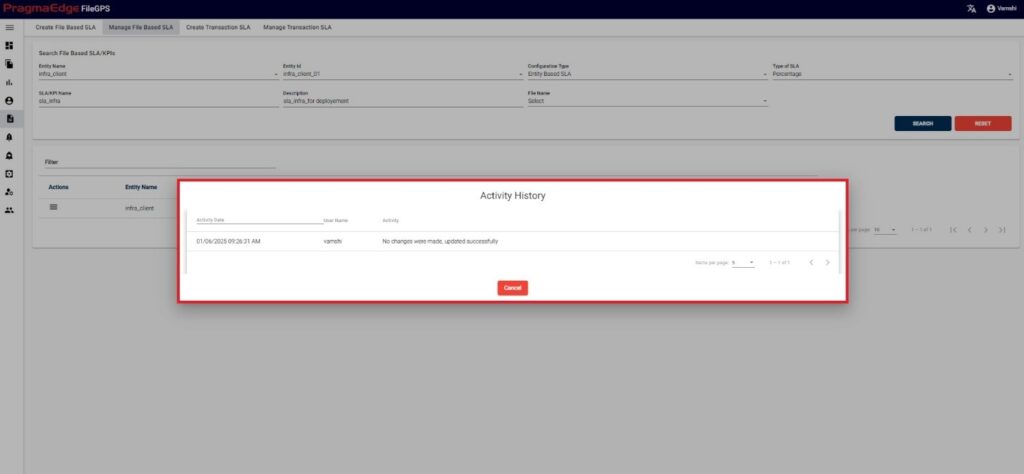
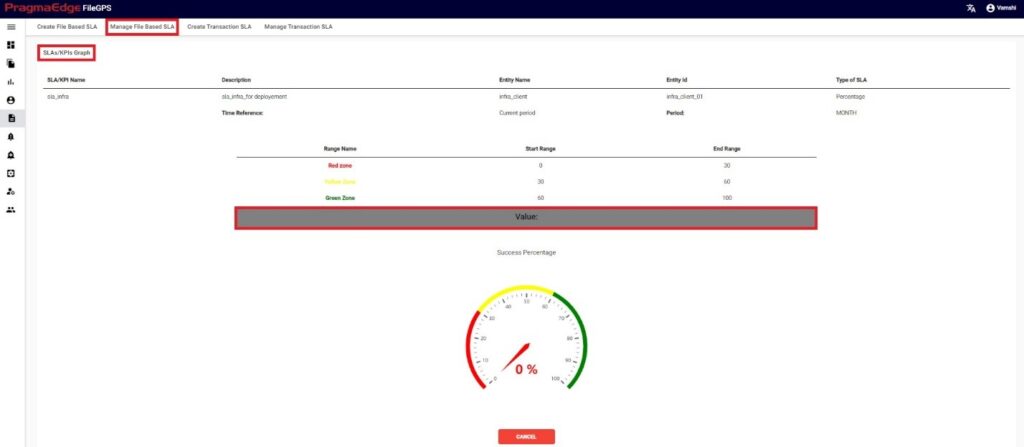
Clicking on ‘View’ in actions button shows the SLA value of that particular SLA/KPI in graphical representation as shown in figure.
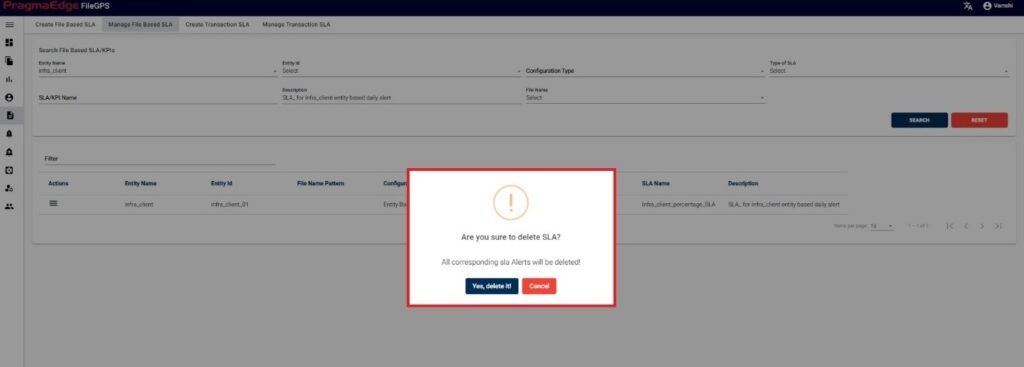
SLA record could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure. Here it will ask for the confirmation to delete all the corresponding SLA alerts related to this SLA. To delete all the related SLA alerts to this particular SLA, click on ‘Yes, delete it!’. If not just cancel
it.
Note: Changes or deletions applied to a created SLA/KPI will be automatically propagated across all instances where the SLA/KPI is employed or utilized.
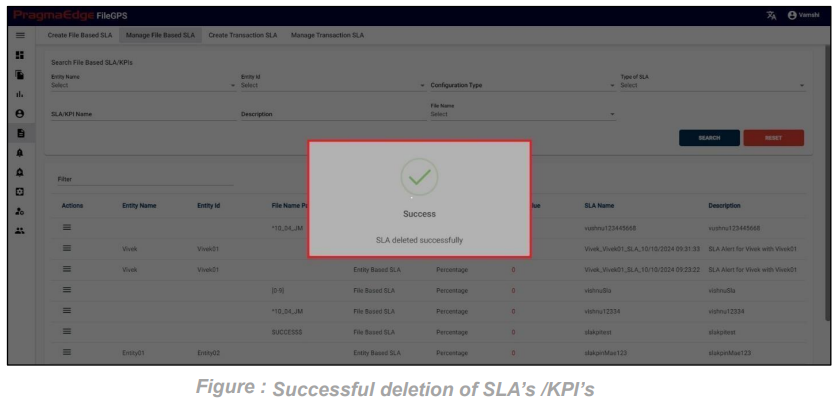
After clicking on yes to delete the SLA. Now SLA record could be permanently deleted with successful deletion message as shown below.
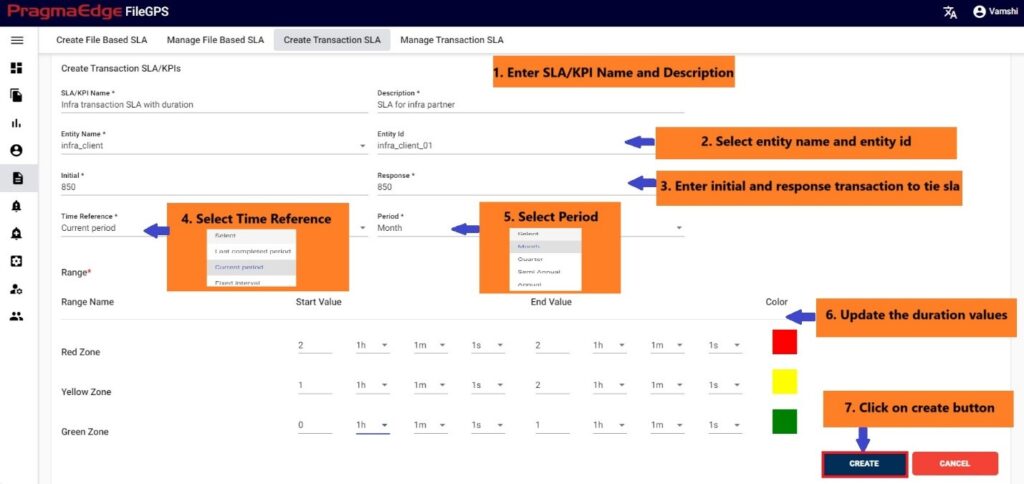
8.3. Create Transaction SLA:
Path:
Login SLAs/KPIs
Create Transaction SLA
In Create Transaction SLA the user can create an SLA for Transaction files with Initial and Response transaction numbers.
Before creating the SLA alert, the user has to create an SLA for the Entity with the required processing parameters to model the condition.
Users can Create SLAs/KPIs for the created entities, file patterns in Duration format SLA’s/KPI’s. Below is a detailed description of mandatory fields that are present in the SLA.
Time Reference:
• It is a mandatory field
• You should select any time period which is mentioned below Last completed period:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the last completed period For example: Last completed Month (As of now: April)
Last completed Quarter (As of now: First Quarter) Current period:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in the current period For example: Current Month (As of now: present month)
Current Quarter (As of now: present quarter)
Fixed Interval:
• It calculates SLA based on the files which are processed in fixed interval
For example: From fixed Period to fixed period
Users can create SLA/KPI’s based on the event status Duration. Here users should provide
durations to raise alerts.
For example, in the scenario an SLA named ‘ACME Transaction SLA with duration’ is created as shown below Figure
In the SLA details please enter the SLA name and description. Here Select the entity name and entity id. And enter the initial and response transaction numbers to tie the SLA. In the Time reference details please enter the time when we are expecting this SLA to tie the files in the time range provided. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Time reference of SLA in detail’.
In type of SLA, we have percentage and duration values to calculate SLA value. Where percentage will be in integer values and duration will be in time range values. Please fill the ranges accordingly.
Successful creation of SLA displays success message with SLA details.
| Property | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
| SLA/KPI Name (Service Level Agreement) | Property is the minimum level of service that a carrier will deliver to you per your agreement | |
| Description | SLA description info | |
| Entity Name | List of entities created | |
| Entity ID | Based on entity name, entity id is generated | |
| Initial | Initial state | |
| Response | Response State | |
| Time Reference | List of Time Intervals | |
| Period | Time range | |
| Start Value | Duration(dd:hrs:min:sec)/Percentage- % | |
| End Value | Duration(dd:hrs:min:sec)/Percentage- % | |
| Color Hexa Code value | Color picked from Color Pickers | |
| Create | Creates New SLA | |
| Cancel | Clear all the input fields to new search |
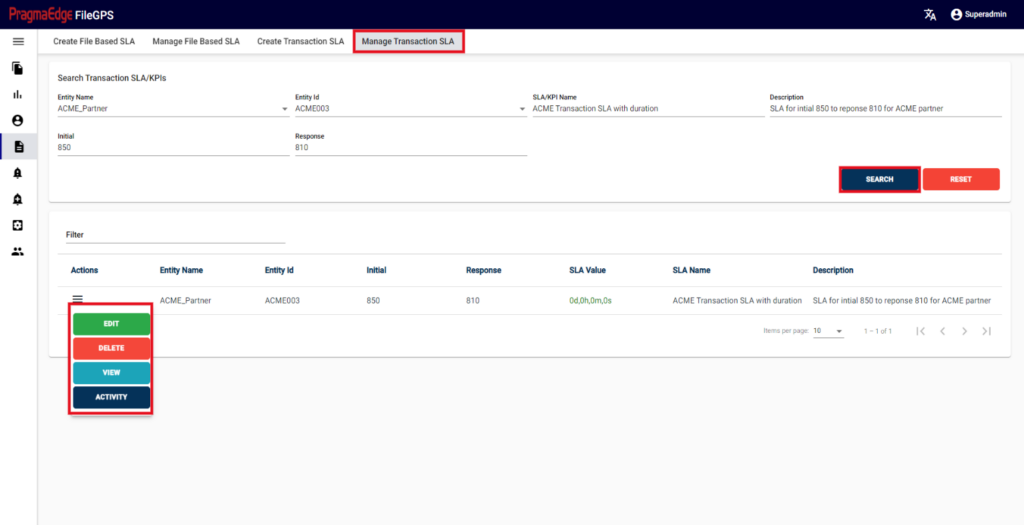
8.4. Manage Transaction SLA:
In Manage Transaction SLA, User can search for the SLAs based on the filters that were provided at the time of SLA creation.
Path:
LoginSLAs/KPIs
Manage Transaction SLA
User has privilege to modify the SLA’s/KPI’s for the created entity. User has access to perform below actions
1.Edit
2.Delete
3.View
4.Activity
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the SLA details. By clicking on the edit option, the page will be navigated to create a page module where we can change details as per requirement.
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the SLA details. By clicking on the edit option, the page will be navigated to create a page module where we can change details as per requirement.
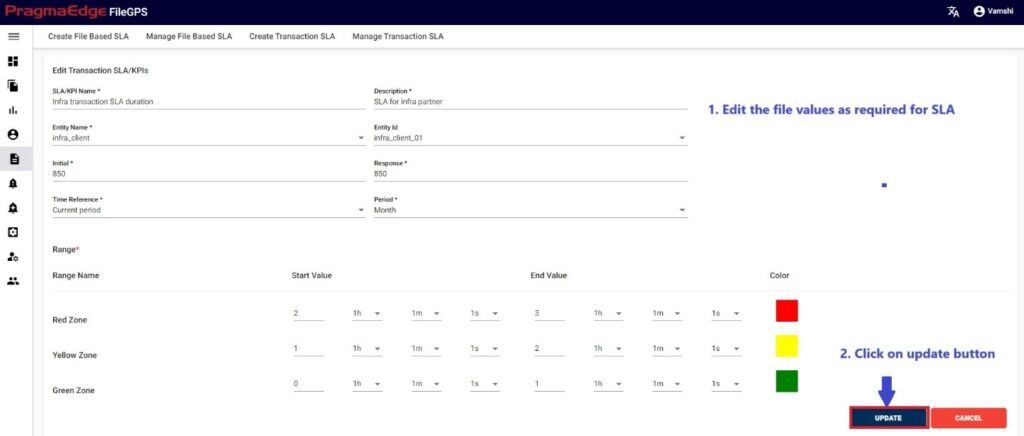
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the SLA details as shown in figure.
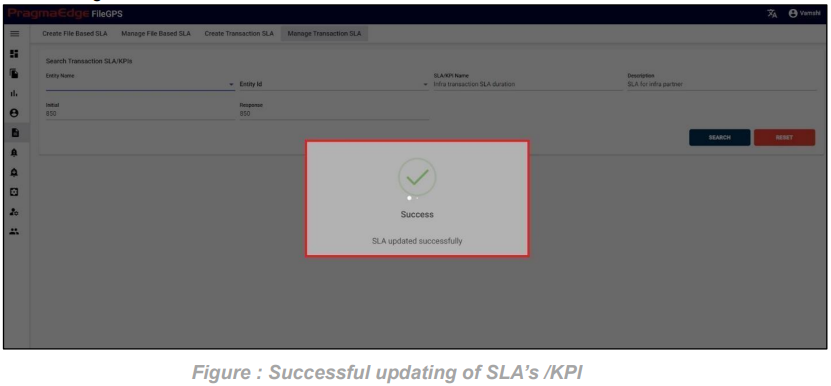
‘Activity’ will have the record of all the actions performed by the users as shown in figure
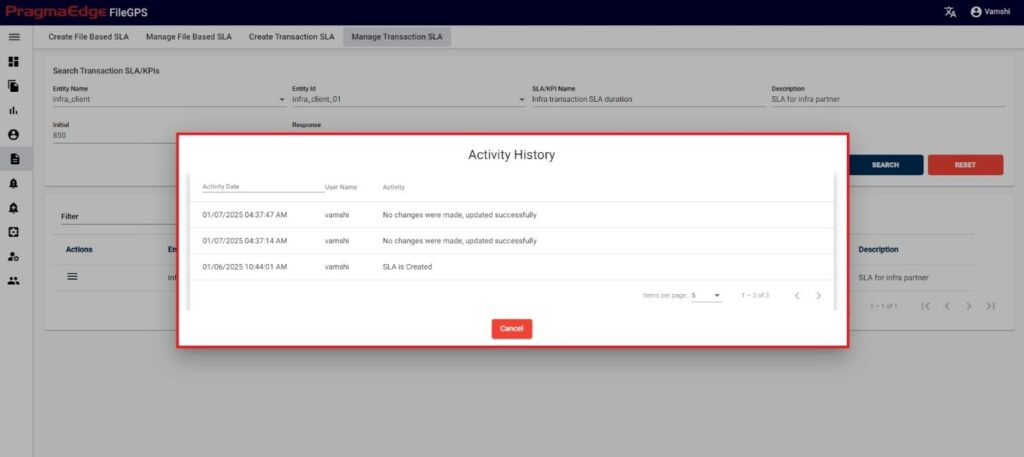
‘View’ in actions button shows the SLA value of that particular SLA/KPI in graphical representation as shown in figure.
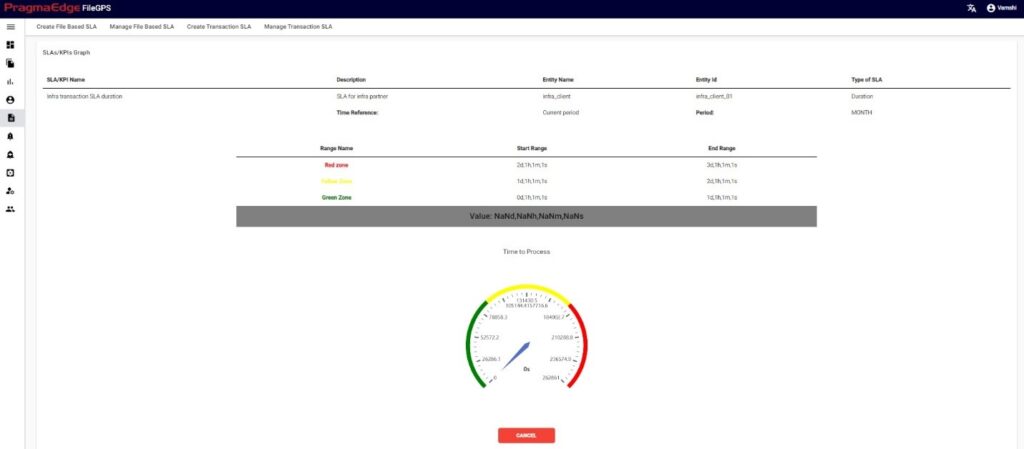
SLA record could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure. Here it will ask for the confirmation to delete all the corresponding SLA alerts related to this SLA. To delete all the related SLA alerts to this particular SLA click on ‘Yes, delete it!’. If not just cancel it.
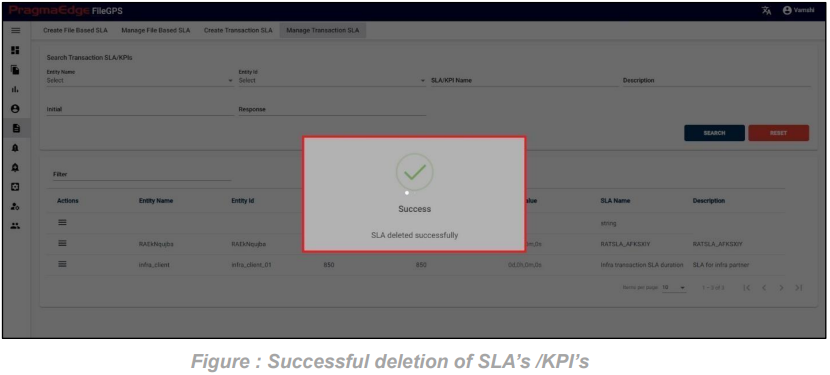
After clicking on yes to delete the SLA. Now SLA record could be permanently deleted with successful deletion message as shown below.
9. Alerts:
Alerts option notify the users in the dashboard when alerts match the condition configured by the user.
Path:
Login Alerts
Users can search for the list of alerts that were generated based on the selected criteria. In the below scenario various application alerts such as SLA Alerts, FNR Alerts, Subscription Alerts, TNA Alerts, TRA Alerts, QDA Alerts and FLA Alerts that were raised are shown in the figure below.
Users can search the alerts that matched the condition notified in this module just by giving the fields provided like data range, entity details, alert type and alert details. After providing the details just click on the search button. The raised alerts will be displayed as shown in the figure below.
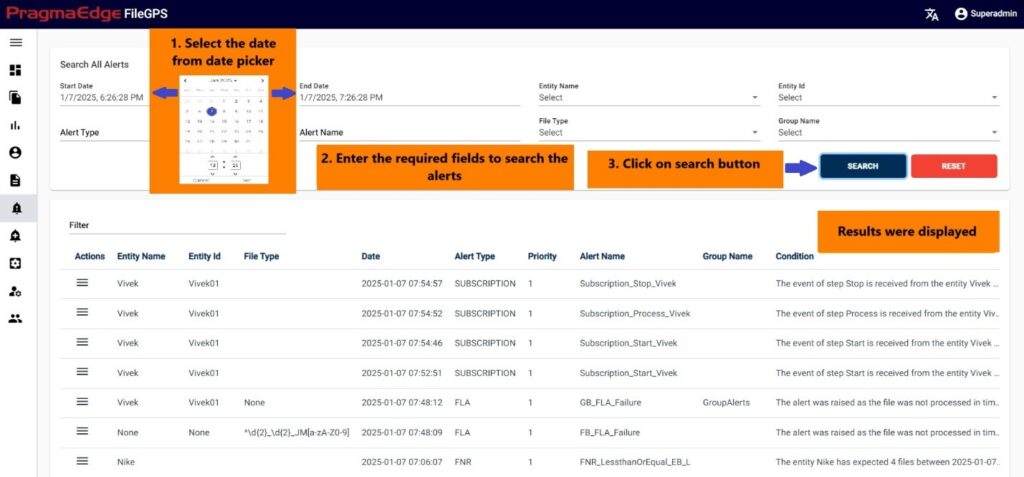
After getting the filtered result we have actions button by clicking on it. It will have a view icon on the left side of the record.by clicking on it will display the alerts details in a clear view.
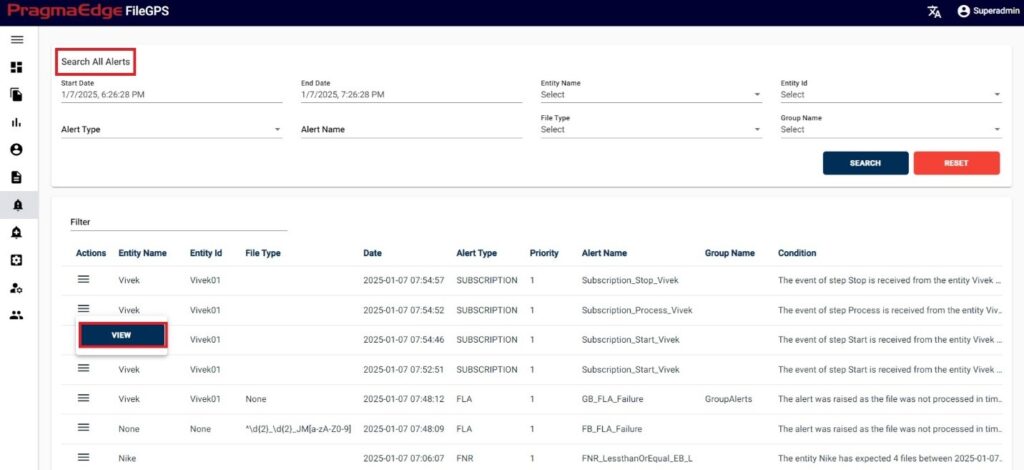
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Date Range | Search can be done within time range, select start and end dates |
| Alert Type | Either may be SLA alert, FNR alert etc., |
| Entity Name | Select created or existing entity name |
| Entity ID | Select created or existing entity id |
| Alert Name | Select the alert name |
| File Type | Select created or existing file pattern |
| Group Name | Select created or existing group name |
| Search | Can perform search on alerts |
| Reset | Clears the form fields |
For example, if Alerts are being searched based on Alert type like FNR Alert, all FNR alerts raised will be displayed.
The alert section has the ‘ACTIONS’ button where the user will have an option to view a particular alert.
By clicking on the ‘View’ option, user can view entire details of particular alert.
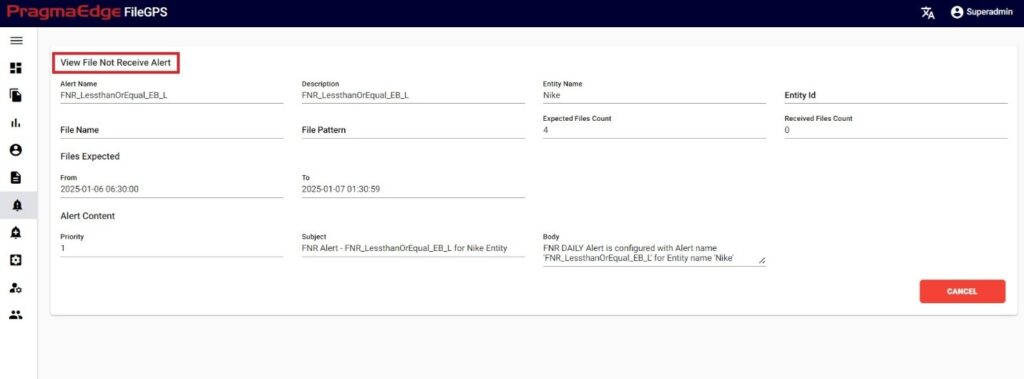
| Property | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Alert Name | Name given while creating alert | |
| Description | Which describes type of the alert | |
| Entity Name | Created Entity Name | |
| KPI Name | Name of SLA | |
| SLA old Value | Previous value | |
| SLA New Value | New Value | |
| File Type | File extension | |
| Type of SLA | Type of the agreement | |
| Time Reference | Time period | |
| From | From Date | |
| To | To Date | |
| Condition | SLA condition | |
| Alert Raised | Type of the alert raised | |
| Priority | Scheduling tasks based on importance | |
| Subject | On which content | |
| Body | Body for email | |
| Cancel | Clears the values |
10. Alert Management:
In Alert Management, the user can configure the alerts based on his requirement and manage the alerts.
Path:
LoginAlert Management
Users can create and manage alerts to track the transmissions of the files to a particular hub. Alerts are categorized into multiple subcategories
1. Manage
2. SLA
3. FNR
4. FLA
5. TNR
6. TRA
7. QDA
8. Subscription
10.1. Manage:
In Manage Alert, User can search for the Alerts based on the filters that were provided at the time of Alerts creation. By searching with the filtered columns, the results will be displayed with alerts.
We will have an action icon on the left side of the record where we can manage a resultant alert.
Path:
Login Alert Management
Manage
Users have edit/delete/activity options to perform on alerts.
All the actions such as edit/delete/activity could be performed when user click on the action icon of the record as shown in figure below.
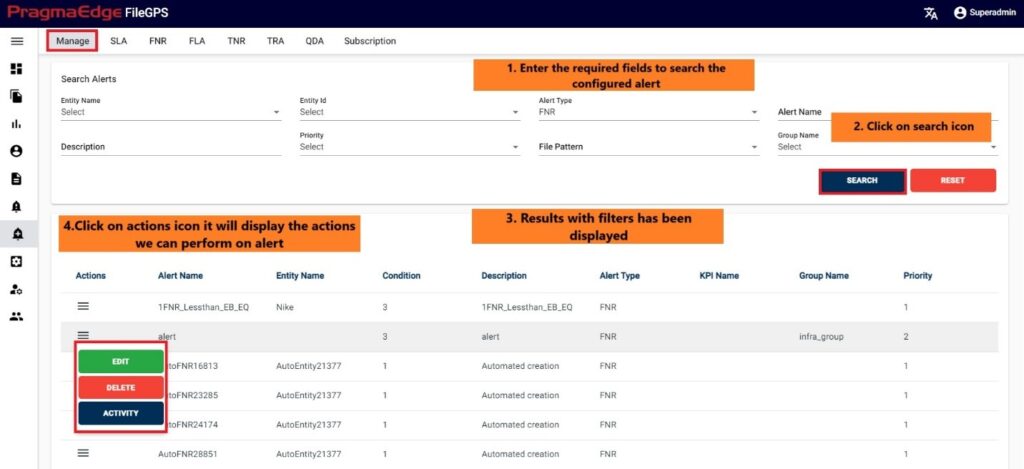
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the Alert details for the columns we have configured while creating alerts.
For example, consider FNR Alert created previously, by clicking on the edit option, the page will be navigated to create page module where we can change details as per requirement.
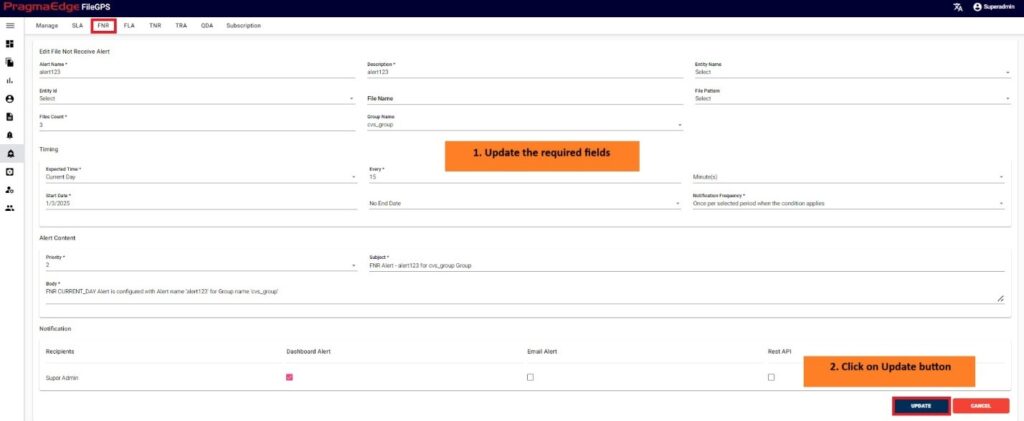
Note: Implemented tagging functionality within the subject field of the alert management system, allowing users to tag specific fields as needed and customize the email subject accordingly in FLA, TRA and Subscription alerts.
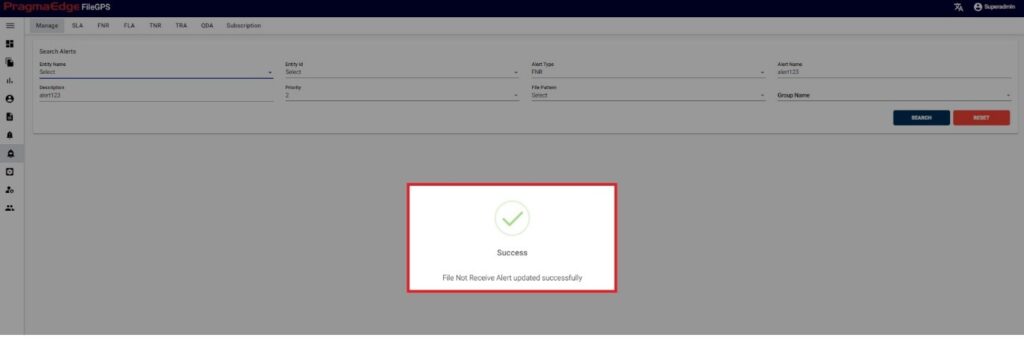
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the Alert details as shown in figure.
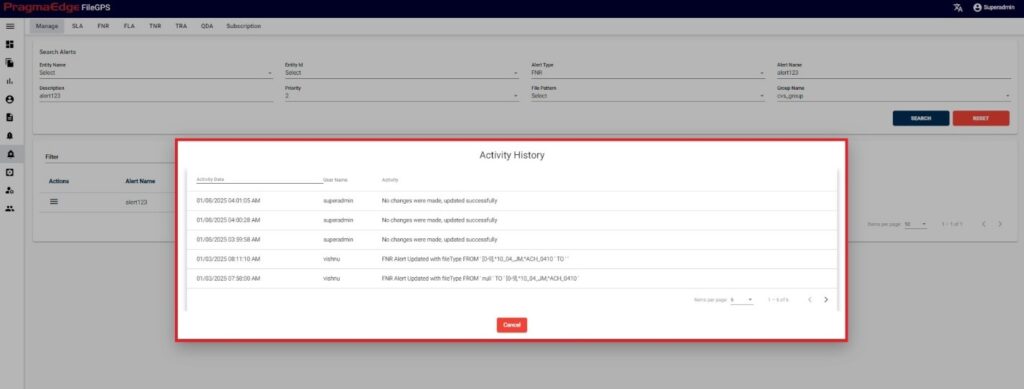
‘Activity’ will have the record of all the actions performed by the users as shown in figure Below.
After clicking on delete option it will ask for confirmation to delete alert. Click on ‘yes, delete it!’
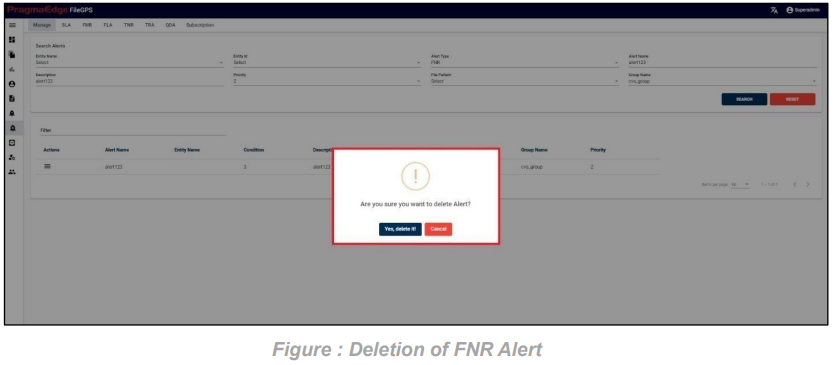
Alert record could be permanently deleted with the ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure.
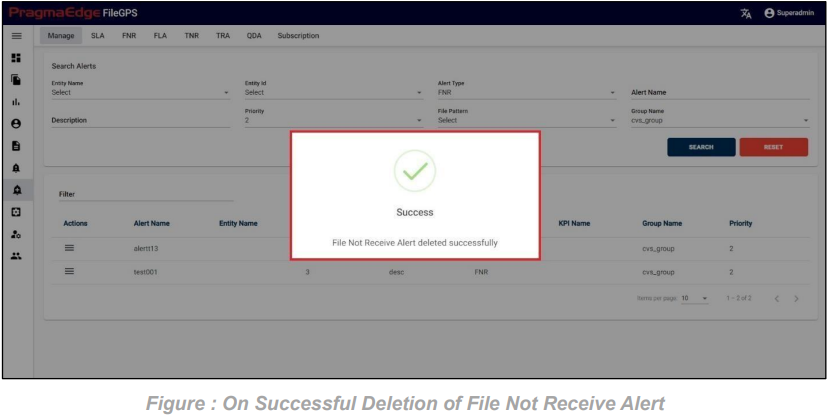
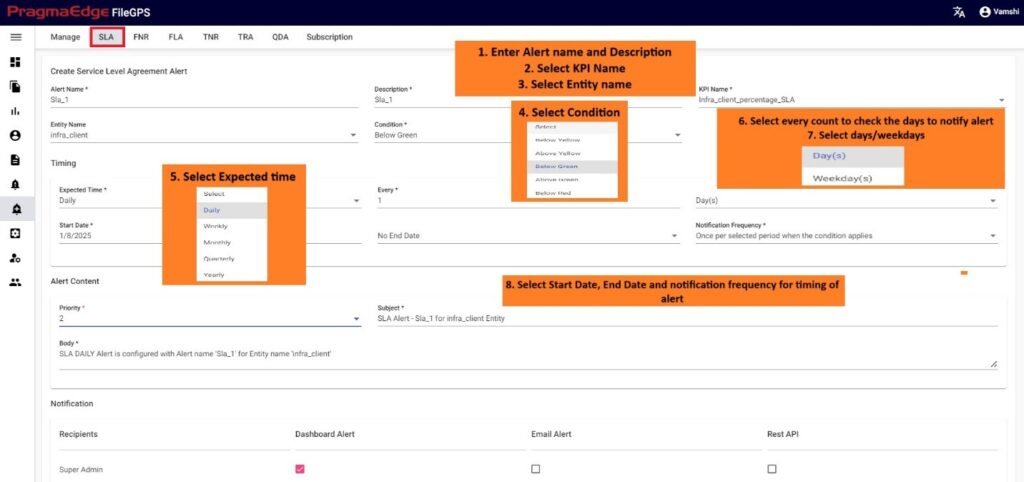
10.2. Service Level Agreement Alert (SLA Alert):
Service Level Agreement Alert can be configured by the user based on the requirement of the time ranges and percentages.
SLA’s can be tied to the files by configuring SLA in SLA/KPI module and tie alert to it to raise notification when SLA is breached. Here in this module, we are going to tie SLA Alert for the SLA created.
Path:
Login Alert Management
SLA Alert
In SLA Alert tab, user can create SLA alert for required Entity or files by committing conditions according to the time ranges and percentages predefined in SLA.
The pre-requisite in order to configure the Alert is, corresponding SLA should be created. For example, in below scenario Figure, user has configured the SLA Alert by giving alert name as ‘Daily SLA Alert for ACME Entity Yellow Zone’ condition based on percentage to the SLA named ‘ACME SLA Percentage’. and entity as ACME Partner.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select SLA name we need to tie this alert and entity name as well. Similarly enter condition of SLA to check the SLA value is in which condition so that if it matched with configured it will raise the alert. In the Timing details please enter the expected time when we are expecting this alert to be notified as we have provided options like daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and yearly details. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Timing of SLA Alert in detail’.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, please provide the method of API whether post or put, URL and auth type with options no auth and basic auth with username password details.
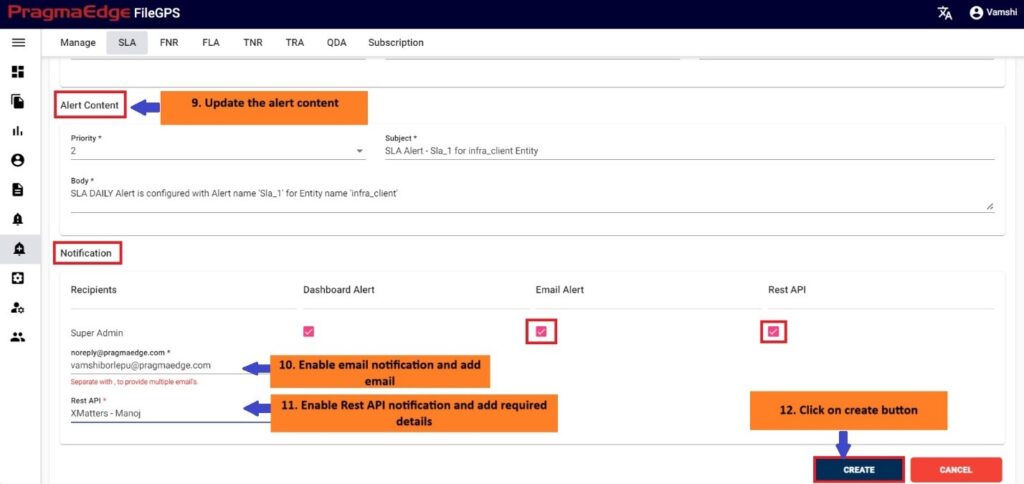
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Created/Existing Alert Name |
| Description | SLA Alert Description info |
| KPI Name | Agreement Name |
| Entity Name | Name of Entity/existing Entity |
| Condition | Select the condition When to raise the alert | Expected Time | Select Time interval like daily/weekly |
| Start Date | Start Date of the file Processed |
| End Date | End Date of the file Processed |
| Notification Frequency | Time interval when occurred |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create an SLA alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
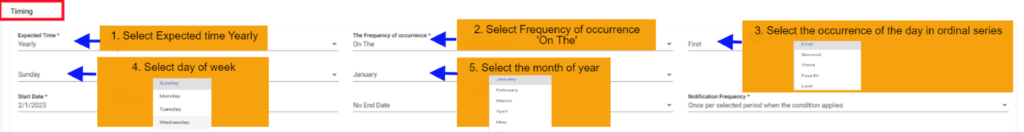
Timing of SLA Alert in detail: SLA Alert Expected time should be selected from the drop down provided so that the alert should check the condition on selected timings. Below are the scenarios we have provided in timing module of the alert under expected time selection so According to this condition SLA alert will check the condition of SLA ranges and raise the notification.
1. SLA Daily days scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the ‘day(s)’ of the week So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for every day
Below example: Checks SLA condition on every day on all days of the week

2. SLA Daily weekdays scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the ‘weekday(s)’ of the week So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for every weekday.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on every day on weekdays of the week.

3. SLA Weekly day of the week scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Day of the week’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week as an integer: 1, 2 etc., and need to select the days of the week So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for every week on the particular selected days.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on every day on the Monday and Tuesday of every week.
Note: We can select multiple days of week to check SLA value

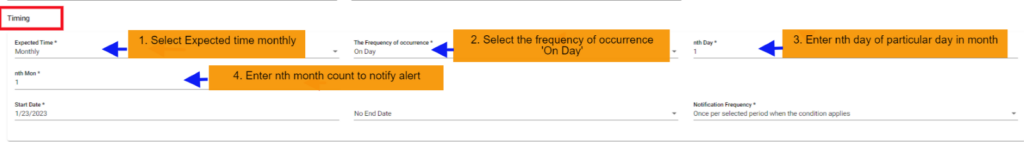
4. SLA Monthly on day scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On Day’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘nth Day’ of particular day in month as an integer: 1, 2 etc., and ‘nth month’ of particular month count. So that the SLA will check the SLA condition for the selected day on the particular month.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on the 1st of every month.
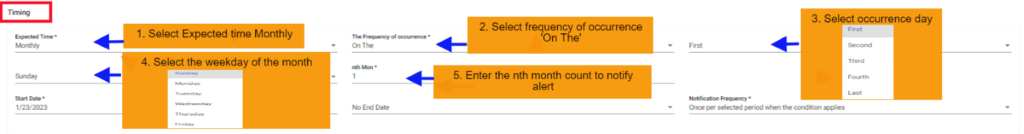
5. SLA Monthly on the scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc., and also ‘nth month’ count of month. So that the SLA will check the SLA condition on the selected day of the particular week of month.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on the first Sunday of every month.
6. SLA Quarterly scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Quarterly’. So that the sla will check the sla condition on quarter end day.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on every quarter end day.

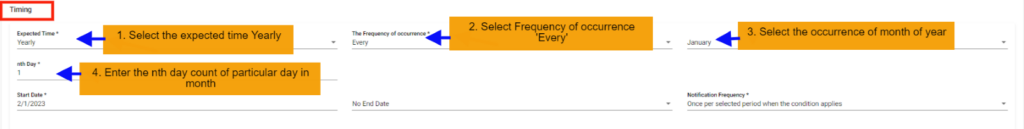
7. SLA Yearly Every Scenario: In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Every’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the month as January, February etc. and also ‘nth Day’ of particular day of month. So that the SLA will check the SLA condition on the selected day on the particular day of month provided considering every month count
Below example: Checks SLA condition on the first of every January for every year.
8. SLA Yearly on the Scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also selects the month of the year. So that the SLA will check the SLA condition on the selected day on the particular week of month in a year.
Below example: Checks SLA condition on the first Sunday of January every year
Raised SLA Alert:
For example, In the above created ‘Daily SLA Alert for ACME Entity Yellow Zone’ when the Entity Based-ACME-Percentage-SLA’ matches the below yellow condition value then alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert SLA with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
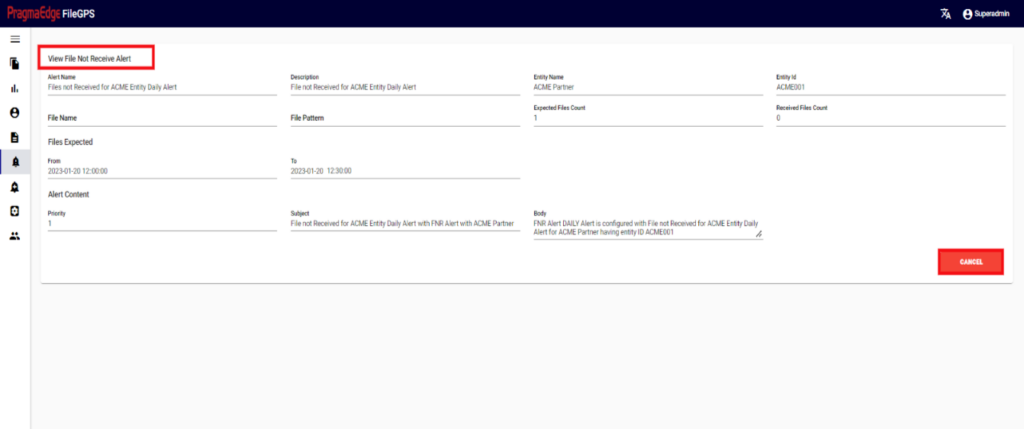
10.3. File Not Received Alert (FNR Alert):
In the File Transfer process, if the file has not reached its destination, in other words, if the event state start was not found then ‘FNR’ alert will be raised. This alert lets the business team know that the file has not been received for the entity or group of entities. File not Received alert will notify the user if the configured expected files count does not match with received file count for the particular entity. We can configure the file count while creating alert as shown below.
Path:
Login Alert Management
FNR
We have two scenarios for configuring FNR alerts: one is FNR for entities, and the other is FNR for groups.
FNR Alert for Entity:
In the below figure user has configured the FNR Alert for Entity by giving alert name as ‘Files Not Received for ACME Entity Daily Alert’ and entity as ACME Partner, Entity Id as ACME001. In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description, select entity name and entity id as well. Enter the filename if we know the exact file name to match while checking the files. Similarly, enter the file pattern or multiple file patterns if there are patterns to match the files. And please enter the files count of the files to match with the received files count condition.
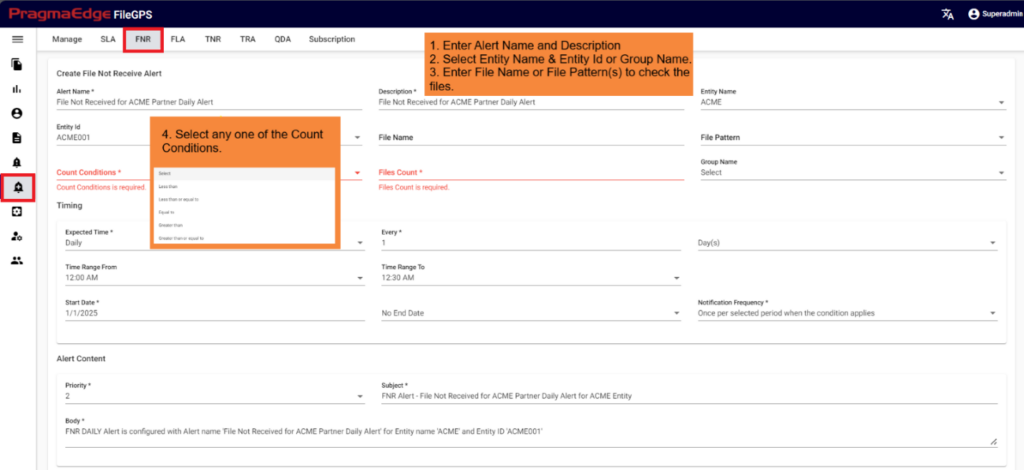
Note:
We have five types of file count conditions, as illustrated in the figure below:
Less Than: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is greater than or equal to the expected file count.
Less Than or Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count exceeds the expected file count.
Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is either less than or greater than the expected file count.
Greater Than: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is less than or equal to the expected file count.
Greater Than or Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is below the expected file count.

In the Timing details please enter the expected time when we are expecting this alert to be notified as we have provided options like daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly details. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these with heading ‘Timing of FNR in detail’ after the alert created.
FNR Alert for Groups:
In the below figure user has configured the FNR Alert for Groups by giving alert name as ‘File Not Received for Group infra_group Daily’ and Group Name as infra_group Group.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and group name as well. Enter the filename if we know the exact file name to match while checking the files. Similarly enter file pattern if we have pattern to match the files. And please enter the files count of the files to match with the received files count condition.
In the Timing details please enter the expected time when we are expecting this alert to be notified as we have provided options like daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly details. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these with heading ‘Timing of FNR in detail’ after the alert created.

Note: The configuration process for FNR Entity and FNR Group is identical for the remaining steps.
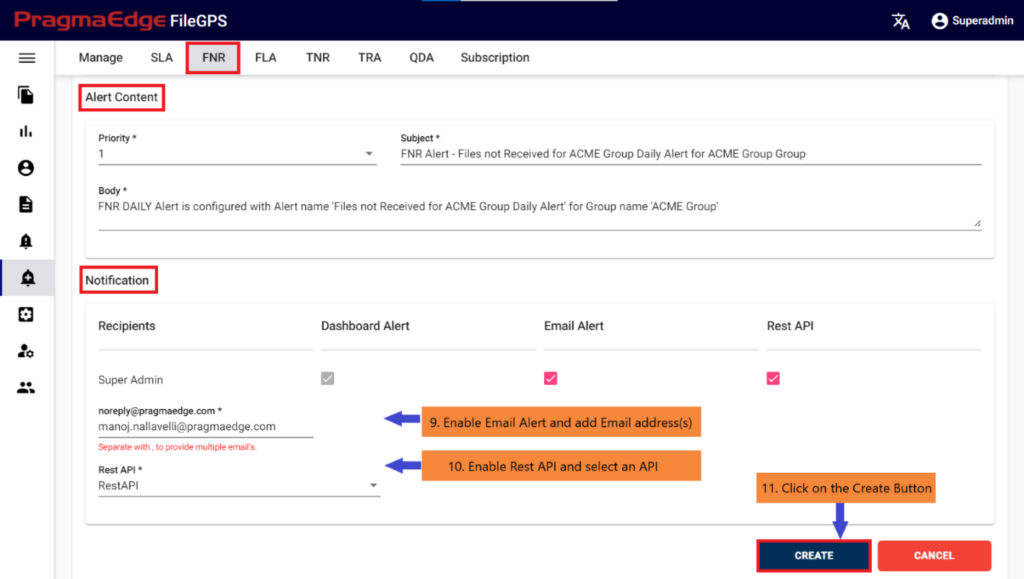
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, please select Rest API from drop down. provide the method of API whether post or put, URL and auth type with options no auth and basic auth with username
password details.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Created/Existing Alert Name |
| Description | FNR Alert Description info |
| Entity Name | Created/Existing Entity Name |
| Entity ID | Create/Existing Entity ID |
| File Name | Name of the file in process |
| File Pattern | File expression pattern |
| File Count | Number of files passed the process |
| Group Name | Created/Existing Group Name |
| Expected Time | Time interval when occurred |
| Time Range From | Starting time in time range |
| Time Range To | Ending Time Range |
| Start Date | Start Date of the file Processed |
| End Date | End Date of the file Processed |
| Notification Frequency | Notification occurrence at regular intervals |
| Alert Content | Description of the alert and its content |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Regarding the alert |
| Body | Miscellaneous |
| Notification | To inform |
| Recipient | Receive |
| Email of the Entity | |
| Create | Create Alerts |
| Cancel | Clears values in input values |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a FNR alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
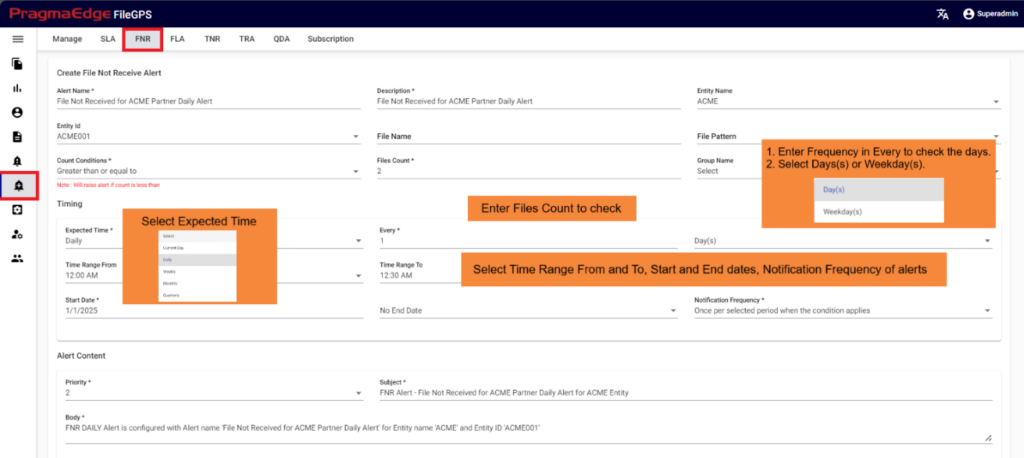
Timing of FNR in detail: FNR Expected time should be selected from the drop down provided so that the alert should check the condition on selected timings. Below are the scenarios we have provided in timing module of the alert under expected time selection so According to this condition FNR will check the files and raise the notification.
1. FNR Current Day Minute’s scenario:
In this scenario, we selected the expected time ‘Current day’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the minute to consider as integers: 1, 2, …59. and need to select the ‘Minute(s)’ of the hour So that the FNR will check current day scenario for selected minutes also with the start and end dates provided.
The example below checks FNR: For every 30 minutes, the FNR (File Not Received) will check for the presence of the expected file. In the event of non-arrival, it will trigger an FNR alert.

2. FNR Current day Hour’s scenario:
In this scenario, we selected the expected time ‘Current day’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the hour to consider as integers: 1, 2, …23. and need to select the ‘Hour(s)’ So that the FNR will check current day scenario for selected hours also with the start and end dates provided.
The example below checks FNR: For every 3 hours, the FNR (File Not Received) will check for the presence of the expected file. In the event of non-arrival, it will trigger an FNR alert.

1.FNR Daily days scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc., and also need to select the ‘day(s)’ of the week So that the FNR will check daily scenario for every day also with time range ranges provided.
Below example checks FNR: On every day on all days of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

2. FNR Daily weekdays scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the ‘weekday(s)’ of the week So that the FNR will check daily scenario for every weekday also with time range provided.
Below example checks FNR: On every day on weekdays of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

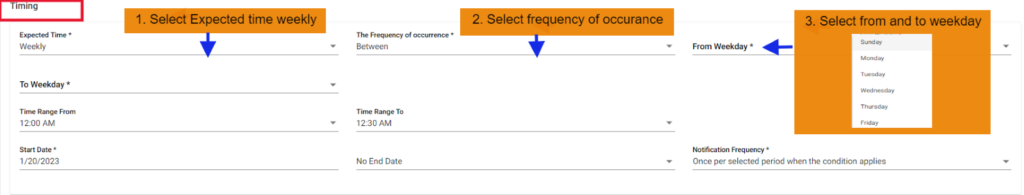
3. FNR Weekly between scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘between’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘from weekday’ and ‘to weekday’ which have the days of the week example: Monday, Tuesday etc. So that the FNR will check weekly in between the selected weekdays with also time range provided
Below example checks FNR: Here we can check 2 scenarios as same week and cross week
Same week: checks on from day (Monday) to today (Thursday) from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
Cross week: checks on from day (Friday) to today (Monday) from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
4. FNR Weekly day of the week scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Day of the week’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week as an integer: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the days of the week So that the FNR will check weekly scenario for every week on the selected days also with time range provided.
Below example checks FNR: On the Monday and Tuesday of every week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
Note: We can select multiple days of week to check FNR

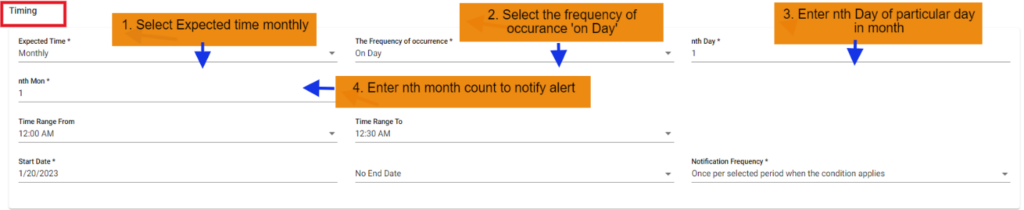
5. FNR Monthly on day scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On Day’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘nth Day’ of particular day in month as integers: 1, 2 etc. and ‘nth month’ of particular month count. So that the FNR will check monthly scenario on the selected day of the particular month also with time range provided. Below example checks FNR: On the 1st of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
6. FNR Monthly on the scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also ‘nth month’ count of month. So that the FNR will check monthly scenario on the selected day on the particular
week of month also with time range ranges provided.
Below example checks FNR: On the first Sunday of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

7. FNR Monthly on interval check scenario:
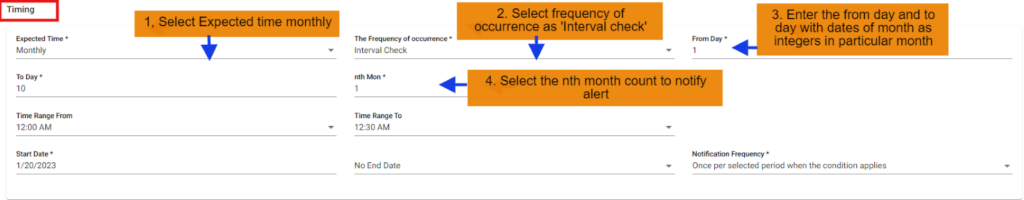
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Interval Check’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘from Day’ and ‘To Day’ of particular day in month as integers: 1, 2 etc. and ‘nth month’ of particular month count. So that the FNR will check monthly interval check scenario from the from day to today selected days on the particular month also with time range ranges provided.
Below example checks FNR: from the 1st to 10th of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
8. FNR Quarterly scenario:
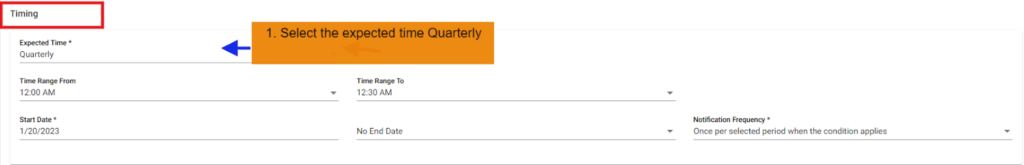
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Quarterly’. So that the FNR will check Quarterly scenario on quarter end day with time range provided.
Below example checks FNR: On quarter end date from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
9. FNR Yearly Every Scenario: In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Every’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the month as January, February etc. and also ‘nth Day’ of particular day of month. So that the FNR will check yearly every scenario on the selected day on the particular day of month provided considering every month count also with time range provided.
Below example checks FNR: On the first of every January for every 1 year from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

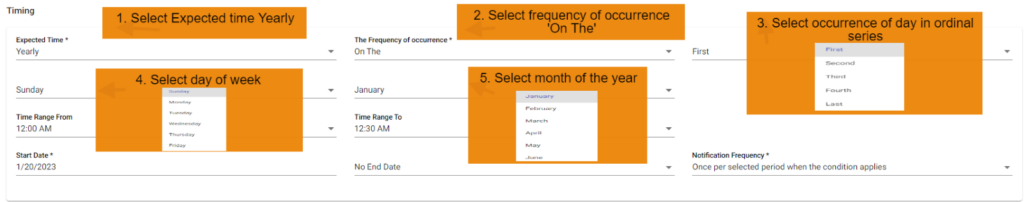
10. FNR Yearly on the Scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also selects the month of the year. So that the FNR will check yearly on the scenario on the selected day on the particular week of month in a year also with time range provided.
Below example checks FNR: On the first Sunday of January every year from 12:00 AM to 12:30
AM
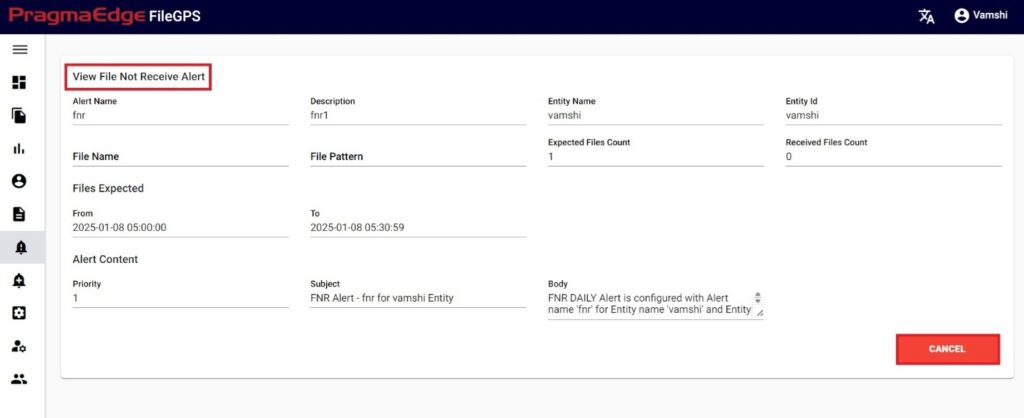
Raised FNR Alert:
For example, In the above created ‘Files not Received for ACME Entity Daily Alert’ if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert FNR with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
10.4. File Load Alert (FLA Alert):
File load alert is raised whenever a file is processed from one node to other, file load alert will raise with success status if the file is transmitted in the prescribed time. Else File load alert is raised with failure status. In either of the cases the file load alert notifies the user on the file transmission.
For Every entity and File pattern we will be configuring ‘time to process’ value while creating it. If the files for the prescribed entity or entities in a group or file pattern, load or received within the time to process, then it’s a success condition. Similarly, if a file fails to load then it is in failure condition. This File load alert will track the success and failure condition for each file while transmitting from one node to another node and raises the notification.
Path:
Login Alert Management
FLA
File load alert can be configured for Entity based, file pattern based, and Group based.
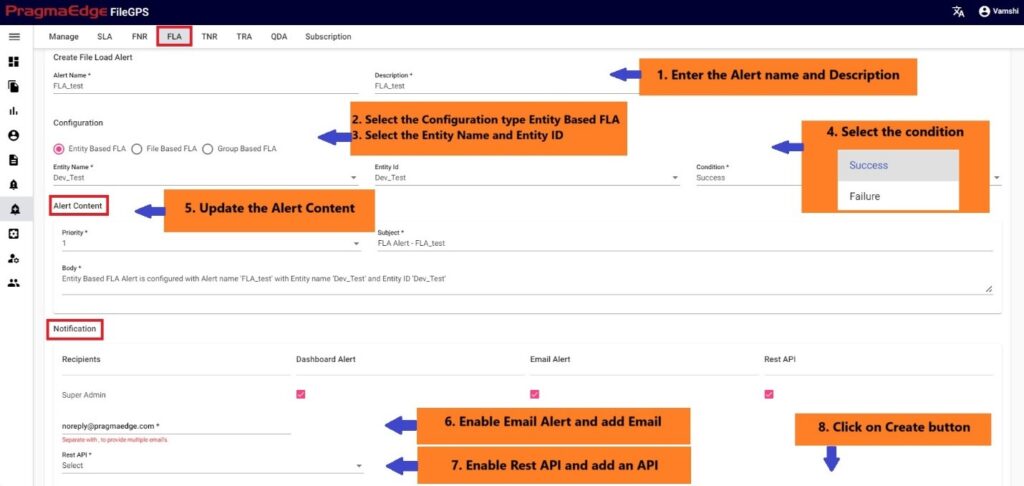
Creation of Entity based FLA:
In the below figure, user has configured the File Load Alert by giving alert name as ‘ACME Entity File Load Success Alert’ for the ACME Entity.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select the configuration type entity based and select entity name and entity id. Similarly, select the condition of the FLA to check for the file.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the Rest API notification, please select the API from the drop down.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | File Load alert name |
| Description | File Load alert information |
| File Pattern | Select Pattern of file |
| Entity Name | Created/Existing Entity Name |
| Entity ID | Created/Existing Entity ID |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Subject Description |
| Body | Body Description |
| Email of the User |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a FLA alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
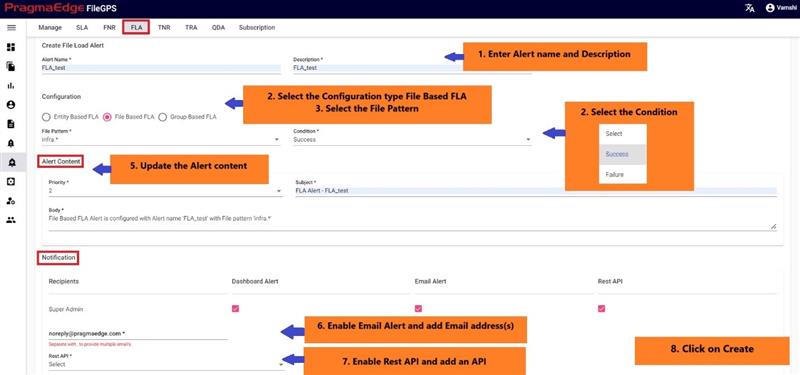
Creation of File based FLA:
In the below figure, user has configured the File Load Alert ‘%ACME% File Based File Load Failure Alert’ for the ACME Entity.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select the configuration type file based and enter file pattern. please select the condition of the FLA to check for the file whether success or failure condition.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the Rest API notification, please select the API from drop down.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | File Load alert name |
| Description | File Load alert information |
| Condition | Success/Failure condition |
| File Pattern | Select Pattern of file |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Subject Description |
| Body | Body Description |
| Email of the User |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a FLA alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
Creation of Group based FLA:
In the below figure, user has configured the File Load Alert by giving alert name as ‘ACME Group File Load Success Alert’ for the ACME Group.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select the configuration type group based. Similarly, select the condition of the FLA to check for the file.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the Rest API notification, please select the API from the drop down.
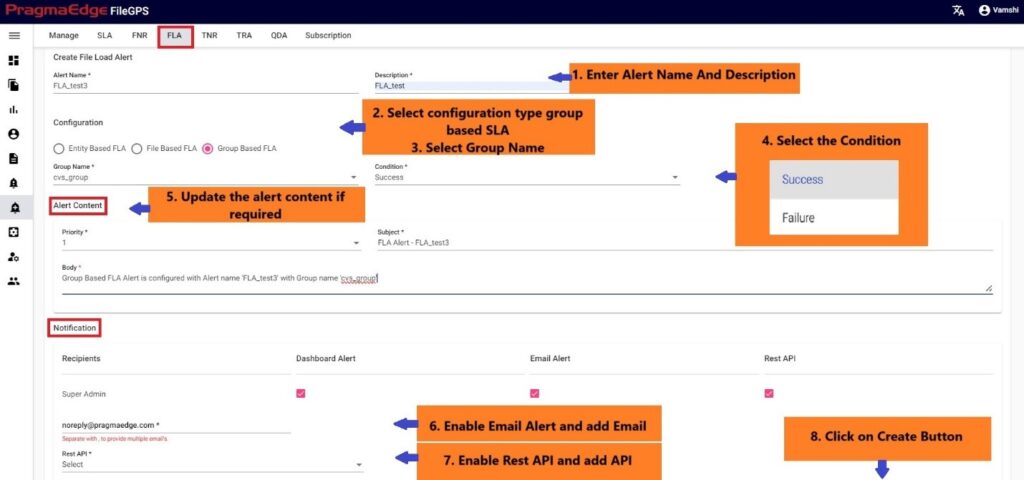
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | File Load alert information |
| Description | File Load alert information |
| Group Name | Created/Existing Group Name | Condition | Success/Failure condition |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Subject Description |
| Body | Body Description | Email of the User |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a FLA alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
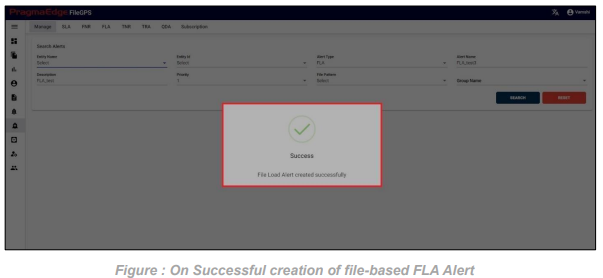
Raised FLA Alert:
For example, In the above created ‘‘ACME Entity File Load Success Alert’ if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert FLA with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
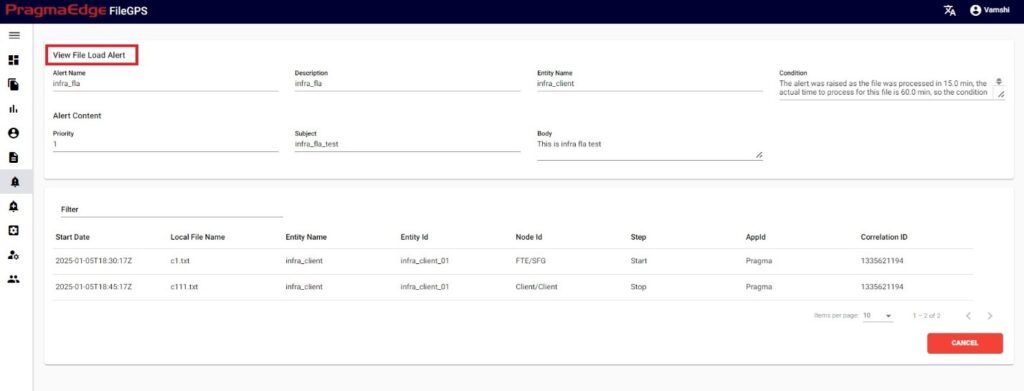
10.5. Transaction Not Received Alert (TNR Alert):
When we don’t receive a transaction like 850,810 etc. for any particular entity and when the count of the transactions expected was not matched with the transaction received count then the Transaction not received alert will rise. This alert lets the user know that the expected transaction has not been received for the entity Transaction not Received alert will notify the user if the configured expected count of transactions does not match with received transaction count for the particular entity. We can configure the files count while creating alert as shown below.
Path:
Login Alert Management
TNR
We have two scenarios for configuring TNR alerts: one is TNR for entities, and the other is TNR for groups.
TNR Alert for Entity:
In the below figure user has configured the TNR Alert ‘ACME Entity Not received 850 transaction Alert’ to receive notifications if configured transaction not received.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select entity and entity id as well. enter the transaction number in transaction field to match while checking the transactions. Enter Sender ID, Receiver ID, App Type and please enter the files count of the files to match with the received files count condition.
In the Timing details please enter the expected time when we are expecting this alert to be notified as we have provided options like daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly details. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Timing of TNR in detail’.
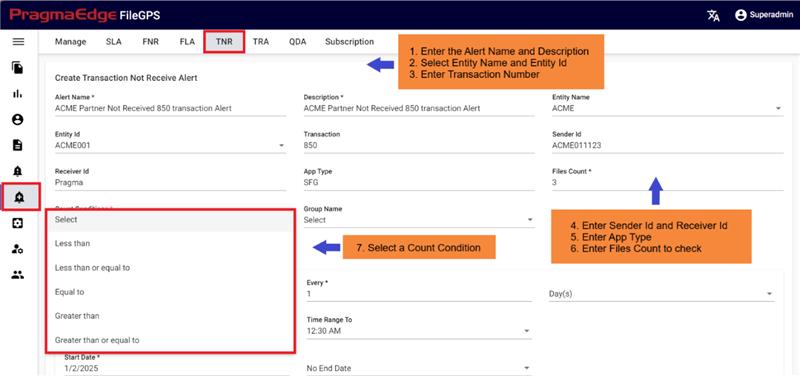
Note:
We have five types of file count conditions, as illustrated in the figure below:
Less Than: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is greater than or equal to the expected file count.
Less Than or Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count exceeds the expected file count.
Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is either less than or greater than the expected file count.
Greater Than: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is less than or equal to the expected file count.
Greater Than or Equal To: FileGPS sends an alert if the file count is below the expected file count.

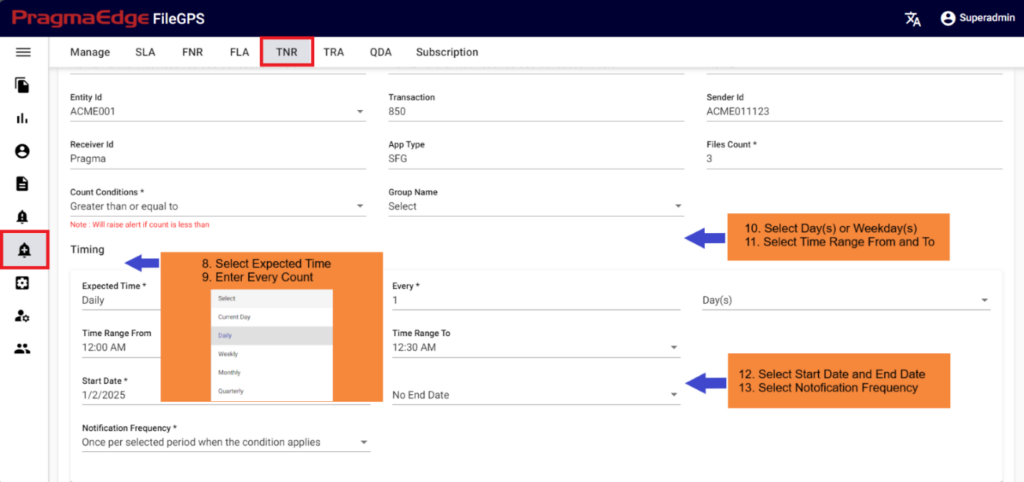
TNR Alert for Group:
In the below figure user has configured the TNR Alert ‘ACME Entity 850 Transaction Not Received Alert’ to receive notifications if configured transaction not received. In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and enter group name as well. Enter the transaction number in the transaction field to match while checking the transactions. Enter Sender ID, Receiver ID, App Type and please enter the files count of the files to match with the received files count condition.
In the Timing details please enter the expected time when we are expecting this alert to be notified as we have provided options like daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly details. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Timing of TNR in detail’.
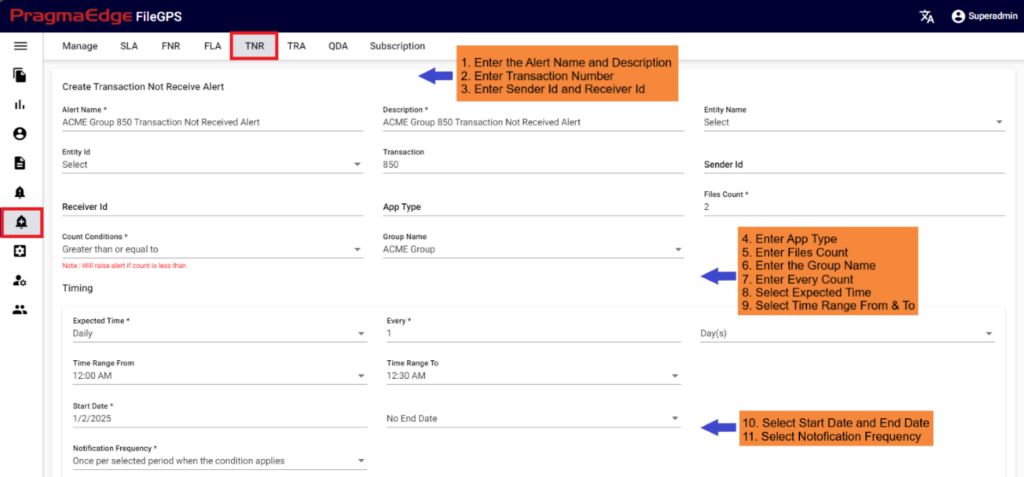
Note: The configuration process for TNR Entity and TNR Group is identical for the remaining
steps.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required. In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, select the API from the drop down.
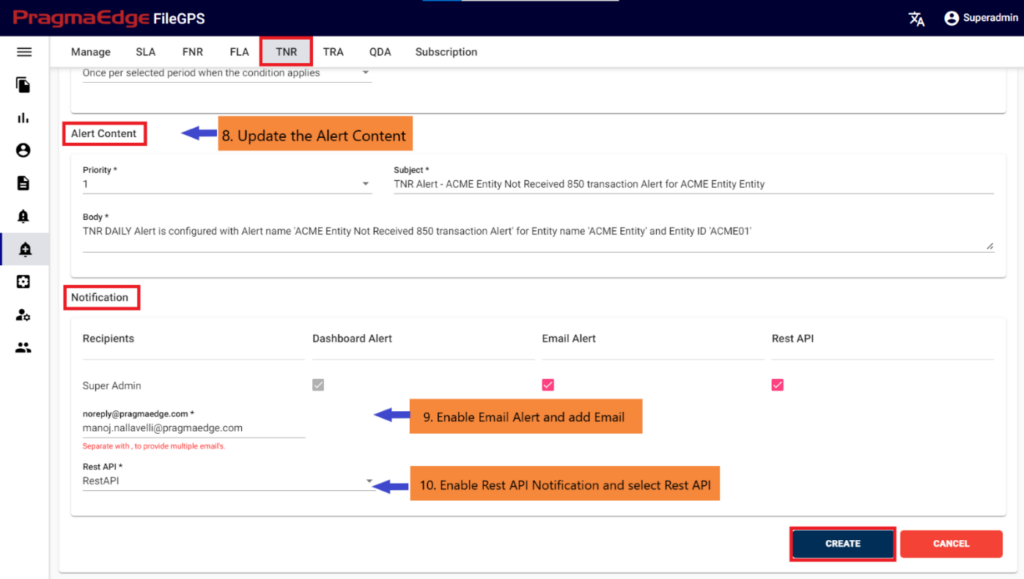
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Created/Existing Alert Name |
| Description | FNR Alert Description info |
| Entity Name | Created/Existing Entity Name |
| Entity ID | Create/Existing Entity ID |
| Group Name | Created/Existing Group Name |
| Transaction Number | Initial Stage of Transaction |
| Sender ID | File Source-Sender ID |
| Receiver ID | File Destination-Receiver ID |
| Expected Time Type | Time interval when occurred |
| App Type | App Type |
| Files Count | Count of files expecting to receive |
| Expected Time Value | Value of time selected |
| Start Date | Start Date of the file Processed |
| End Date | End Date of the file Processed |
| Notification Frequency | Notification occurrence at regular intervals |
| Alert Content | Description of the alert and its content |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Regarding the alert |
| Body | Miscellaneous |
| Notification | To inform |
| Recipient | Receive |
| Email of the Entity | |
| Create | Create Alerts |
| Cancel | Clears values in input values |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a TNR alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
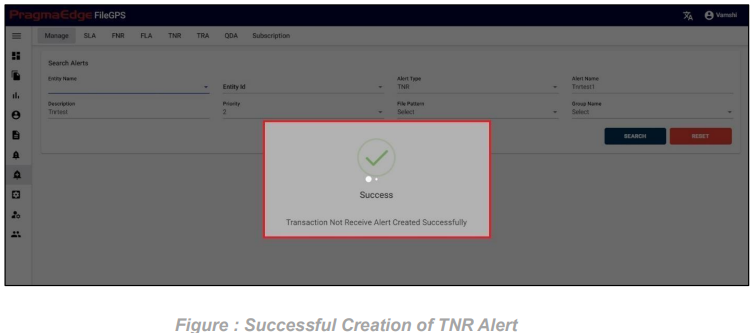
Timing of TNR in detail: TNR Expected time should be selected from the drop down provided so that the alert should check the condition on selected timings. Below are the scenarios we have provided in timing module of the alert under expected time selection so According to this condition TNR will check the transactions and raise the notification.
1. TNR Current Day Minute’s scenario:
In this scenario, we selected the expected time ‘Current day’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the minute to consider as integers: 1, 2, …59. and need to select the ‘Minute(s)’ of the hour So that the TNR will check current day scenario for selected minutes also with the start and end dates provided.
The example below checks TNR: For every 30 minutes, the TNR (Transaction Not Received) will check for the presence of the expected file. In the event of non-arrival, it will trigger a TNR alert.

2. TNR Current Day Hour’s scenario:
In this scenario, we selected the expected time ‘Current day’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the hour to consider as integers: 1, 2, …23. and need to select the ‘Hour(s)’ So that the TNR will check current day scenario for selected hours also with the start and end dates provided.
The example below checks TNR: For every 3 hours, the TNR (Transaction Not Received) will check for the presence of the expected file. In the event of non-arrival, it will trigger an TNR
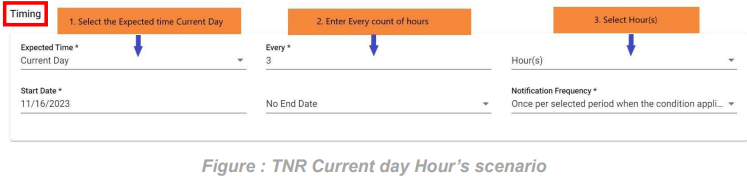
3. TNR Daily days scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and also need to select the ‘day(s)’ of the week So that the TNR will check daily scenario for every day also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On every day on all days of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

2. TNR Daily weekdays scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and also need to select the ‘weekday(s)’ of the week So that the TNR will check daily scenario for every weekday also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On every day on weekdays of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

3.TNR Weekly day of the week scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Day of the week’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week as integers: 1, 2 etc. and also need to select the days of the week So that the TNR will check weekly scenario for every week on the particular selected days also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On the Monday and Tuesday of every week from
12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
Note: We can select multiple days of week to check TNR
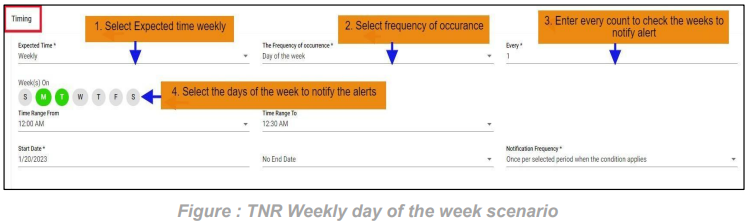
4.TNR Monthly on day scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On Day’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘nth Day’ of particular day in month as integers: 1, 2 etc. and ‘nth month’ of particular month count. So that the TNR will check monthly scenario on the selected day of the particular month with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On the 1st of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
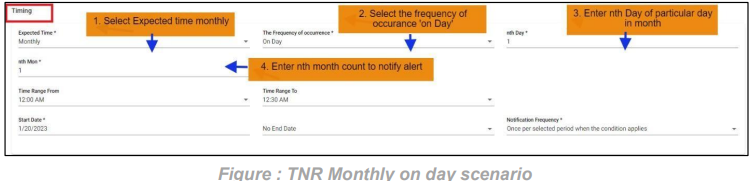
5.TNR Monthly on the scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also ‘nth month’ count of month. So that the TNR will check monthly scenario on the selected day on the particular week of month also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On the first Sunday of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
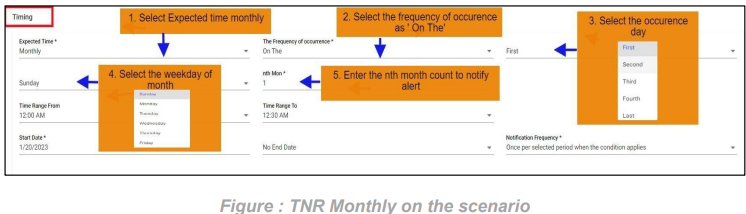
6. TNR Quarterly scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Quarterly’. So that the TNR will check Quarterly scenario on quarter end day with time range ranges provided.

7. TNR Yearly Every Scenario: In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Every’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the month as January, February etc. and ‘nth Day’ of particular day of month. So that the TNR will check yearly every scenario on the selected day on the particular day of month provided considering every month count also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On the first of every January for every 1 year from
12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.
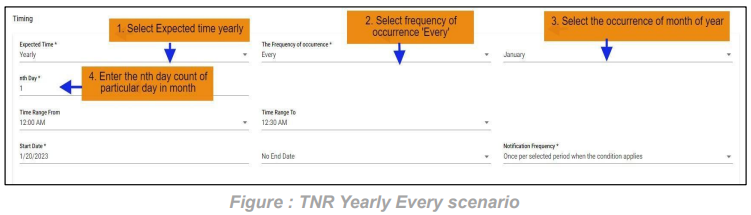
8. TNR Yearly on the Scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also selects the month of the year. So that the TNR will check yearly on the scenario on the selected day on the particular week of month in a year also with time range ranges provided.
Below example TNR checks transactions: On the first Sunday of January every year from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.
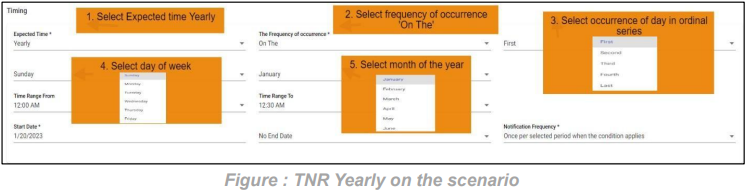
Raised TNR Alert:
For example, In the above created ‘ACME Entity Not received 850 transaction Alert’ if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert TNR with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
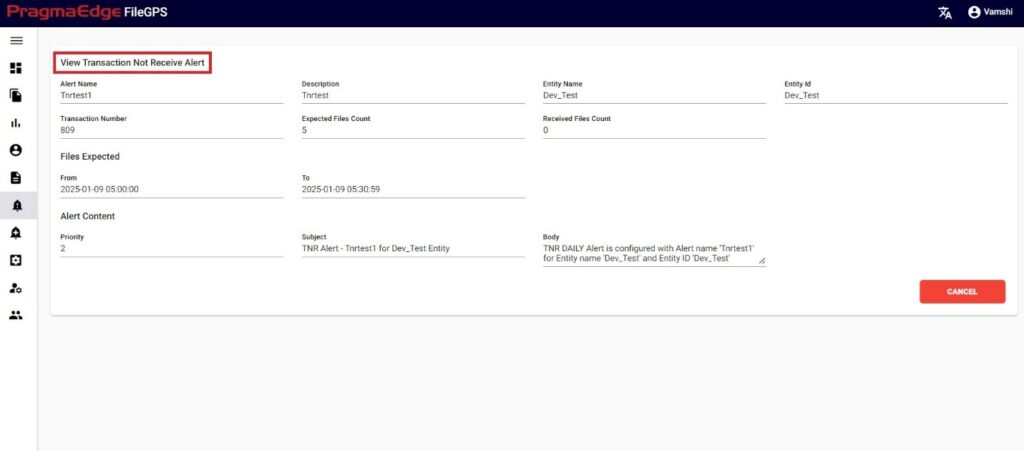
10.6. Transaction Response Alert (TRA Alert):
In File Transfer process, if the transaction is not received to its destination, in other words, if transaction of a file from initial stage to response stage is not received in the given time interval, then ‘TRA’ Alert is raised.
This alert let the business team know that the transaction has not been received for the entity. In this compilation process of file case, we can check where the process event has stopped for any Entity.
Path:
Login Alert Management
TRA
TRA Alert for Entity:
In the below figure user has configured the TRA Alert by giving alert name as ‘ACME Entity Transaction response not received Alert’ and entity as ACME Entity, Entity Id as ACME01. In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select entity name and entity id as well. enter the initial and response transaction numbers to check transaction of a file from initial stage to response stage is not received in the given time interval.
In the Timing details please enter the expected time type to check the time interval like days, hours, minutes. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Timing of TRA in detail’.
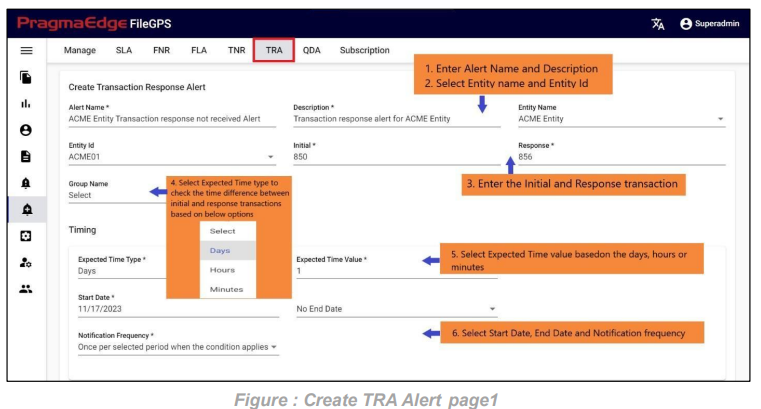
TRA Alert for Group:
In the below figure user has configured the TRA Alert by giving alert name as ‘ACME Group Transaction response not received Alert’ and group name as ACME Group. In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and enter group name as well. Enter the initial and response transaction numbers to check transaction of a file from initial stage to response stage is not received in the given time interval.
In the Timing details please enter the expected time type to check the time interval like days, hours, minutes. We have provided a detailed explanation regarding these after the alert created with heading ‘Timing of TRA in detail’.
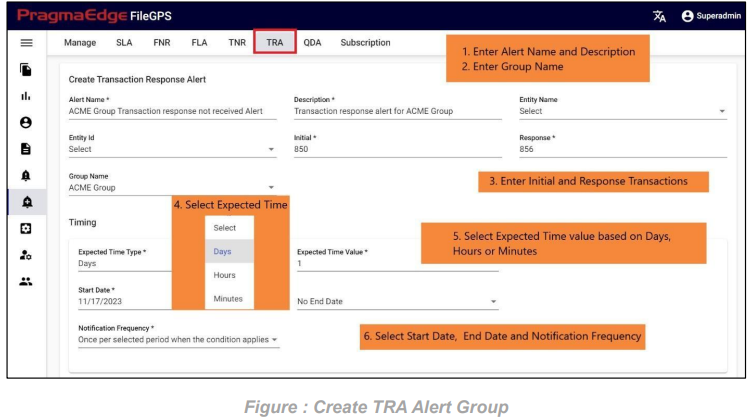
Note: The configuration process for TRA Entity and TRA Group is identical for the remaining steps.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, select the API from the drop down.
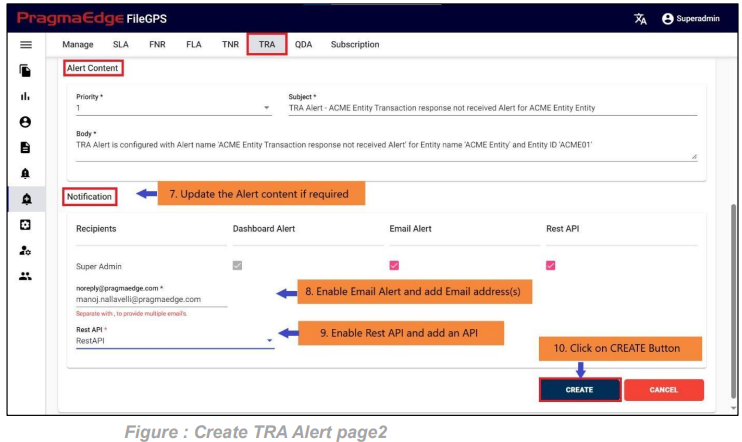
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Created/Existing Alert Name |
| Description | FNR Alert Description info |
| Entity Name | Created/Existing Entity Name |
| Entity ID | Create/Existing Entity ID |
| Group Name | Created/Existing Group Name |
| Initial | Initial Stage of Transaction |
| Final | Final Stage of Transaction |
| Expected Time Type | Time interval when occurred |
| Expected Time Value | Value of time selected |
| Start Date | Start Date of the file Processed |
| End Date | End Date of the file Processed |
| Notification Frequency | Notification occurrence at regular intervals |
| Alert Content | Description of the alert and its content |
| Priority | Level of importance given to alert |
| Subject | Regarding the alert |
| Body | Miscellaneous |
| Notification | To inform |
| Recipient | Receive |
| Email of the Entity |
After providing the details click on the create button which will create a TRA alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
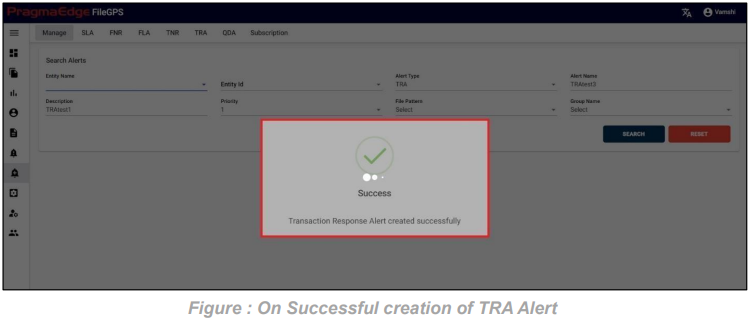
Timing of TRA in detail:
TRA Expected time should be selected from the drop down provided so that the alert should check the difference between the initial and response transaction numbers condition on selected timings. Below are the scenarios we have provided in timing module of the alert under expected time type and value selection so According to this condition TRA will check the transactions and raise the notification.
1. TRA Time type days scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time type ‘Days’. After selecting it will ask you to select the expected time value as days count as integers: 1, 2 etc. It ranges from 1 to 14 days. So that the TRA will check the difference between the initial and response transaction numbers within the days configured in time value and based on that condition if matches it raises the notification.
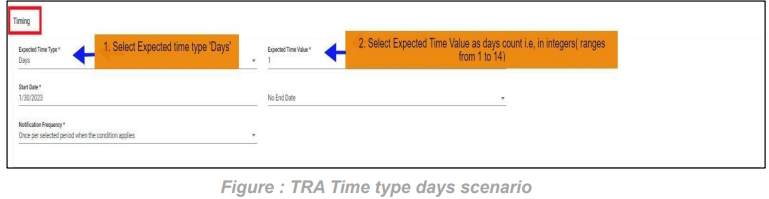
2. TRA Time type hours scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time type ‘Hours’. After selecting it will ask you to select the expected time value as hours count as integers: 1, 2 etc. It ranges from 1 to 24 hours. So that the TRA will check the difference between the initial and response transaction numbers within the hours configured in time value and based on that condition if matches it raises the notification.

3. TRA Time type minutes scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time type ‘Minutes’. After selecting it will ask you to select the expected time value as minutes count as integers: 1, 2 etc. It ranges from 1 to 60 minutes. So that the TRA will check the difference between the initial and response transaction numbers within the minutes configured in time value and based on that condition if matches it raises the notification.

Raised TRA Alert:
For example, In the above created ACME Entity Transaction response not received Alert if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert TRA with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
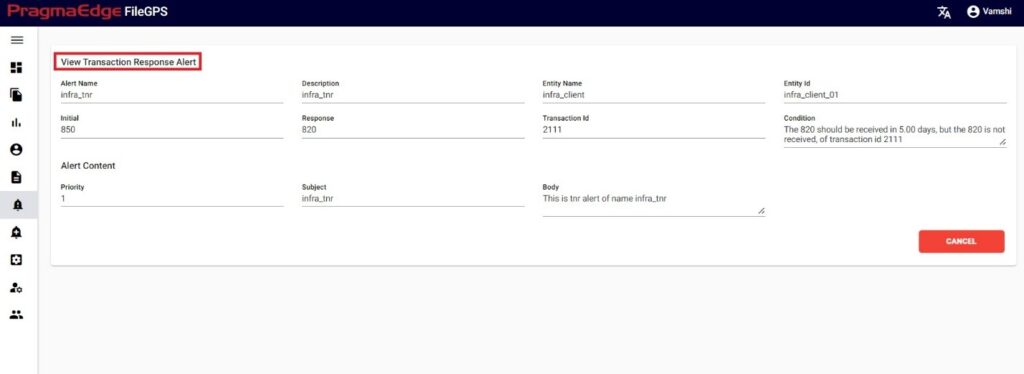
10.7. Queue Depth Alert (QDA Alert):
Queue Depth Alert will be raised when user having files with Particular Agent for given Queue Name, when the depth of the files in the particular queue reaches the configured value count it will raise the alert.
For This Queue depth alert, we have default agents to be entered were Kafka, SI and MQ. We can configure this depth alert for any agent queues to check its depth and notify the alert.
Path:
Login Alert Management
QDA
In the below figure user has configured the QDA Alert by giving alert name as ‘Kafka Queue Depth Alert’.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and enter agent name and queue name as well. Now enter the depth count to check the queue depth of the particular agent.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, please provide the method of API whether post or put, URL and auth type with options no auth and basic auth with username password details.
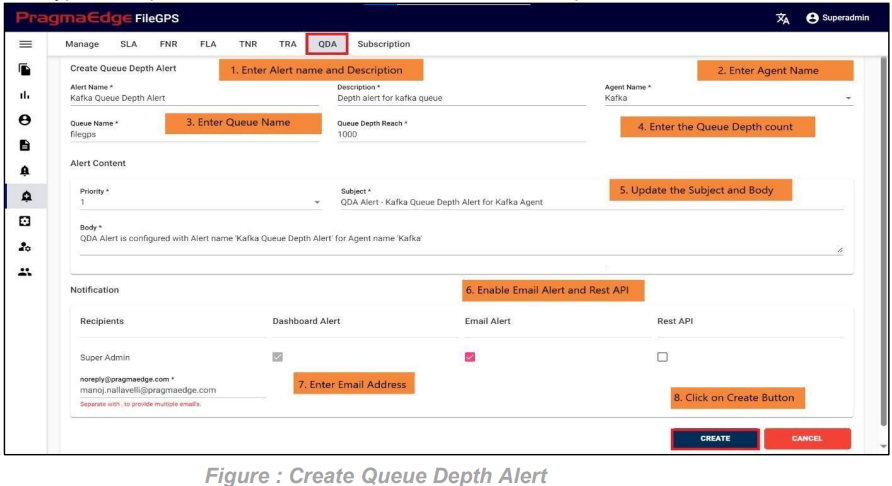
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Queue Depth alert name |
| Description | Queue Depth alert information |
| Agent Name | Agent for Sending the Files |
| Queue Name | Given Queue Name |
| Queue Depth Reach | Given Queue Depth Reach |
| Priority | |
| Subject | |
| Body | |
Below Figure refers to the successful creation of a Queue Depth alert
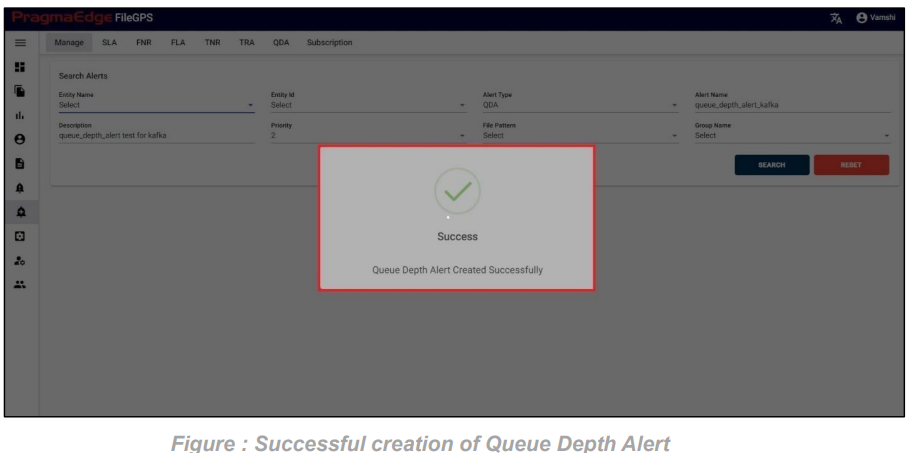
Raised QDA Alert:
For example, In the above created Kafka Queue Depth Alert if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert QDA with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
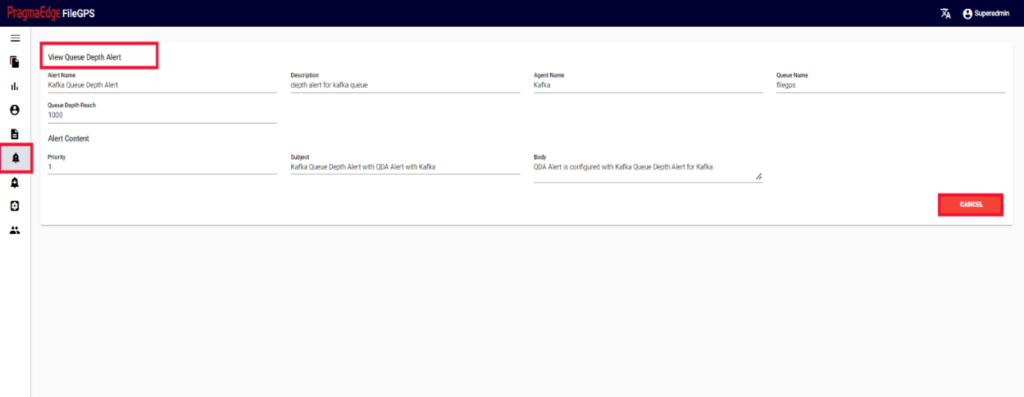
10.8. Subscription Alert (SUB Alert):
Subscription Alert will be raised when user subscribes to a particular event in the file transfer process and a file matches a particular subscription.
In a file transfer we have many stages of file such as start, process, reprocess, error and stop. Here in this subscription alert, we can subscribe to any stage of the file by configuring the type while creating the subscription alert. So, when the particular stage of the file arrives it notifies the alert to the subscribed user.
Path:
Login Alert Management
Subscription
We have two scenarios for configuring Subscription alerts: one is Subscription for entities, and the other is Subscription for groups.
Subscription Alert for Entity:
In the below figure user has configured the Subscription Alert ‘ACME Entity received Start
Subscription Alert’.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and select entity name and entity id. Enter sent from and sent to details as well. Similarly select the type of the file to match the stage of the file arrived to notify alert. Input the File Name, File Pattern, Transaction, Sender Id, Receiver Id, and App Type to specify the conditions if the user desires to match a particular set of criteria.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, please select an API from the drop down.
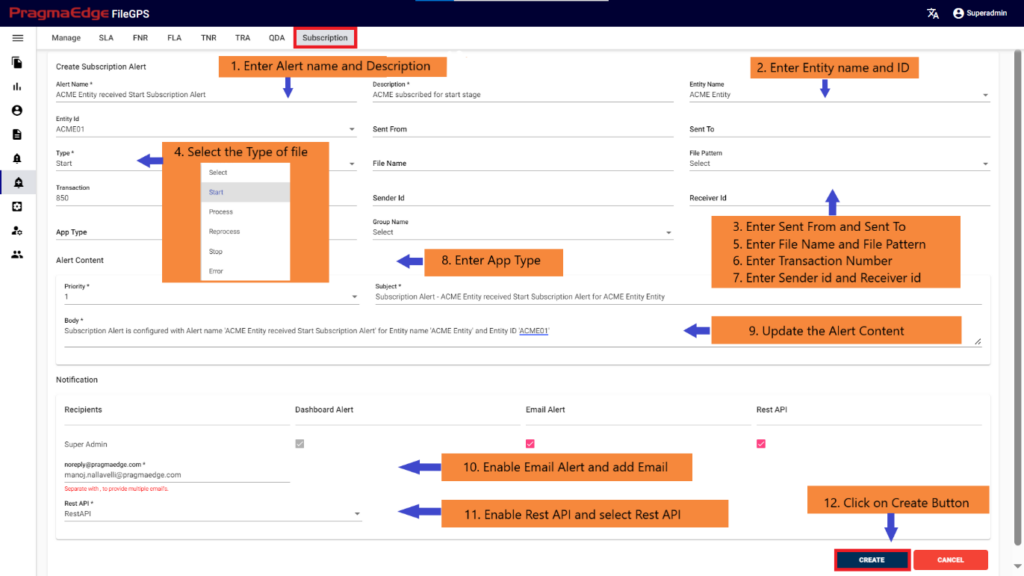
Subscription Alert for Group:
In the below figure user has configured the Subscription Alert ‘ACME Group received Start Subscription Alert’.
In the Alert details please enter the alert name, description and enter group name. Enter sent from and sent to details as well. Similarly select the type of the file to match the stage of the file arrived to notify alert. Input the File Name, File Pattern, Transaction, Sender Id, Receiver Id, and App Type to specify the conditions if the user desires to match a particular set of criteria.
Update the alert content details by providing the priority of the alert to be in alerts modules, subject and body will be default added with some selected alert information. Update it if required.
In notifications details dashboard alert notification is default selected for every alert and please enable the other notifications email and rest API by providing the details required as shown in below figure. If we enable the email notification, please provide an email address. Similarly, if we select the rest API notification, please select an API from the drop down.
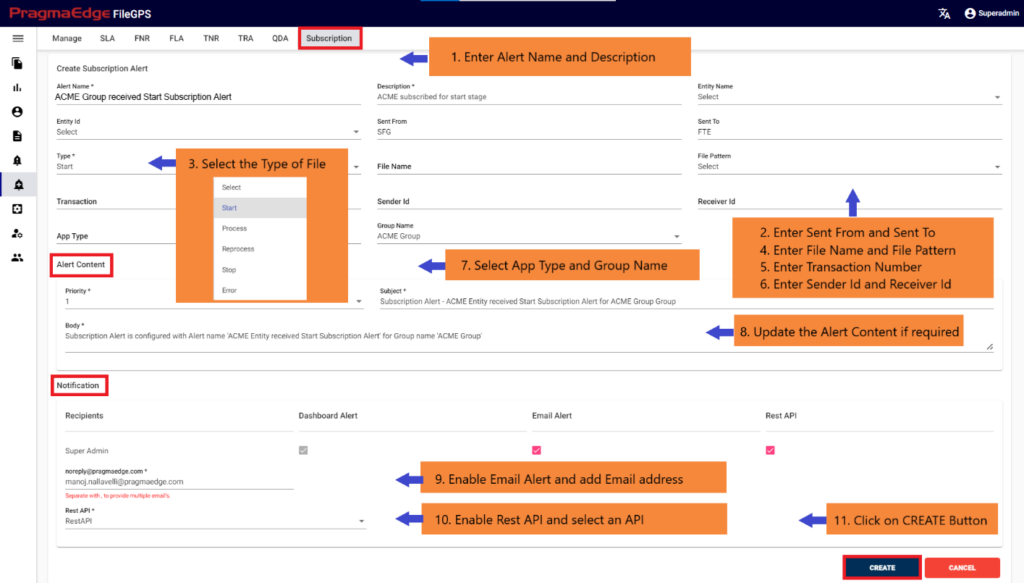
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Alert Name | Subscription alert name |
| Description | Subscription alert information |
| Entity Name | Created/existing entity name |
| Entity ID | Created/existing entity ID |
| Sent From | Application sent from |
| Sent To | Application sent to |
| Type | Type of the file |
| File Name | Name of the file |
| File Pattern | Regular Expression |
| Transaction | Transaction Number of the File |
| Sender ID | Sender id of the file |
| Receiver ID | Receiver Id of the file |
| App Type | App type |
| Group Name | Created/existing Group Name |
| Priority | Priority of alert |
| Subject | Subject in email |
| Body | Body in email |
Note: The configuration process for Subscription Entity and Subscription Group is identical for the remaining steps.
After providing the details click on create button which will create a SUB alert successfully, all the pages will be redirected to manage alerts screen with a success message.
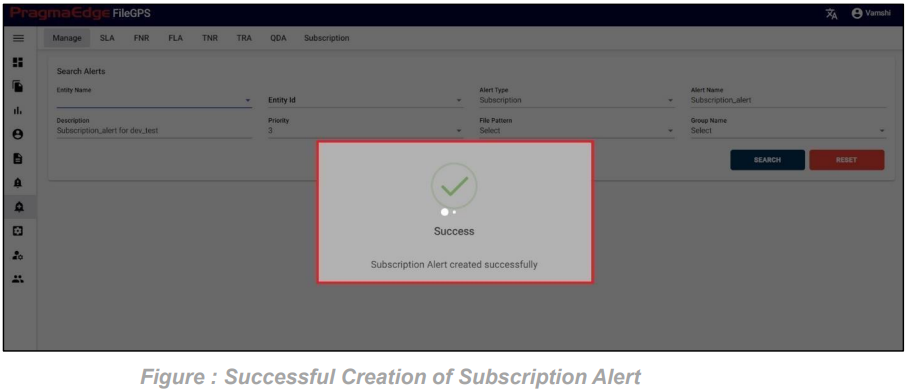
Raised Subscription Alert:
For example, In the above created ACME Entity received Start Subscription Alert if condition is matched and an alert notification is raised as shown below in FileGPS Dashboard all alerts module by searching with type of alert SUB with time range filter. In the displayed result alert click on action button it will display view by clicking on it will display the details of the raised notification.
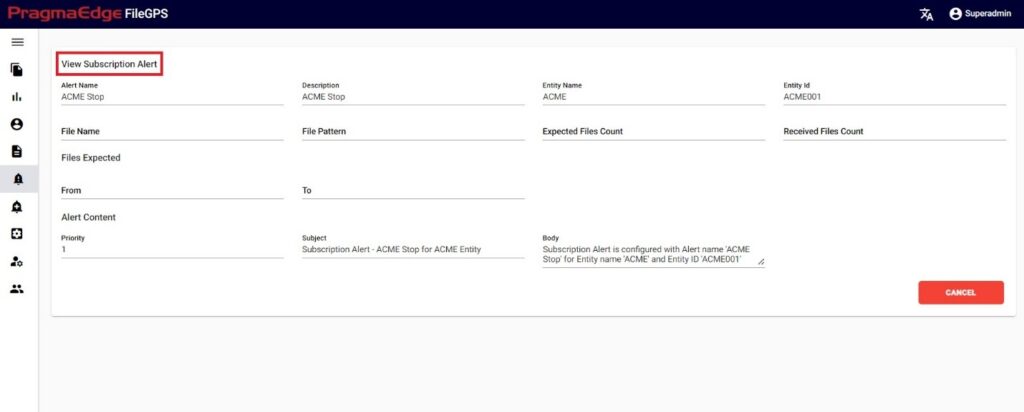
11. Configure:
Users can configure the Routes, Business Unit, File Search, Agent Config to ease the management of the file transmissions
11.1. Business Unit:
A business unit is an organization or organizational subset that is independent of one or more accounting or operational functions. The admin will configure the business unit and assign the groups associated for the business unit based on access level.
Path:
Login Configure
Business Unit
By clicking on the business unit sub menu. It will land on the create business unit page where we will provide details of the business unit to configure. In the below figure user has configured the Business unit ‘CSR Team’ for the ACME Group.
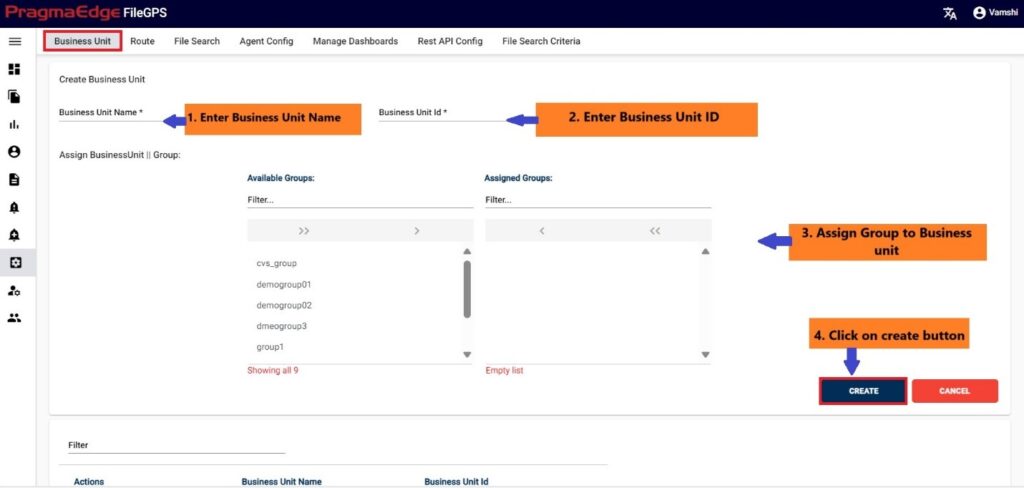
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Unit Name | Name of the collection of groups |
| Business Unit ID | Unique ID of the collection of groups |
| Assign Groups | Can assign groups to partners |
| Update | Update the inout fields of bussiness unit |
| Delete | Deletes particular row of records |
Below Figure refers to the successful creation of a business unit.
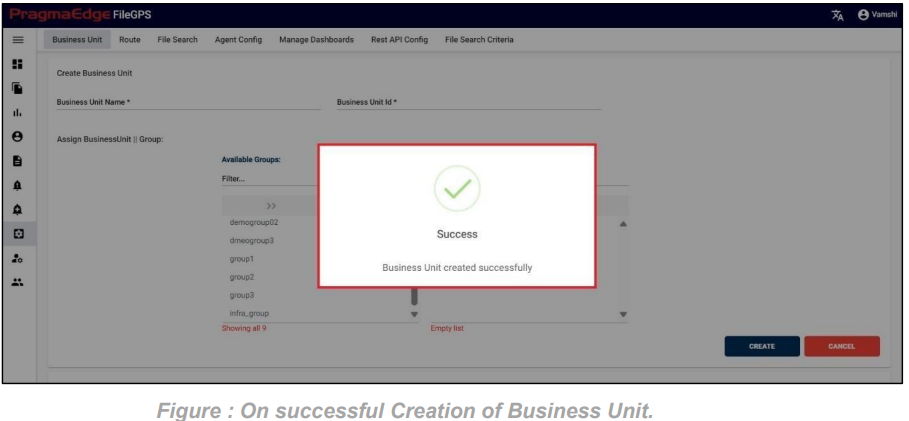
In Manage Section User have edit/delete options to perform on business units.
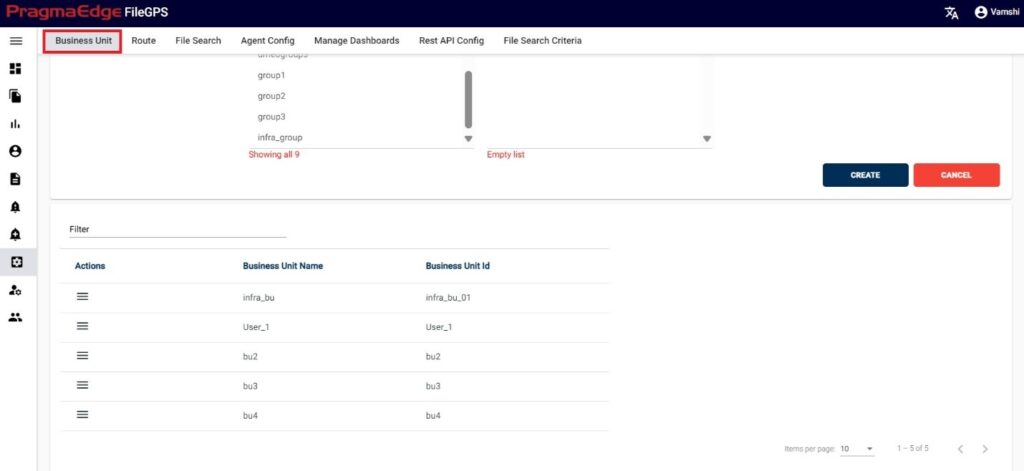
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the Business unit details. For example, Business unit that was created previously could be modified, by clicking on the edit option, consequently the page will be navigated to create page module where user could change details as per requirement.
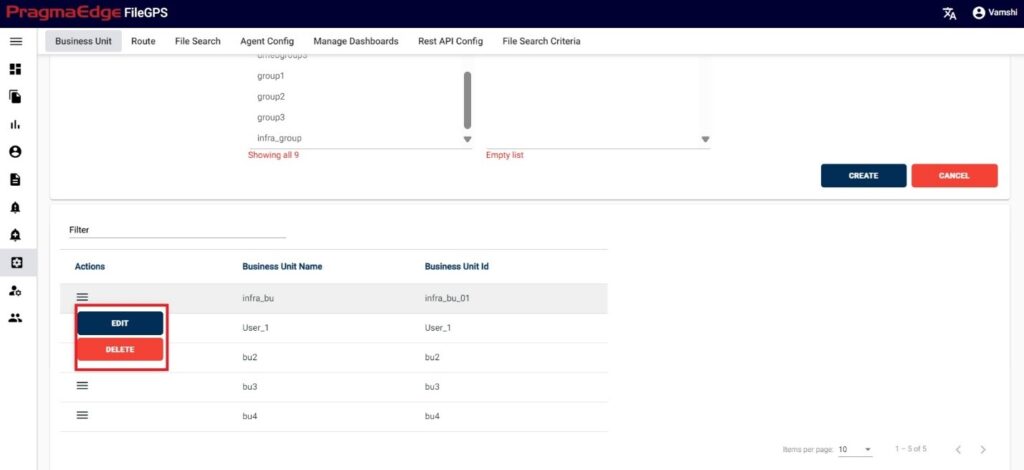
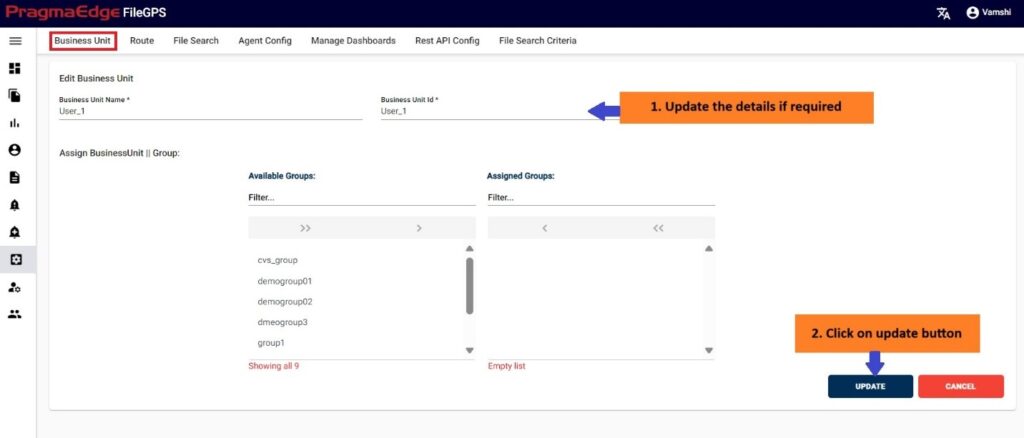
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the Business unit details as shown in below figure.
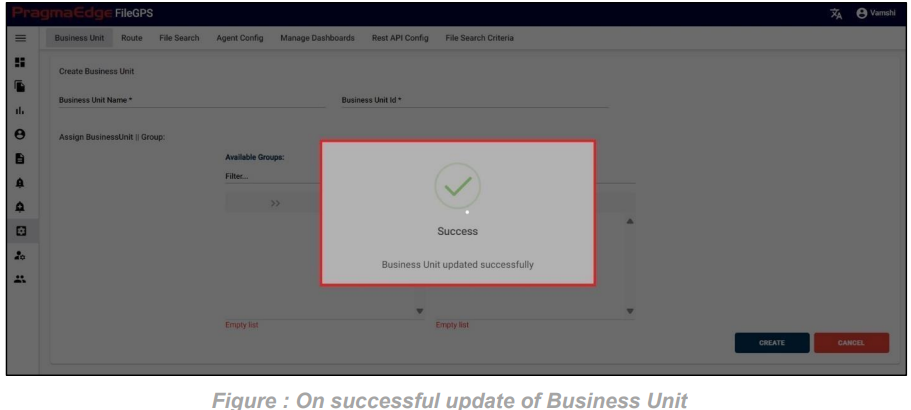
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Unit Name | Name of the collection of groups |
| Business Unit ID | Unique ID of the collection of groups |
| Assign Groups | Can assign groups to partners |
| Update | Update the inout fields of bussiness unit |
| Delete | Deletes particular row of records |
Business unit record could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure.
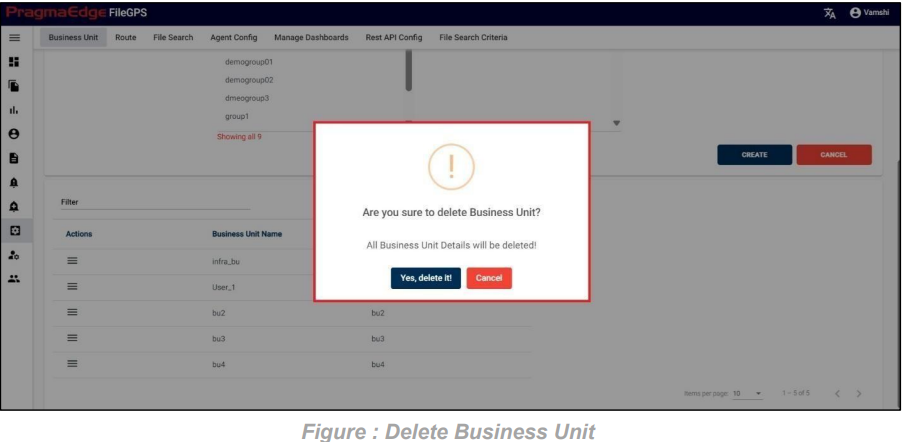
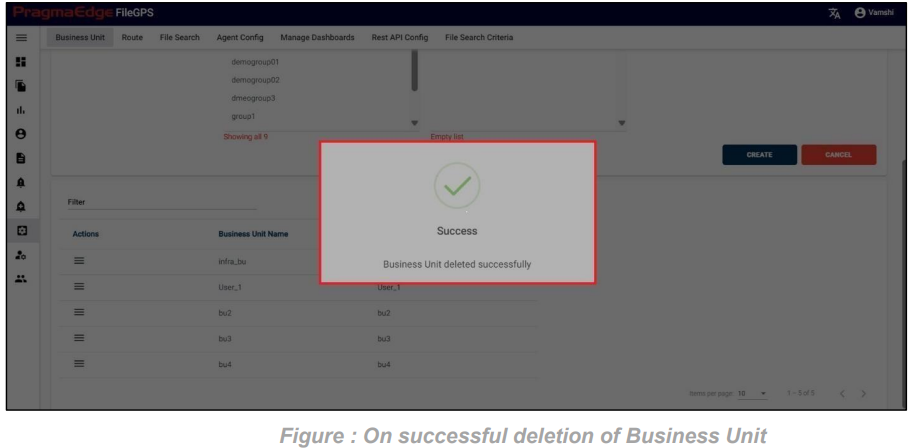
11.2. Route:
Route means the various communication channels the trading partner use to transmit the file from a source application and destination application. User can configure the Various routes that Entity will expect the file from their Trading partners.
Path:
Login Configure
Route
By clicking on Route sub menu. It will land on the create Route page where we will provide details of route to configure.
In the below figure user has configured the Business unit ‘SFG to FS’ for the ACME Entity.
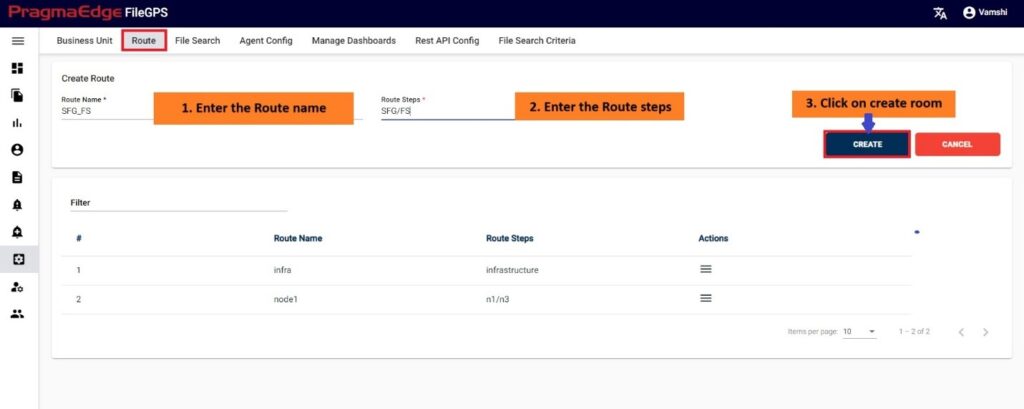
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Route Name | Route name of applications |
| Route Steps | Step by Step of application names separate by |
| Update | Update/edit the name of the routes |
| Cancel | Clear the values of inputs |
The below Figure refers to the successful creation of a Route.
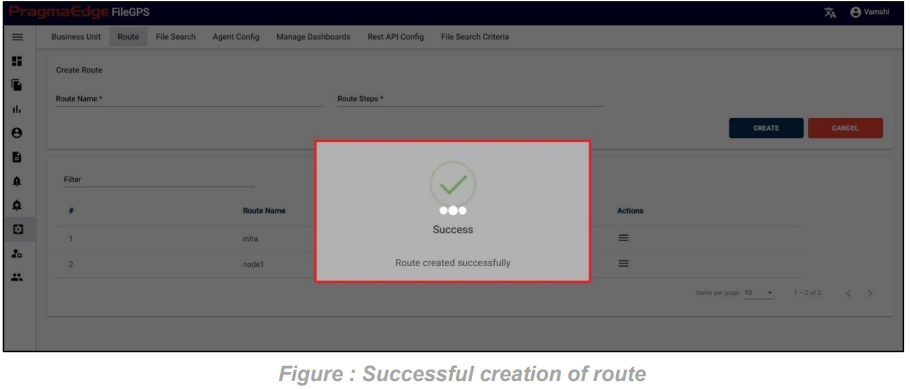
In the Manage Section, users have edit/delete options to perform on Routes as shown in below figure.
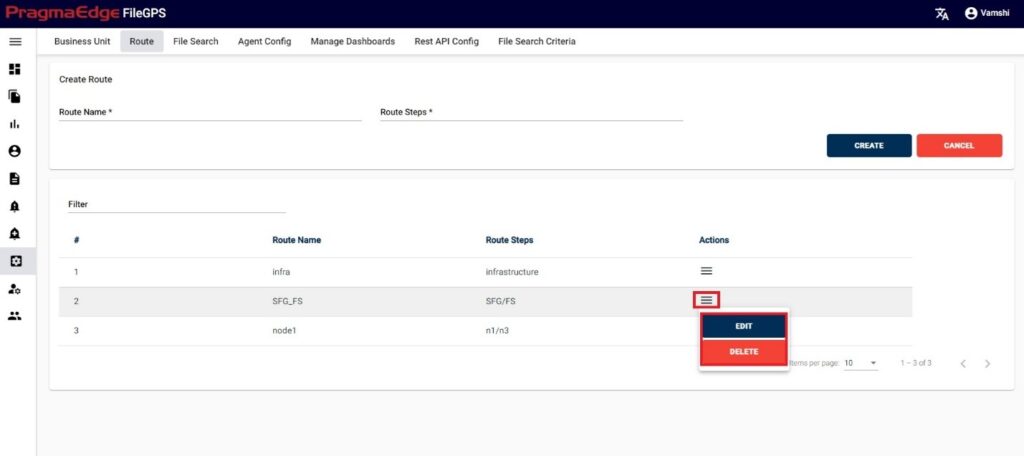
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the Route details. For example, Route that was created previously could be modified, by clicking on the edit option, consequently the page will be navigated to create page module where user could change details as per requirement.
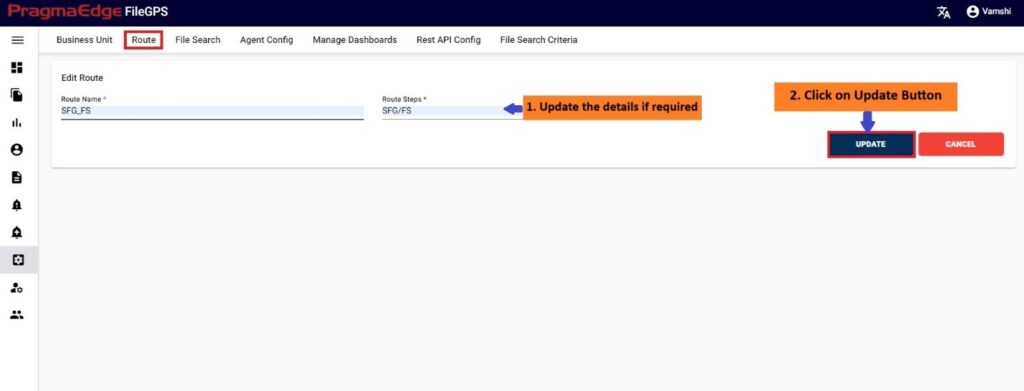
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the Route details as shown in figure below.
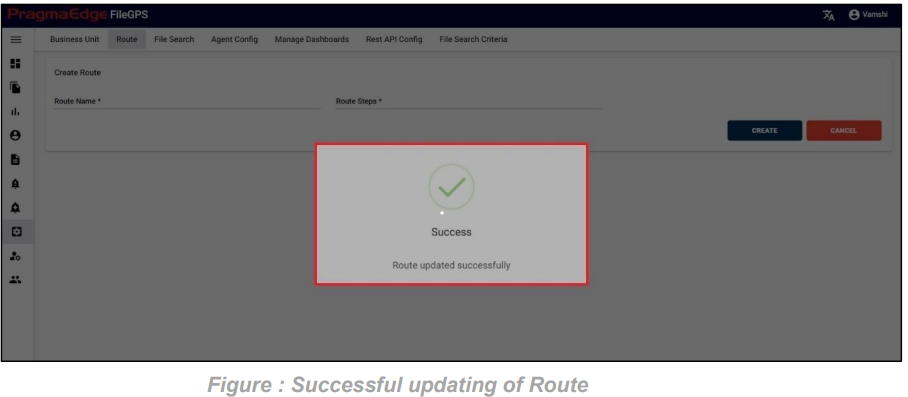
Route record could be permanently deleted with the ‘DELETE’ option as shown in the figure below.
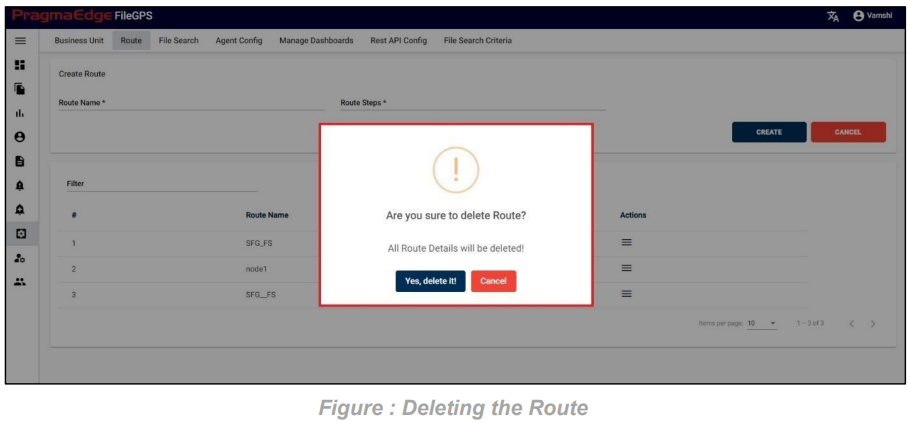
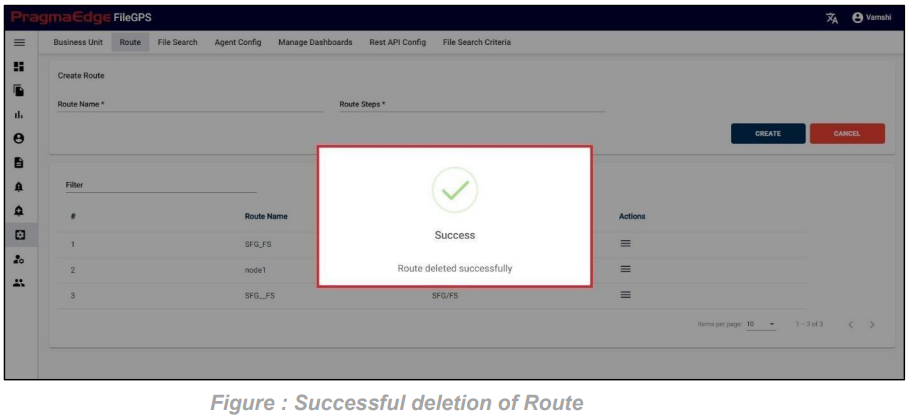
11.3. File Search:
Users can personalize the File search with desired fields that they want to view in the different kinds of grids of File Life cycle.
Path:
Login Configure
File Search
In this file search we can configure different kinds of grids like main grid, child grid and step grid. Users can select or deselect the fields in sections accordingly so we can view the information of configured fields in the search file page results. By default, it shows Main Grid as filled in choose grid field
a. Main grid: In the below Figure User can select or deselect the fields in main grid config section.
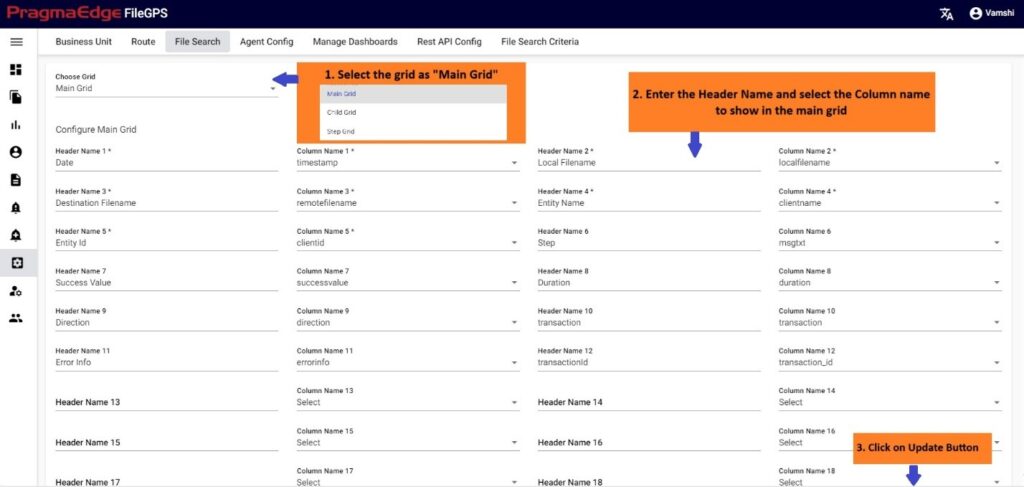
After selecting all desired fields in this Main grid config section.
By Clicking on ‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the main grid details as shown in figure.
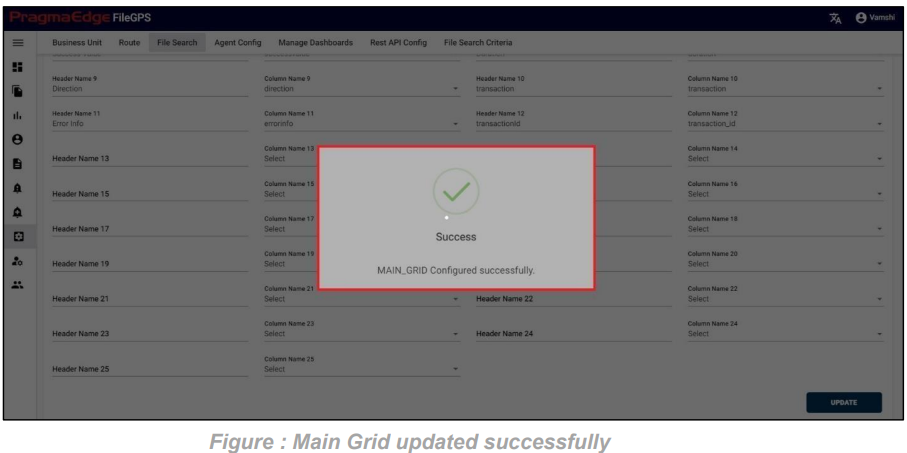
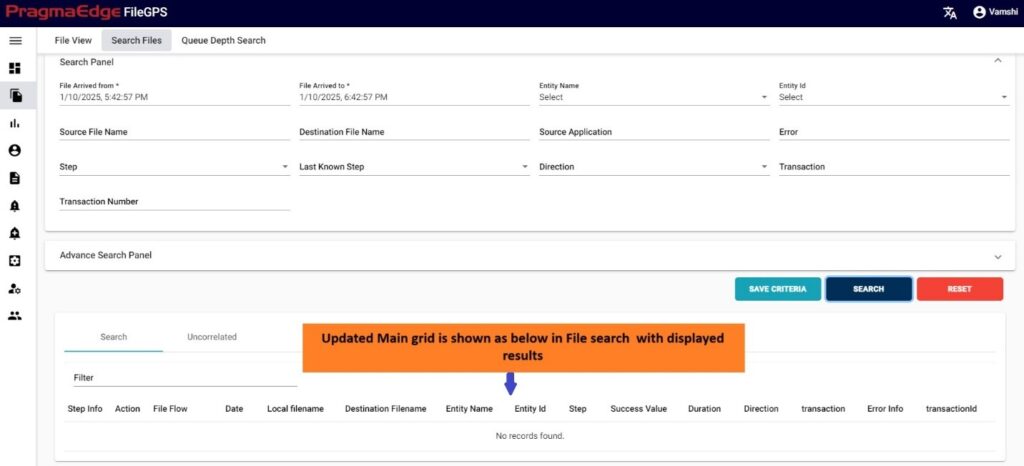
b. Child grid: In the below Figure User can select or deselect the fields in child grid config section.
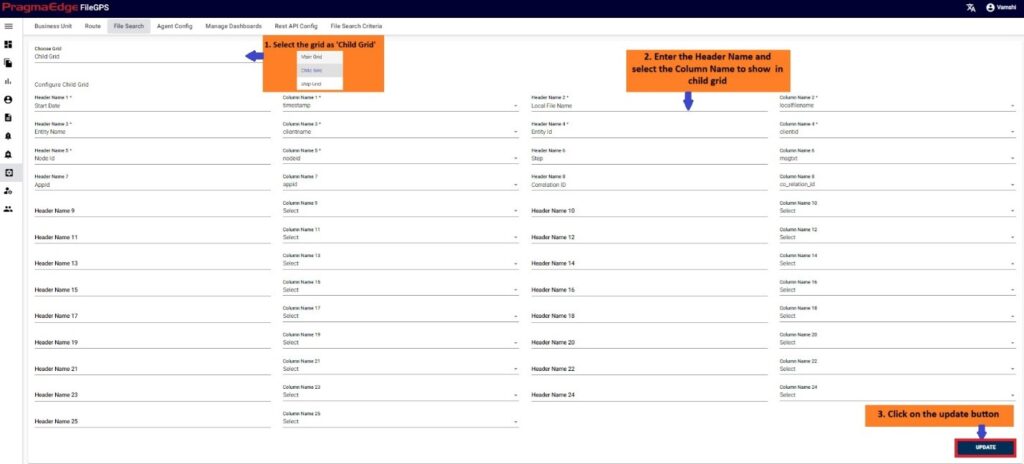
After selecting all desired fields in this Child grid config section. By Clicking on ‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the child grid details as shown in figure.
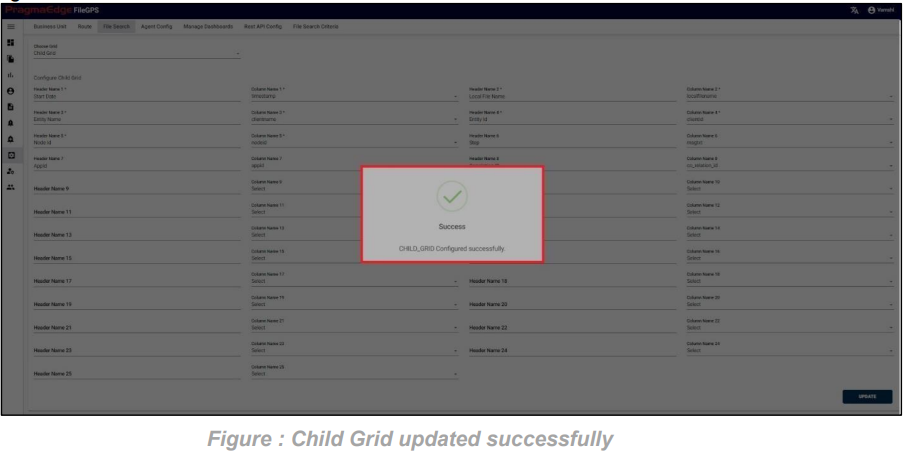
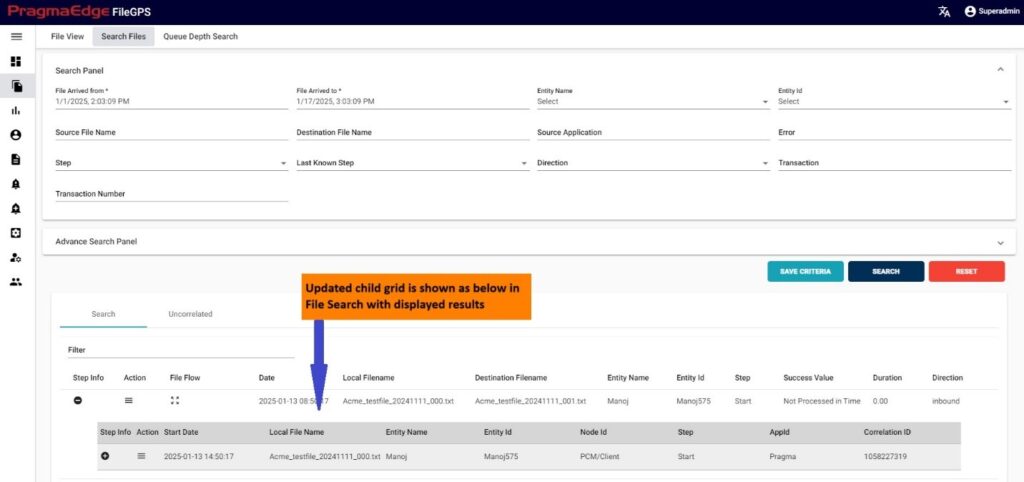
Steps grid: In the below Figure User can select or deselect the fields in steps grid config section.
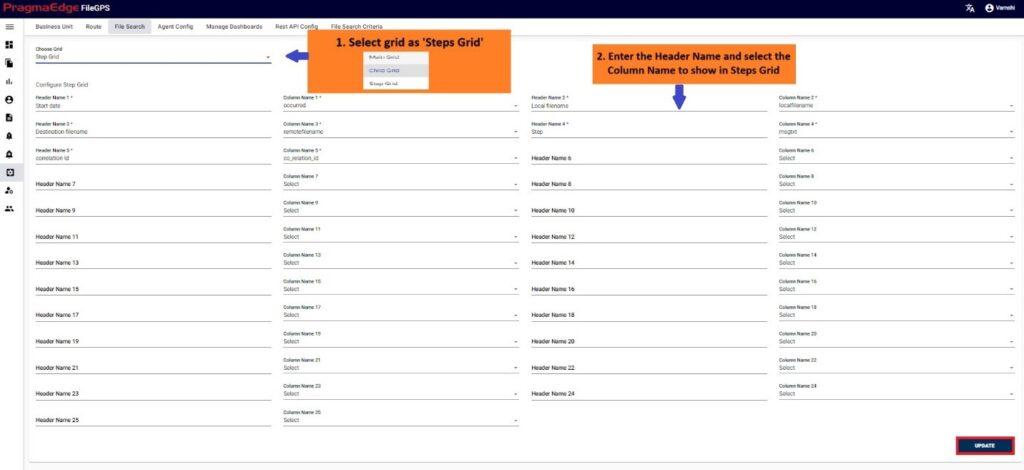
After selecting all desired fields in this Steps grid config section. By Clicking on ‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the steps grid details as shown in figure.
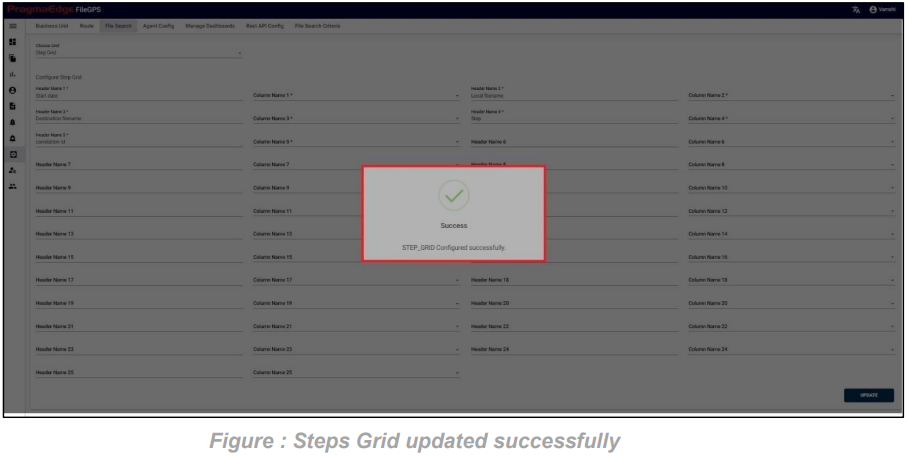
11.4. Agent Config:
Path:
Login Configure
Agent Config
This Agent config raises an alert when the agent is down, in this we need to give some of the mandatory data for generation of the alert as follows:
1.Down Time: Which will get values in minutes/hours -> This value determines the after how much time once an agent is down, an alert should be raised.
2.Notification Frequency Type: Which will get values in minutes/hours ->This value determines how frequently an alert should rise. Once the agent’s down condition is met.
3.Email: Which gets multiple mail ID’s separated by comma. -> The Mail ids to which alert should be raised once the FileGPS Entity is down for specified down time which is configured above.
4.Notification Days: It should take two-values weekdays or all days. -> This determines whether the alert should be raised on the weekdays or all the days.
5.Agent ID: we need to select an agent id to which we are checking for the data and generating
the Alert. In the below figure user has configured the creation of Agent Config Alert as follows:
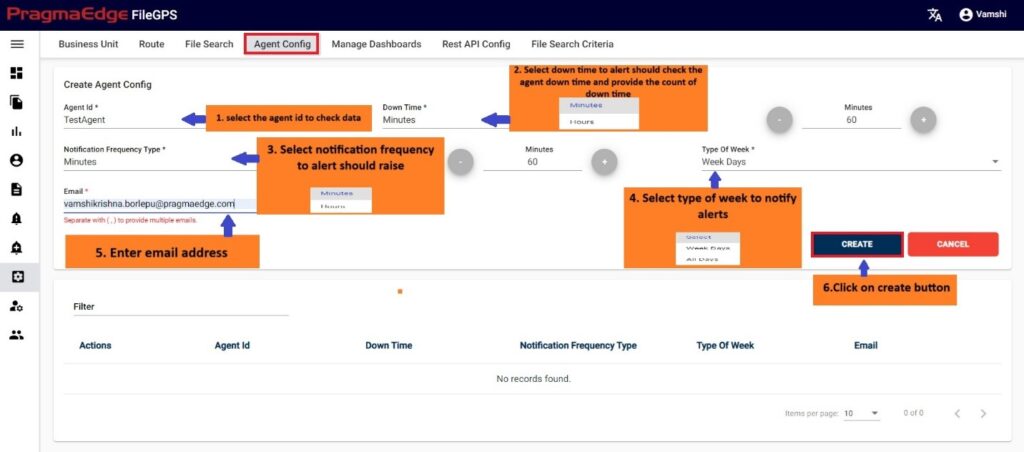
Successful creation of Agent Config will display the Success message as shown below.
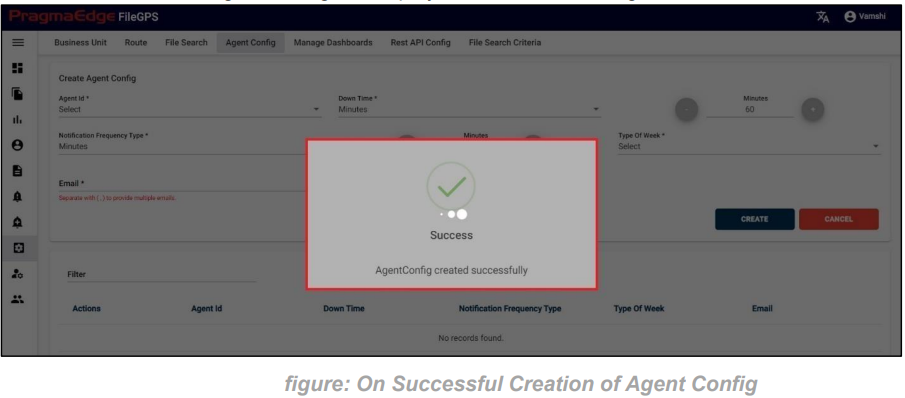
In the Manage Section, users have edit/delete options to perform on Routes as shown in below figure.
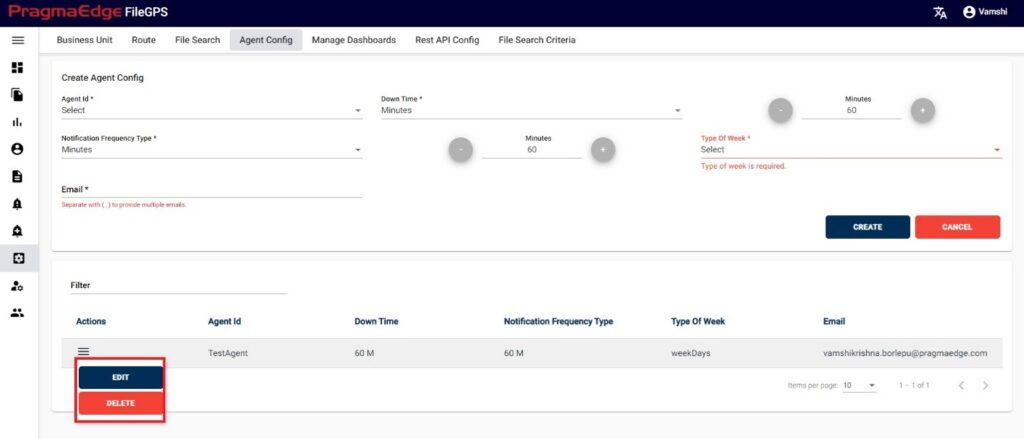
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the Route details. For example, Route that was created previously could be modified, by clicking on the edit option, consequently the page will be navigated to create page module where user could change details as per requirement.
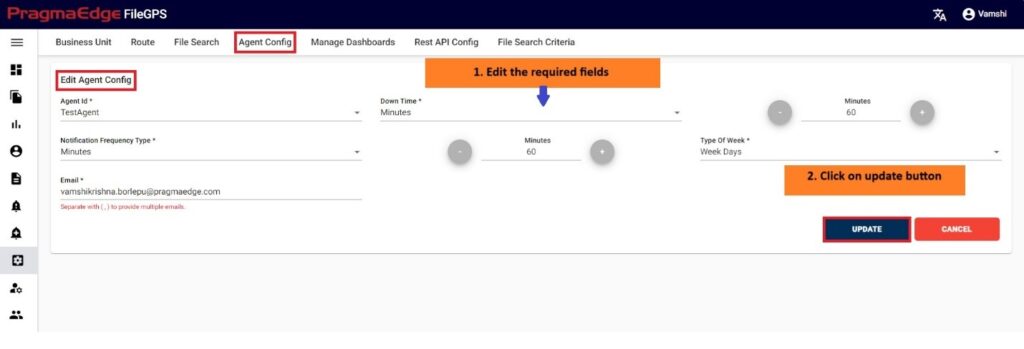
‘Update’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the Route details as shown in figure below.
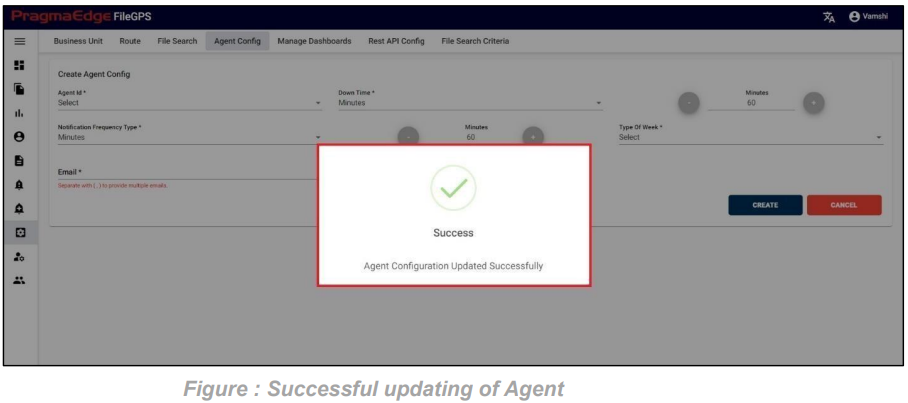
Route record could be permanently deleted with the ‘DELETE’ option as shown in the figure below.
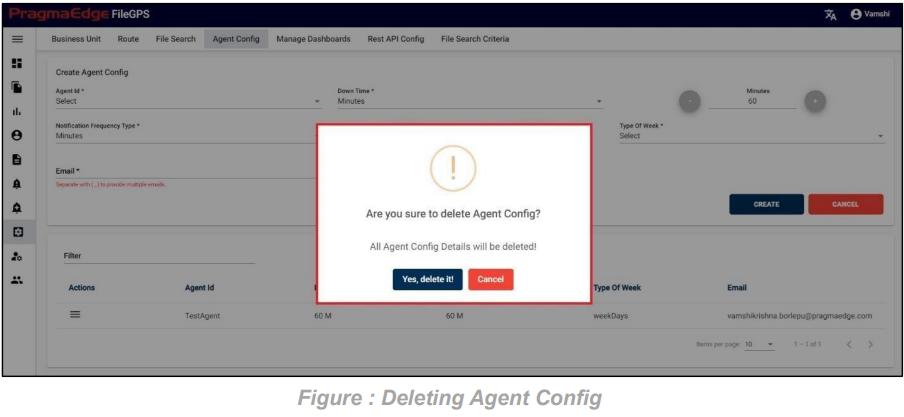
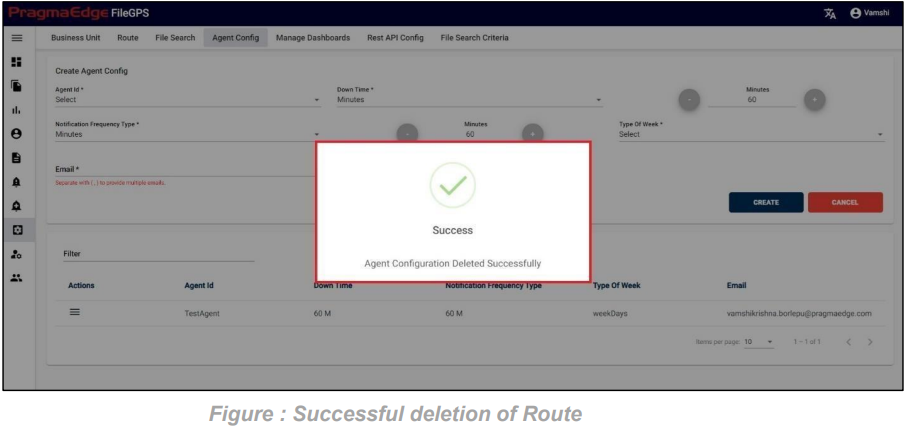
12. Administration:
12.1. Retention Policy:
Path:
Login Administration
Retention Policy
The administrator has the capability to create a retention policy via user interface as shown in the figure below. Within this UI, the administrator can select a specific table and define the default number of days. The implemented policy will govern the deletion of data from the selected table based on the specified number of days. This feature enables the efficient management and automated removal of data according to the established retention criteria.
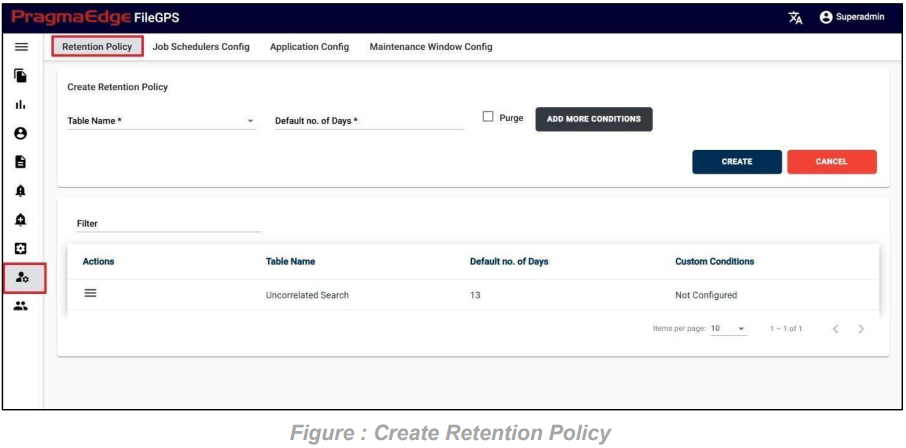
We can configure retention policies for the following three tables:
1. File Search
2. Queue Depth Search
3. Uncorrelated Search
Each of these tables may have unique data retention requirements, and by configuring retention policies for them, we ensure that data is managed and deleted based on the specific criteria we define. This helps in maintaining data relevance, optimizing storage, and adhering to any regulatory or business requirements regarding data retention and removal.
File Search Table:
In the “Create Retention Policy” screen, Select File Search from the “Table Name” dropdown menu. Enter a positive number of days in the “Default Number of Days” field. The specified data retention configuration for the File Search table will result in the deletion of data, excluding the data from the last specified number of days. For instance, if 5 days are specified, all the data in the File Search table, except the data from the last 5 days, will be deleted.
As an illustration, choose the “File Search” table from the Table Name dropdown. Enter ’30’ in the Default Number of Days field and proceed to click the “Create” button. This action will generate a retention policy for the “File Search” table, as depicted in the figure below.
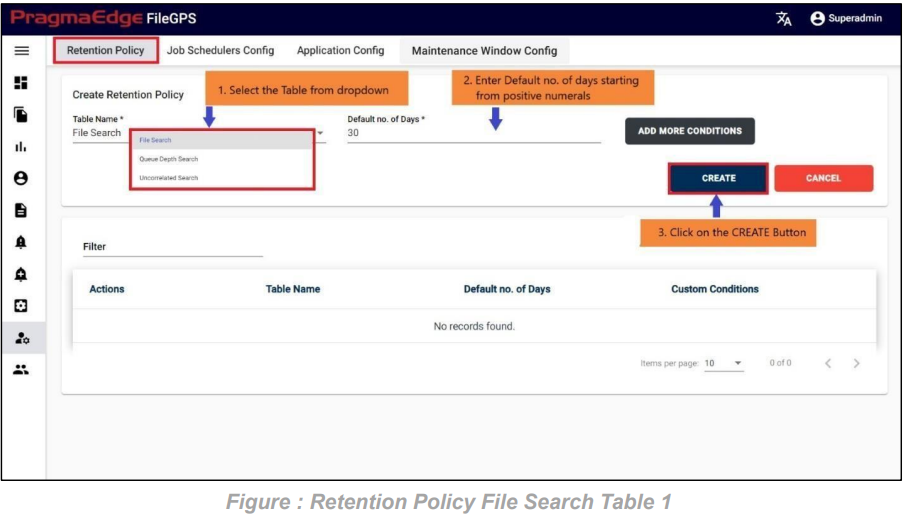
Additionally, users have the capability to create a retention policy for individual columns within the selected table, such as the “File Search” table.
For instance, users can establish custom conditions for the selected table. By choosing a column name from the available “Column Name” options, entering a value in the “Column Value” field, and specifying the number of days in the “No. of Days” field, the user configures a retention policy. This ensures that data corresponding to the specified column name in the previously selected table will persist for the specified duration.
As illustrated in the figure below, the user has configured a custom condition for the “clientname” column with the value “ACME” for a duration of 14 days. Consequently, data corresponding to this condition will be retained for the specified 14-day period, while the remaining data will be subject to deletion.
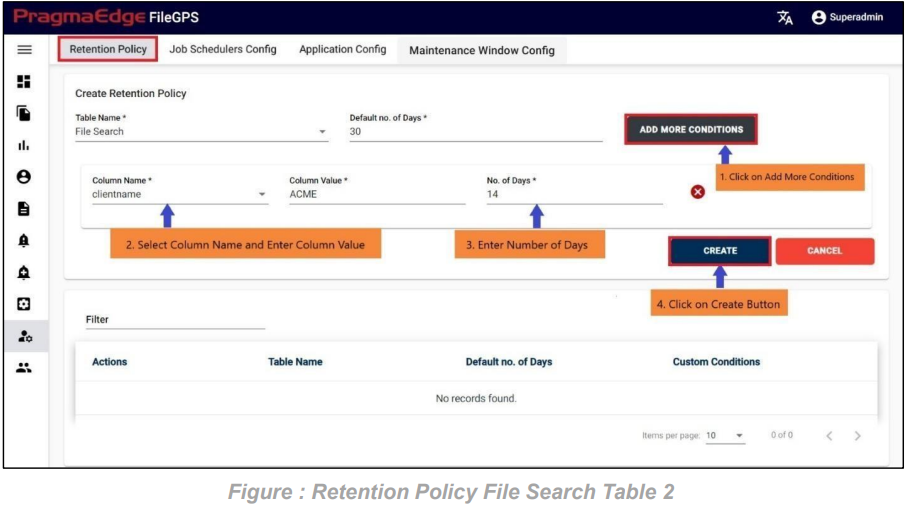
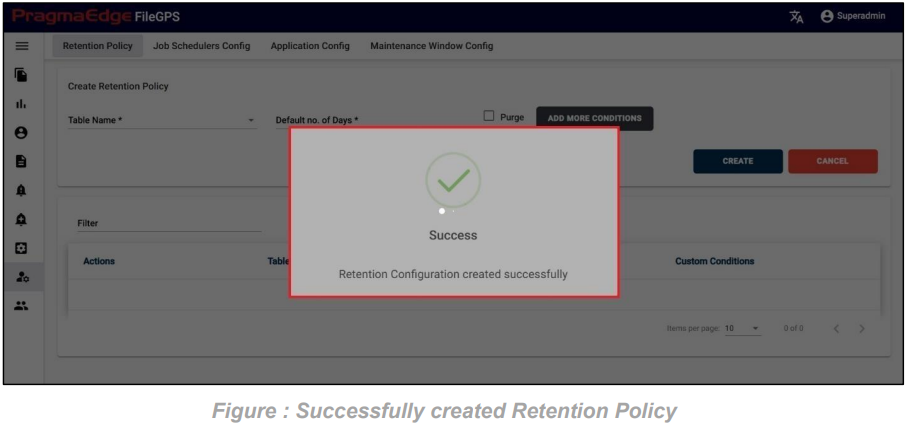
Users have the ability to view, edit, update, and delete the retention policies they have created. This empowers users with full control and flexibility in managing their configured retention policies based on evolving requirements.
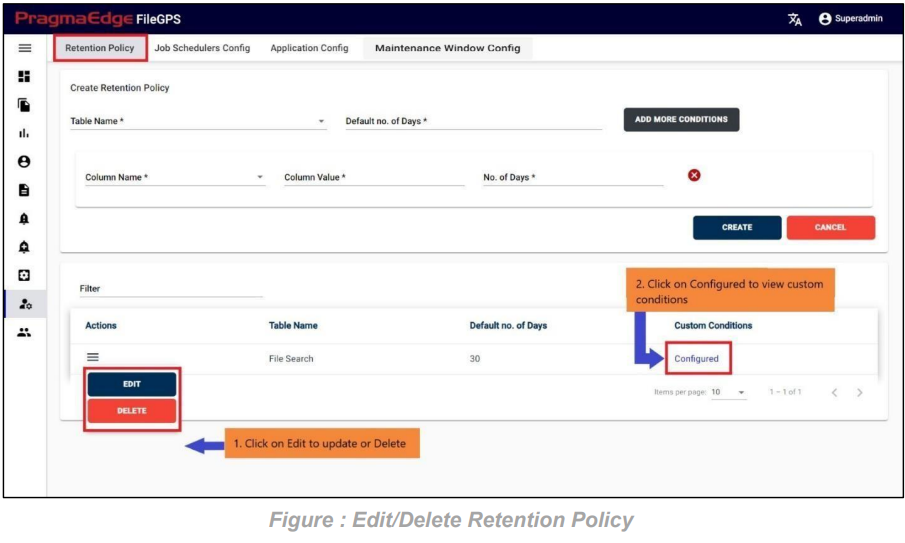
As depicted in the figure below, the user has modified the “Number of Days” in the custom conditions, changing it from 14 to 15. This adjustment reflects an update to the retention policy, allowing for the extension of the specified duration for data retention.
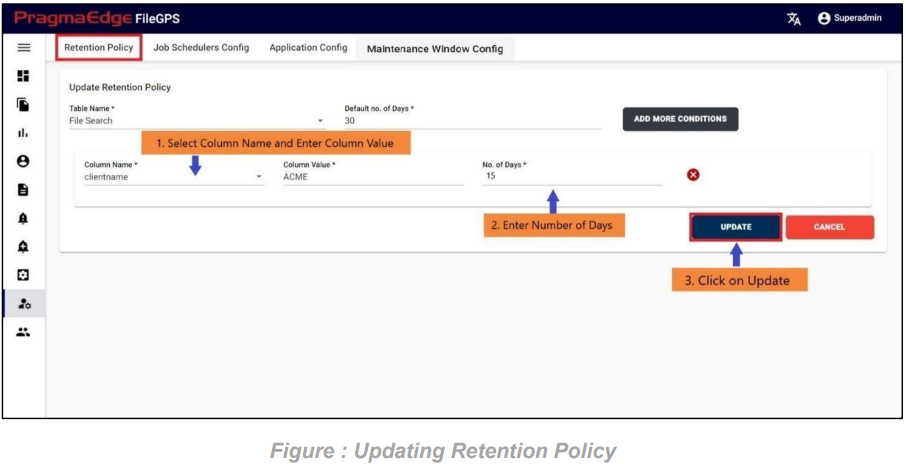
Application will update the retention policy details as shown in the figure below.
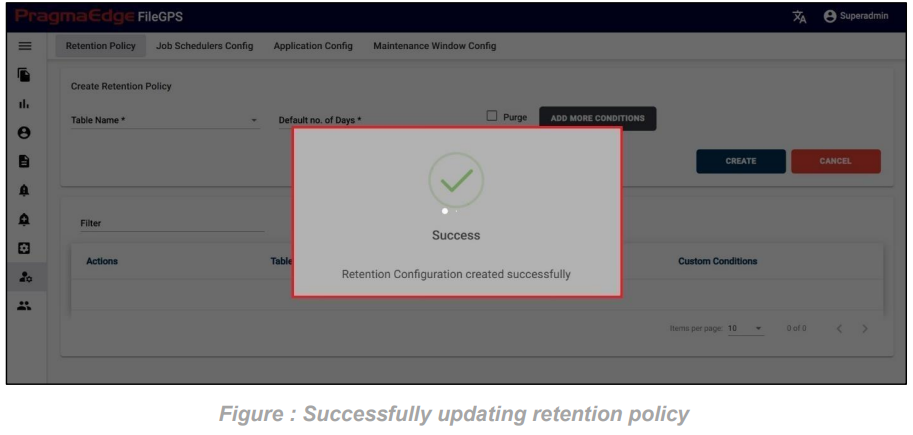
As shown in Figure 221, users can click on ‘Delete’ to remove the selected retention policy.
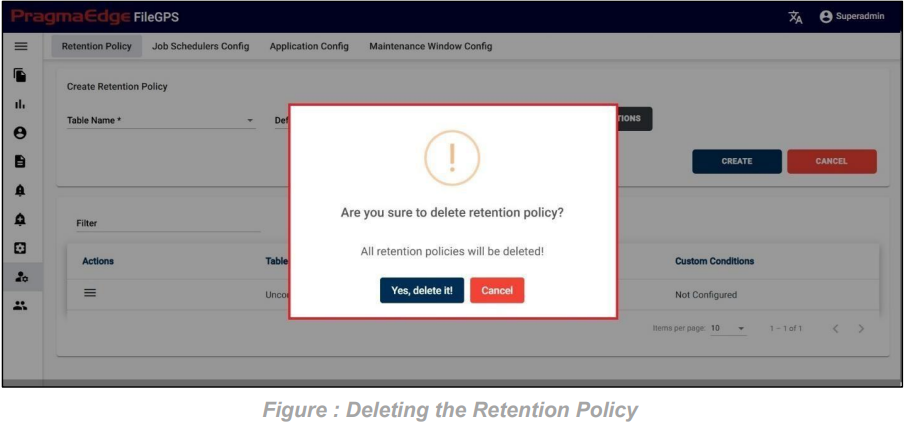
The File Search Retention Policy is successfully deleted as shown in the below figure.
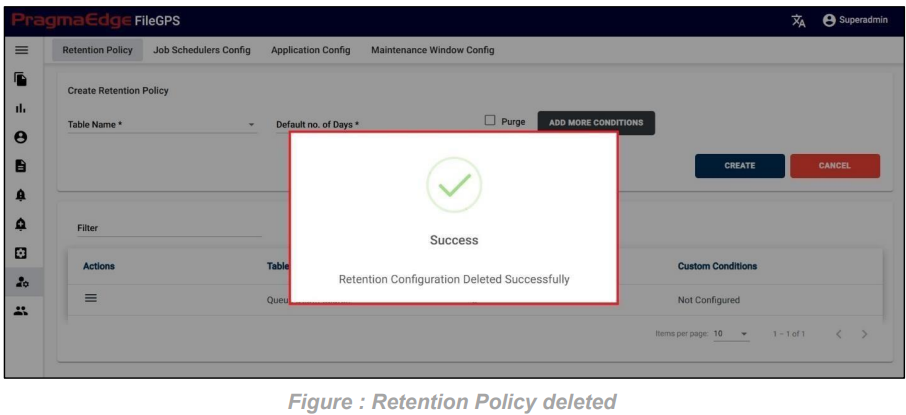
Note: Similarly, we can configure retention policy for Queue Depth Search and Uncorrelated Search tables.
12.2. Retention Policy purge feature:
The Retention Policy Purge Feature allows users to efficiently manage and customize data retention in the FileGPS system. Follow these steps to configure and use this feature
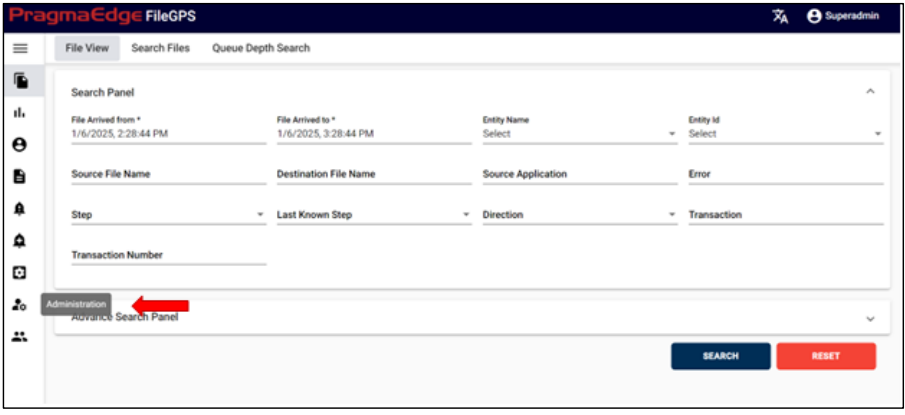
1) Accessing the Administration Panel:
• Log in to the FileGPS system.
• Navigate to the Administration Panel on the left-hand side menu.
2) Finding the Retention Policy Option:
• After clicking on the Administration Panel, locate the Retention Policy option in the top navigation bar and click on it.
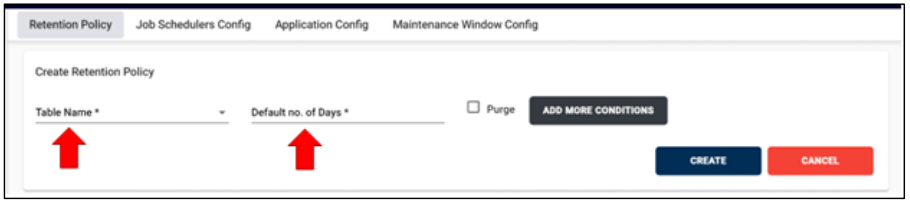
3) Creating a New Retention Policy:
• On the Retention Policy page, you will see the option to Create Retention Policy. Click on this option to proceed.
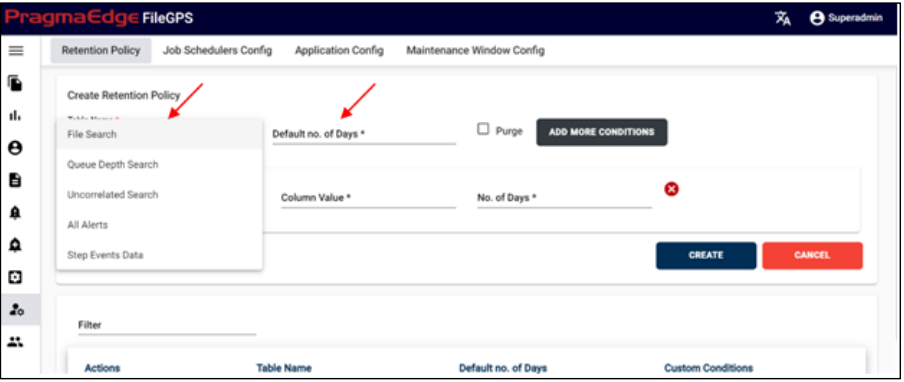
4) Selecting a Table for the Retention Policy:
• A list of tables will be displayed. Select the appropriate table based on your requirements. Enter the default number of days for which the data should be retained.
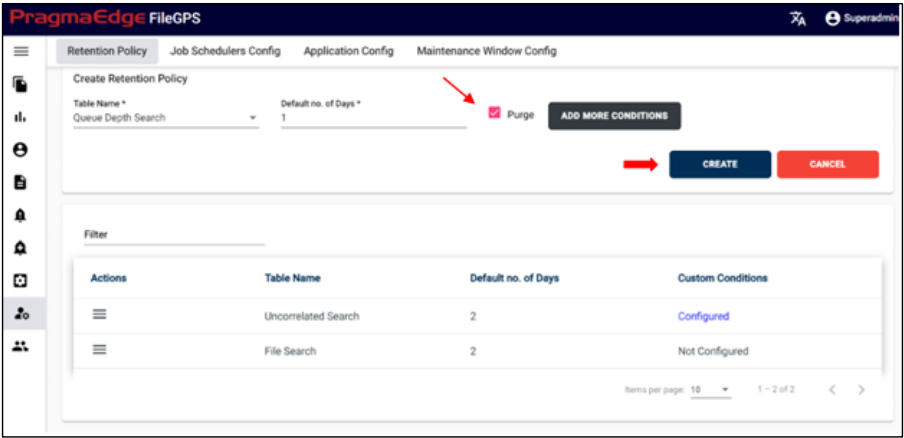
5) Enabling Purge for a Table:
For example, if you select the Queue Depth Search table:
Specify the Default Number of Days (e.g., 1).
Enable the Purge option.
Click on the Create button.
6) Viewing and Managing Created Policies:
• After creating the retention policy, it will be stored and visible on the Retention Policy page.
• You can review and manage all the policies from this page.
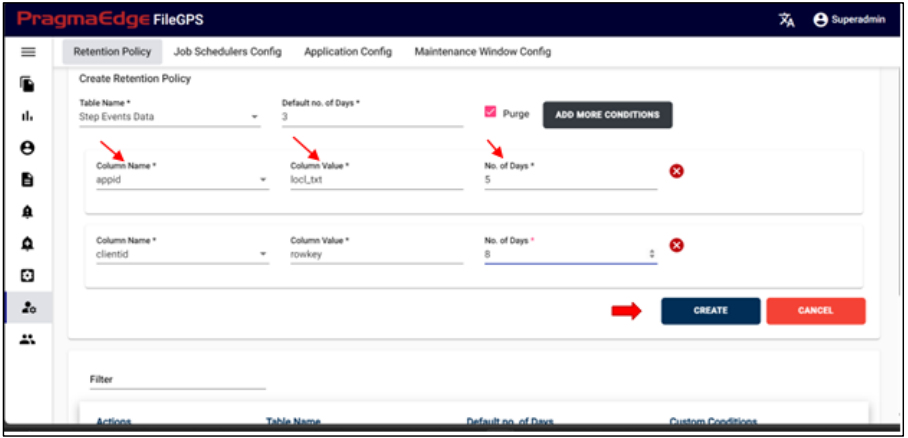
7) Adding Custom Conditions:
• To add specific conditions for purging, click on the Add More Conditions button.
• Enter the required Column Name, Column Value, and the Number of Days for which the data should be retained.
• Click on Create to save the customized policy.
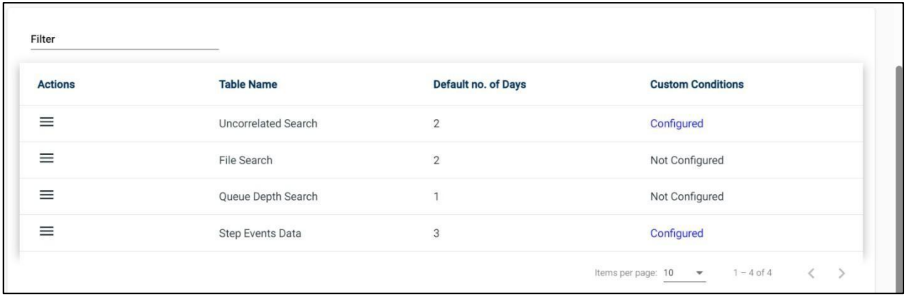
8) Reviewing Customized Policies:
• Once the custom conditions are added, you can view and manage all the tables with the customized retention settings on the Retention Policy page.
12.2. Job Schedulers:
Path:
Login Administration
Job Scheduler Config
Users now have the capability to observe the scheduler status (backend job status) and manage them directly from the FileGPS UI. This includes functions like pausing, resuming, and updating the scheduler running time. Furthermore, users can access comprehensive details about the jobs, encompassing job name, description, last and next timestamps, scheduler type, and more.
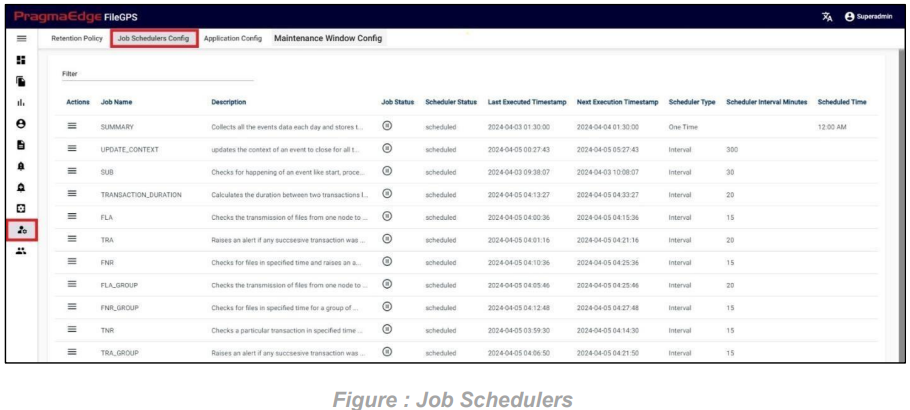
The Actions tab offers options to edit the scheduler status, scheduler type, interval minutes, and scheduler time for the respective backend job.
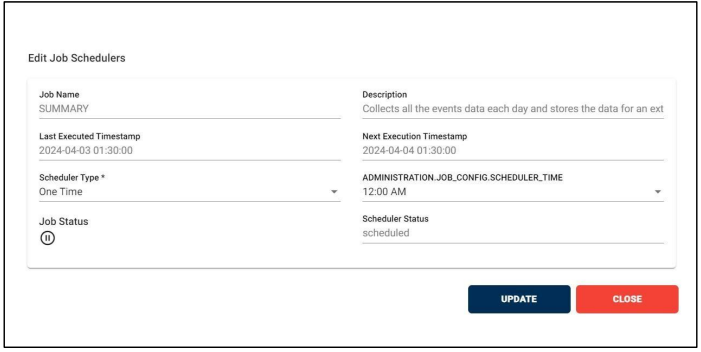
In the image above, we observe that the SUMMARY job is scheduled as a “One Time” scheduler, which runs daily at 12:00 AM, and the job status is currently running. Here, we can update the Scheduler type, Scheduler time/minutes, and Job Status.
The Job Name refers to the name of the backend job.
The Description provides brief information about the corresponding backend job.
The Job Status provides information about whether the job is in a running state or paused.
The above job SUMMARY is in Running State.
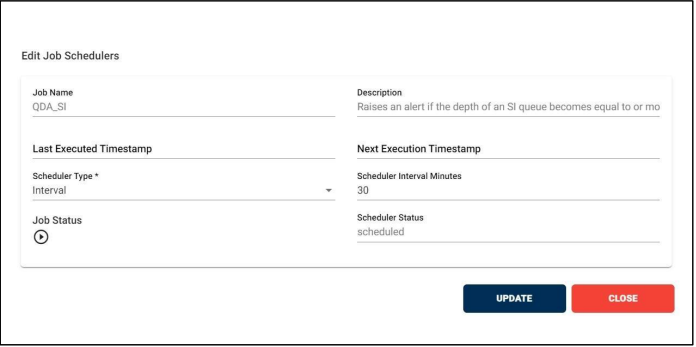
The above job QDA_SI is in Pause State.
The Scheduler Status provides information about whether the scheduler is scheduled or paused.
The Last Executed Timestamp indicates the time when the scheduler last ran.
The Next Execution Timestamp indicates when the scheduler will run next.
We have two types of schedulers available in our Job Schedulers module.
1. One Time: When configured as a “One Time” scheduler, we specify a particular time for the scheduler. This results in the job running once every day at the designated time. From the Actions tab, we can modify the Scheduled Time.
2. Interval: When configuring the scheduler type as “Interval,” we must specify the interval duration in minutes. This ensures that the job runs at regular intervals based on the specified duration. We can modify scheduler interval minutes from Actions tab.
12.3. Application Configuration:
Path:
Login Administration
Application Config
Users can configure application configuration directly from the FileGPS UI. This functionality includes adding, updating, and deleting YAML configurations through the Application Configuration page in the Administration Module.
To create a new application configuration, input the Key, Value, and Config parameters in the Create Application Configuration panel. Then, click on the Create button to finalize the creation of the new application configuration as shown in the below figure.
The application config is successfully created as shown in the below picture.
To edit or delete an application configuration, simply expand the desired configuration from the list. Then, make the necessary changes to the key and value fields, and click on the “Update” button to save the updated configuration. If you wish to delete any key from the config, click on the “Delete” button instead.
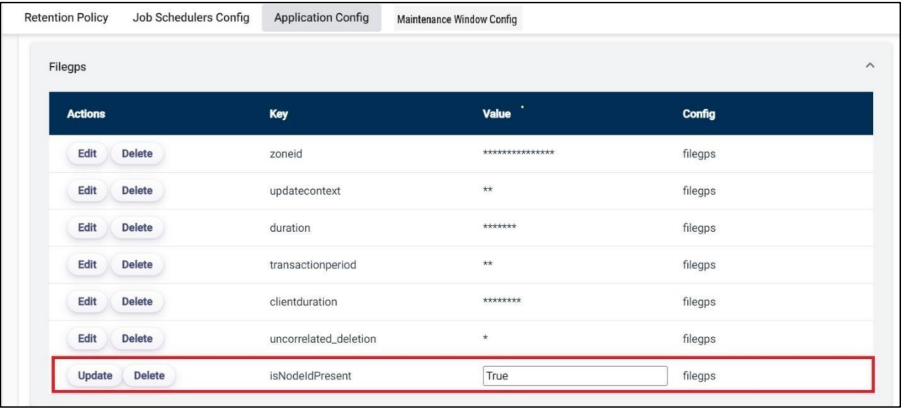
Click on the Update to successfully update the application config.
12.4. Maintenance Window:
Path:
Login Administration
Maintenance Window
The Maintenance Window enhances the flexibility and efficiency of alert management within the system. This feature allows users to create Maintenance Alerts, which temporarily pause existing alerts during specified time periods.
In the Alert Management module, users configure various alerts such as FNR, TNR, SLA and Subscription etc., with defined start dates, end dates, start times, and end times to monitor files or transactions within a specific time window. When a Maintenance Alert is created, it overrides these active alerts for the duration of the maintenance window.
During this time:
• The original alerts are paused.
• The system does not check for files or transactions within the specified time window.
This functionality ensures that the system remains unaffected by scheduled maintenance activities, preventing unnecessary alerts or disruptions during planned downtime.
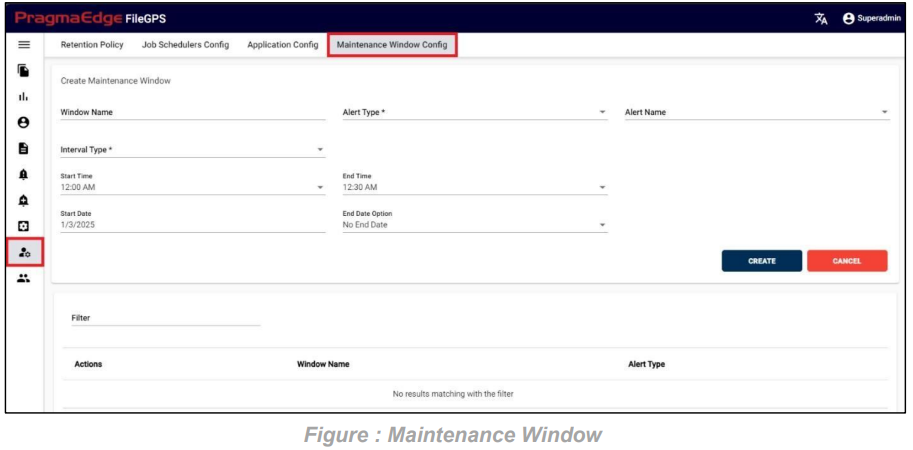
12.4.1 Types of Maintenance Window Alerts:
The Maintenance Window feature supports two types of alerts, providing users with flexibility based on their needs:
All Alerts:
This option allows users to create a Maintenance Window that applies to all active alerts in the system. When selected, the system will pause the monitoring for all alerts during the specified maintenance time frame.
Follow these steps to create a Maintenance Alert:
1. Enter Alert Name:
Provide a unique and descriptive name for the Maintenance Alert.
2. Select Alert Type:
Choose the desired alert type. For applying the alert to all alerts, select ALL.
3. Select Interval Type:
Choose from the following interval types based on the required schedule:
a.Daily
b. Weekly
c. Monthly
d. Quarterly
e. Yearly
4. Set Start and End Times:
Define the time window during which the Maintenance Alert will be active.
5. Set Start and End Dates:
Specify the start and end dates for the Maintenance Window. If the alert is indefinite, you can select the No End Date option.
6. Save the Alert:
Once all fields are completed, click on the CREATE button to save the Maintenance Alert. The system will pause monitoring during the specified time intervals based on the selected configuration.
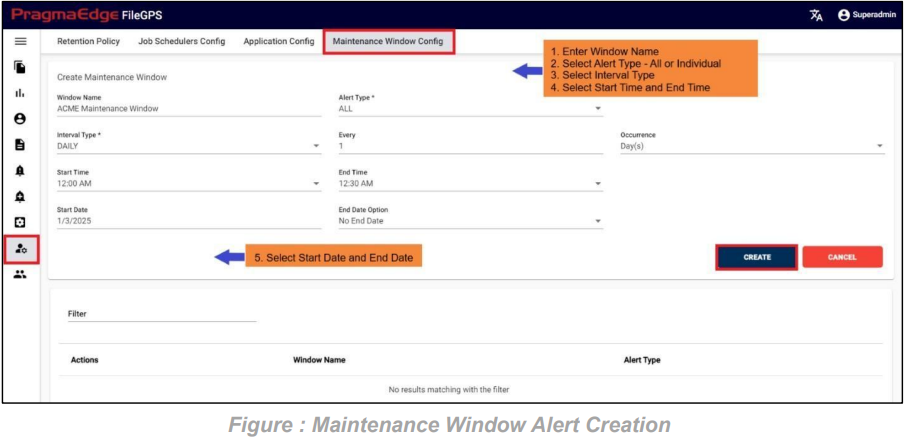
After completing the alert configuration and clicking the CREATE button, a dialog popup will appear, as shown in the image below.
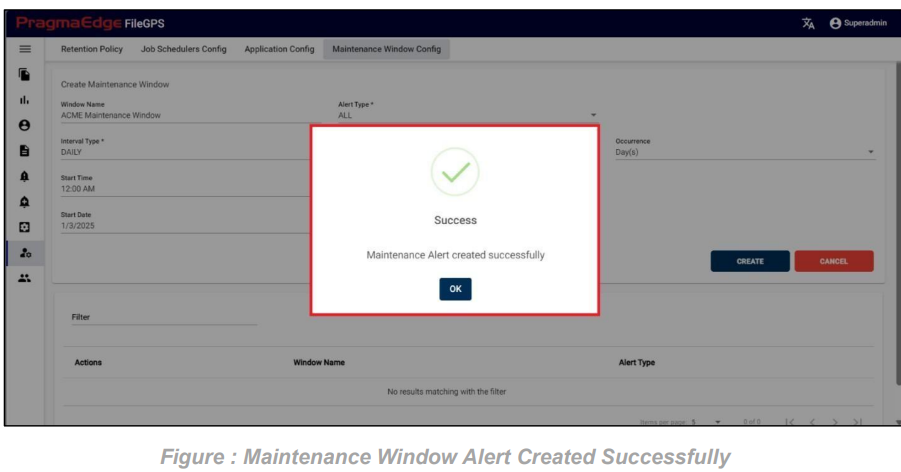
Once the Maintenance Alerts are created, they will be displayed in a list format, as shown in the figure below.
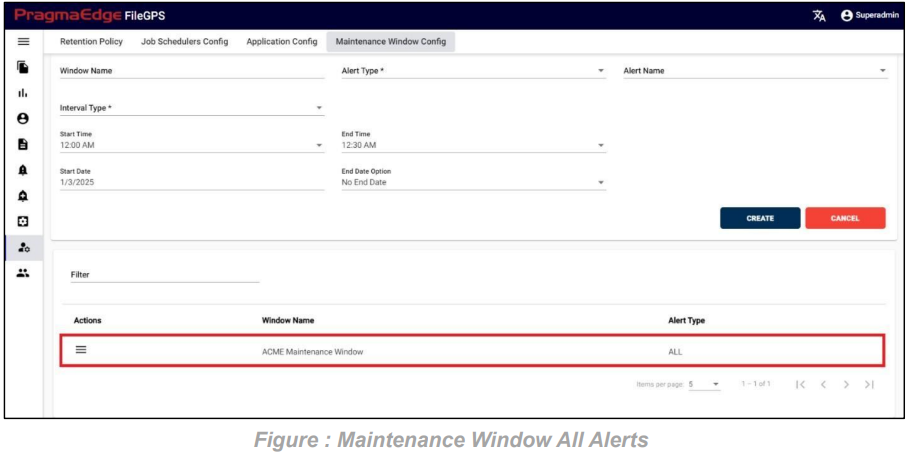
Individual Alerts:
This option enables users to set a Maintenance Window for specific alerts by selecting the alert type. Only the selected alerts will be paused during the specified maintenance period, while others will continue to function as usual.
Follow these steps to create a Maintenance Alert:
1. Enter Alert Name:
Provide a unique and descriptive name for the Maintenance Alert.
2. Select Alert Type:
Select an alert type from the provided drop-down menu as given below.

3. Select Alert Name:
From the available Alerts list, you can select ALL, a single alert, or multiple alerts by checking the corresponding boxes.

4. Select Interval Type:
Choose from the following interval types based on the required schedule: a. Daily
b. Weekly
c. Monthly
d. Quarterly
e. Yearly
5. Set Start and End Times:
Define the time window during which the Maintenance Alert will be active.
6. Set Start and End Dates:
Specify the start and end dates for the Maintenance Window. If the alert is indefinite, you can select the No End Date option.
7. Save the Alert:
Once all fields are completed, click on the CREATE button to save the Maintenance Alert. The system will pause monitoring during the specified time intervals based on the selected configuration.
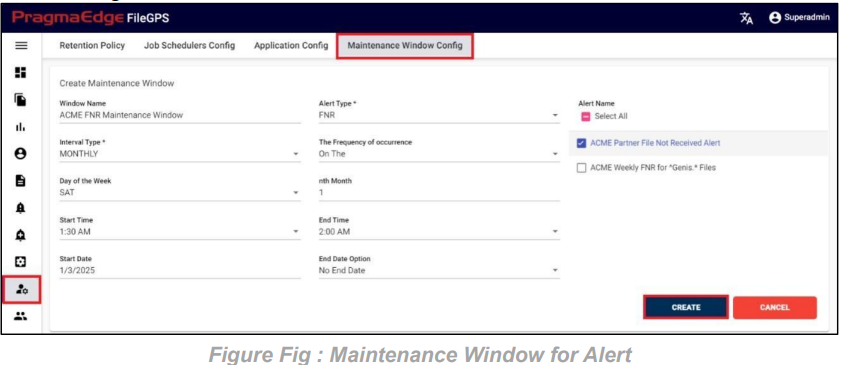
12.4.2 Maintenance Window Scenarios:
We have multiple time-based scenarios to configure the Maintenance Window, including Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Quarterly, and Yearly options.
Maintenance Window Daily ‘day(s)’ scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc., and need to select the ‘day(s)’ of the week So that the Maintenance Window will check daily scenario for every day also with time range ranges provided.
Example: Maintenance Alert is configured on every day on all days of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.

Figure : Maintenance Window for Daily day(s) scenario
Maintenance Window Daily ‘Weekday(s)’ scenario:
In this scenario we select the expected time ‘Daily’. After selecting it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week to consider as integers: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the ‘weekday(s)’ of the week So that the Maintenance Window will check daily scenario for every weekday also with time range provided.
Example: On every day on weekdays of the week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

Maintenance Window Weekly between scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘between’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘from weekday’ and ‘to weekday’ which have the days of the week example: Monday, Tuesday etc. So that the Maintenance Window will check weekly in between the selected weekdays with also time range provided
Example: Here we can check 2 scenarios as same week and cross week
Same week: checks on from day (Monday) to today (Thursday) from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
Cross week: checks on from day (Friday) to today (Monday) from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
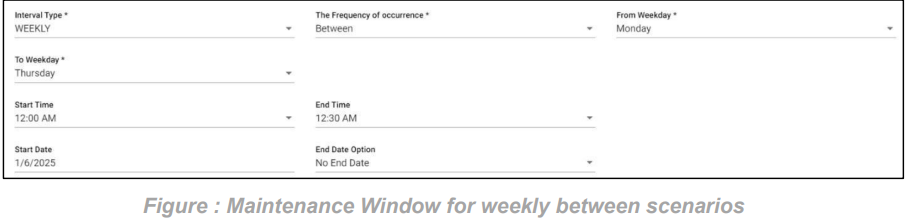
Maintenance Window Weekly day of the week scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘weekly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Day of the week’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘every’ count of the week as an integer: 1, 2 etc. and need to select the days of the week So that the Maintenance Window will check weekly scenario for every week on the selected days also with time range provided.
Example: On the Monday and Tuesday of every week from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
Note: We can select multiple days of week to check Maintenance Window.
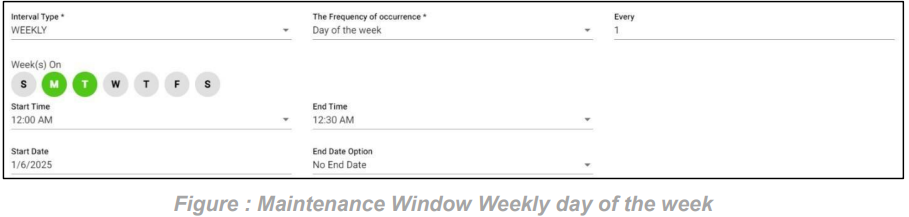
Maintenance Window Monthly on day scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On Day’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the ‘nth Day’ of particular day in month as integers: 1, 2 etc. and ‘nth month’ of particular month count. So that the Maintenance Window will check monthly scenario on the selected day of the particular month also with time range provided.
Example: On the 1st of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM
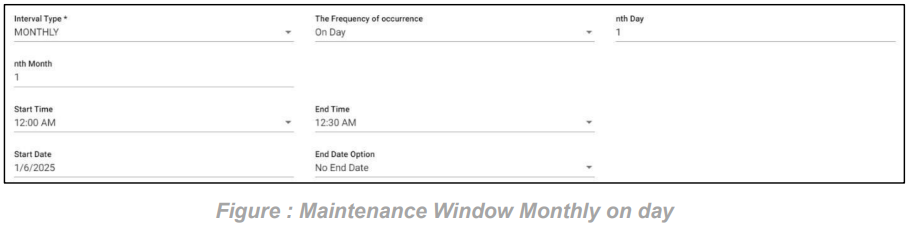
Maintenance Window Monthly on the scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘monthly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also ‘nth month’ count of month. So that the Maintenance Window will check monthly scenario on the selected day on the particular week of month also with time range ranges provided.
Example: On the first Sunday of every month from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.
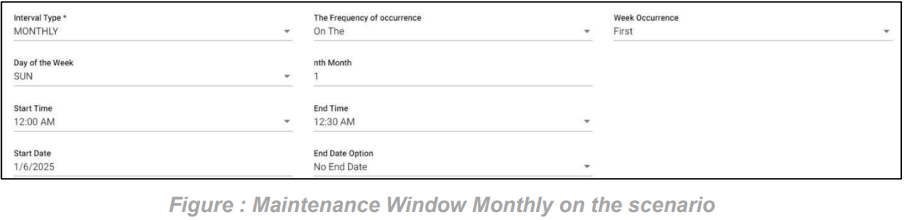
Maintenance Window Quarterly scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘Quarterly’. So that the Maintenance Window will check Quarterly scenario on quarter end day with time range provided.
Example: On quarter end date from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM

Maintenance Window Yearly Every Scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘Every’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the month as January, February etc. and also ‘nth Day’ of particular day of month. So that the Maintenance Window will check yearly every scenario on the selected day on the particular day of month provided considering every month count also with time range provided.
Example: On the first of every January for every 1 year from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.
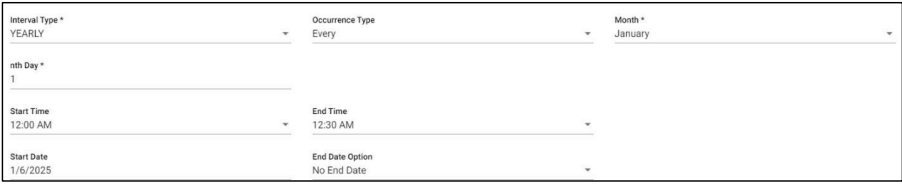
Maintenance Window Yearly on the Scenario:
In this scenario we selected the expected time ‘yearly’ and frequency of occurrence as ‘On The’. After selecting these it will ask you to select the occurrence of the day in month as first, second etc. and day of week of particular month as Sunday, Monday etc. and also selects the month of the year. So that the Maintenance Window will check yearly on the scenario on the selected day on the particular week of month in a year also with time range provided.
Example: On the first Sunday of January every year from 12:00 AM to 12:30 AM.
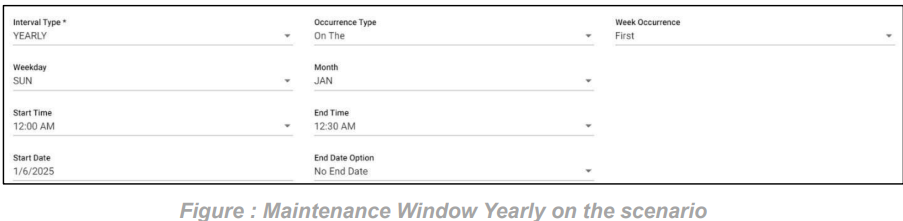
13. Access Management:
Path:
Login Access Management
Users can create and manage users, also create and manage groups in this Access Management module. It has four sub modules as follows:
1. Create User
2. Manage User
3. Create Group
4. Manage Group
13.1. Create User:
In this screen, we can create various users by giving information about them and by assigning their role and we can also assign business Partners and groups to it.
There are Seven types of users:
1) Super Admin
2) Admin
3) Business Admin
4) Business User
5) Business User Executive
6) Data Admin
7) File Operator
‘Super Admin’ is a privileged user with unrestricted access to the entire application and all its data.
‘Data Admin’ has access to all modules of the application, except the administration, access management module, and can view all data.
‘Admin’ can create various users such as Admin, Data Admin, Business Admin, Business User and Business User Executive, File Operator and give access privileges to them. He will have access to Dashboard, configure and access management only. However, the access privileges vary hierarchical pattern.
‘Business Admin’ He will have access to the entire application other than configure, administration and access management and can view the data of assigned business units and groups and Un assigned Entities.
‘Business User’ He will have access to Dashboard, Search files, reports, SLAs and Alerts modules and can view the data of assigned business units and Un assigned Entities.
‘Business User Executive’ has access to all modules of the application, except the administration, access management module, can view the data of assigned business units and groups and Un assigned Entities.
‘File Operator’ has access to all modules of the application, except the administration, access management module, can view the data of assigned business units, groups
Path:
Login Access Management
Create User
As discussed earlier in this screen we can create user by giving information accordingly. In the below Fig, Admin user has created a User ‘FileGPS User’ and had given access privileges to him.
In the Create User Module User can assign two types of Business Units, they are ‘Assign Business Unit All’ and ‘Assign Business Unit Group’. In Assign Business Unit All we can select a particular business unit after clicking on the above single arrow ‘>’ it will assign it to the user we are creating, now this user has access to all the groups in that business unit and all the entities in those groups. Similarly, we have double arrow ‘>>’ by clicking on it will assign all the business units in left section to the user we are creating.
In Assign Business Unit Group, we can select a Business unit Group and then we click on above single arrow ‘>’ to assign it to the user creating, the user has access to all the entities in that group.
Note: If we want to Assign all the business units or all the business unit groups, then we need to click on the above double arrow ‘>>’
Here we are creating a User ‘FileGPS User’ with the role of business admin and had given access privileges to him.
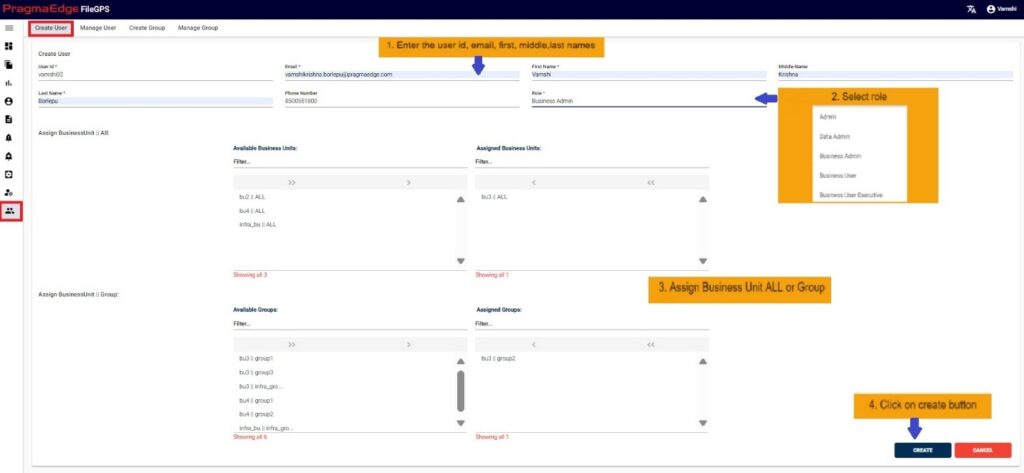
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| User ID | Created User ID |
| Password | Password |
| Email Id of the user | |
| First Name | First name if the user |
| Last Name | Last name if the user |
| Middle Name | Middle name if the user |
| Phone | XXXXXXXXXX |
| Role | Role Assigned |
| Status | Active/In Active |
| Assign Business Unit | Dual list box interchangeable |
| Assign Business Group | Dual list box interchangeable |
After assigning the information to the user click on the create button. It will create user accordingly. The below Figure refers to the successful creation of a User named ‘FileGPS User’.
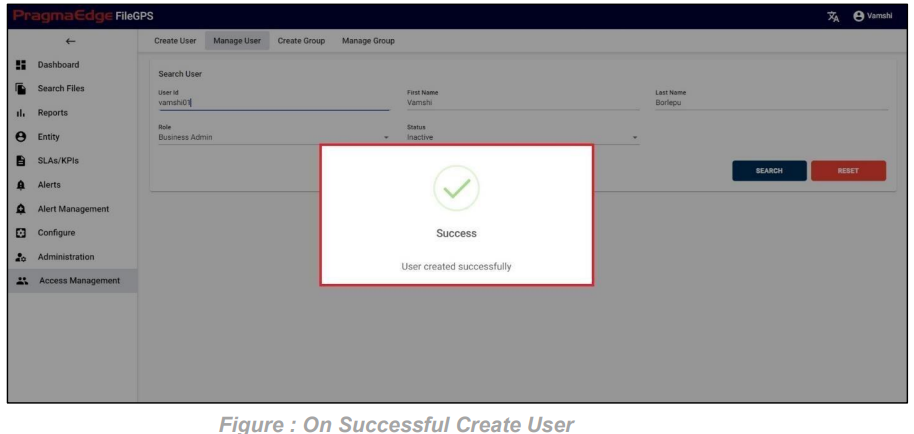
On successful user creation, success messages will be displayed as a notification where the input fields will be filled with previously created user details.
Below Figure Explains the access to list of modules that Super admin user has.
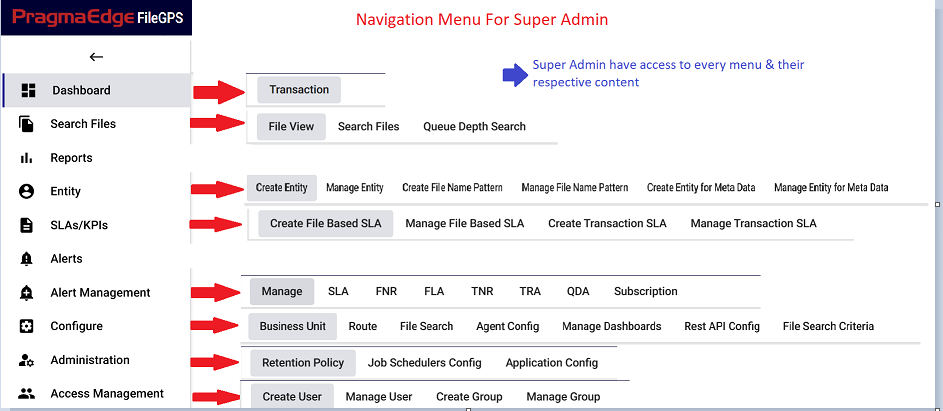
Similarly, as we have sub tab access according to the navigation menu. We will be having access restriction to other users as below figure shows the various roles that are present in the FileGPS application along with the access details.
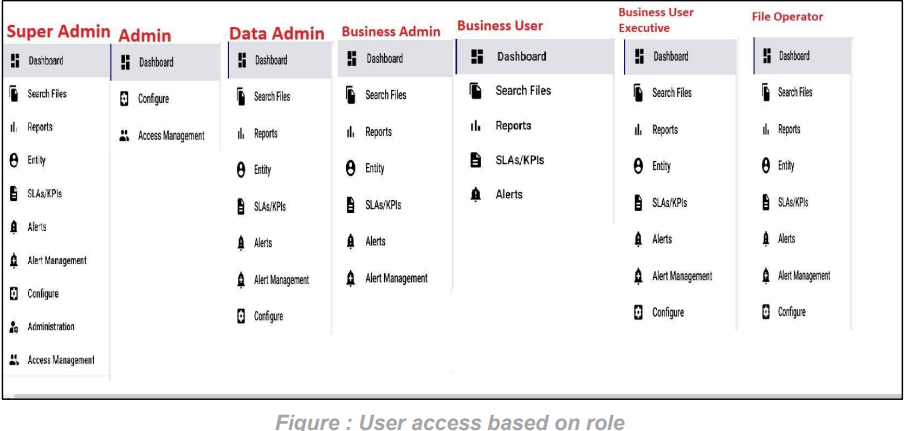
13.2. Manage User:
Admin, who has created a user can search the list of created users and provide access privileges to users. Super Admin has the privilege to Activate, Deactivate, update & delete the user.
Path:
Login Access Management
Manage User
In Manage User Section, Admin have Edit/Delete/Deactivate/Activate options to perform on Users as shown in below figure.
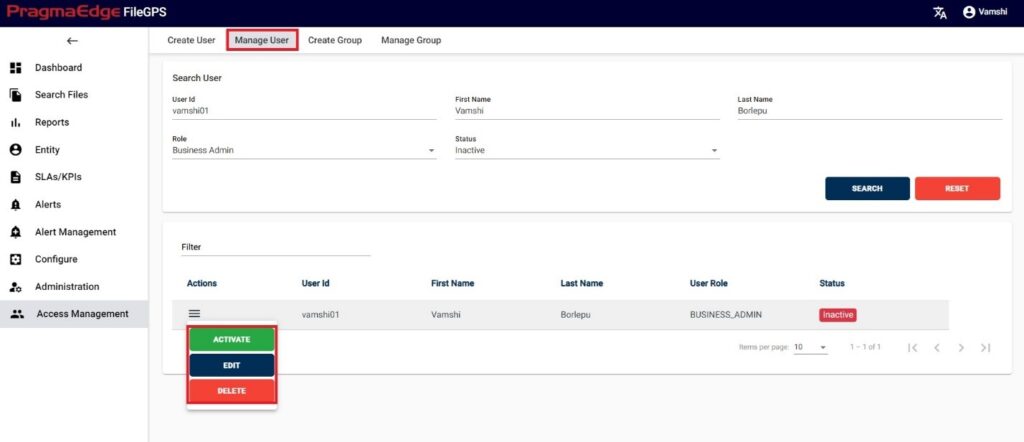
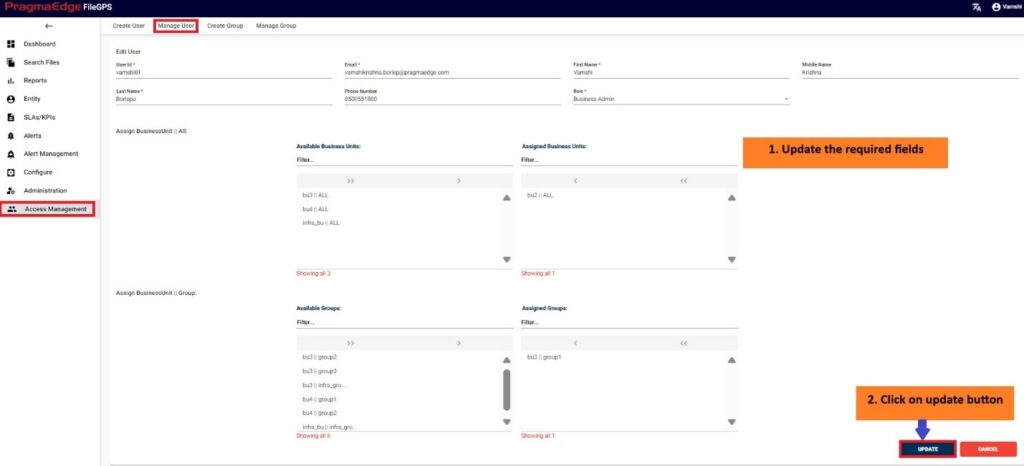
Note: User ID cannot be changed after successful creation.
In case of any modifications to the existing user details, the Update button saves and displays the success message as a notification where the input fields will be filled with updated user data as shown in below figure.
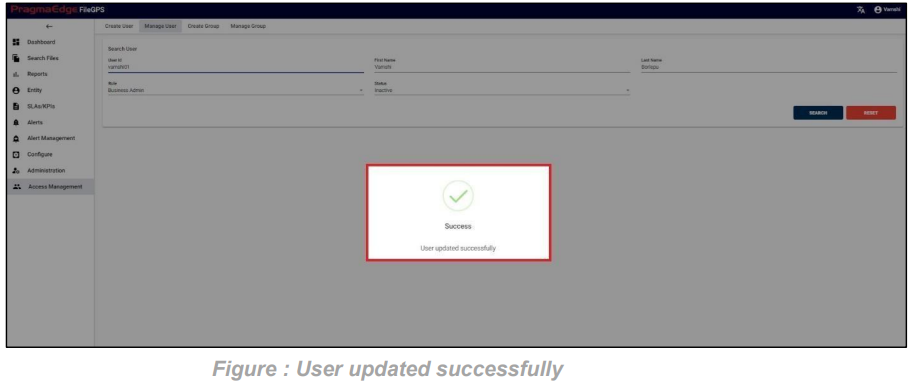
Super Admin will have access to list all the users and their account status (Active/Inactive) Super Admin can Deactivate the users with ‘Deactivate’ option as shown in below figure.
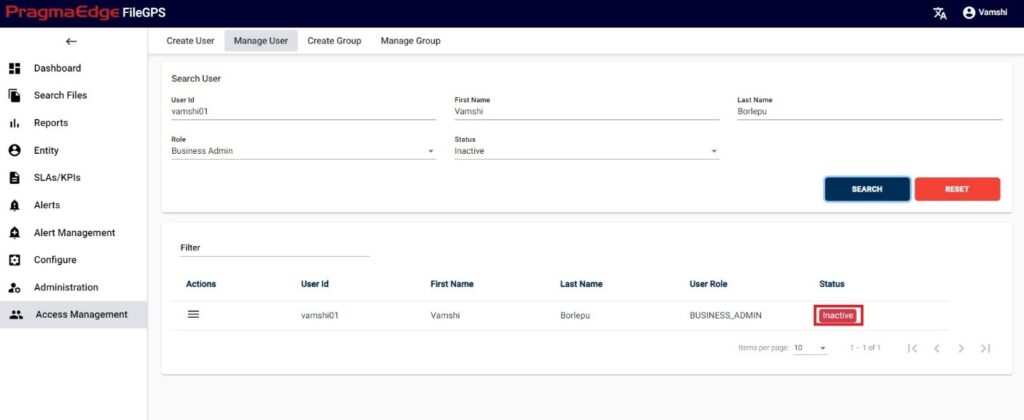
Super admin after clicking on the active/deactivate option the user states will be updated as shown in below figure

Super Admin has access to deleting any user if found to be inactive for a long period of time. User records could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure.
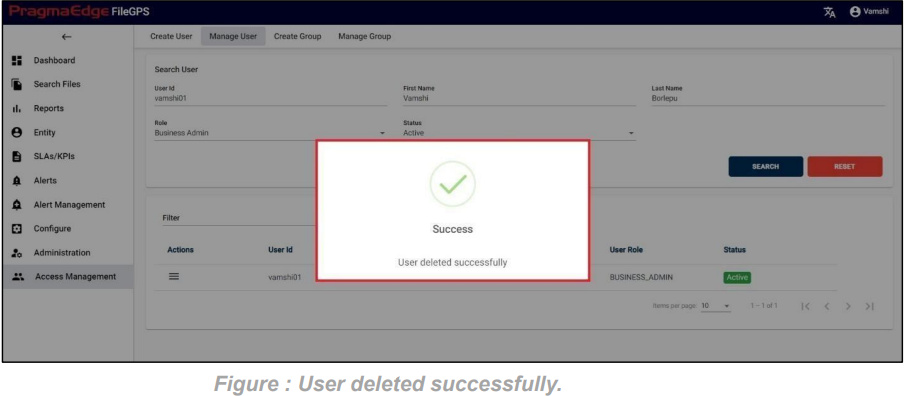
13.3. Create Group:
In Create Group, the user creates a Group by assigning Entities to it. So, a group of Entities is nothing but a Group here.
Path:
Login Access Management
Create Group
Admin can create user groups in this access management and assign the partners to it. In the below figure admin has configured the Group ‘ACME Group’ for the ACME Entity, Acme133 with Entity ID’s ACME1 and 123 respectively.
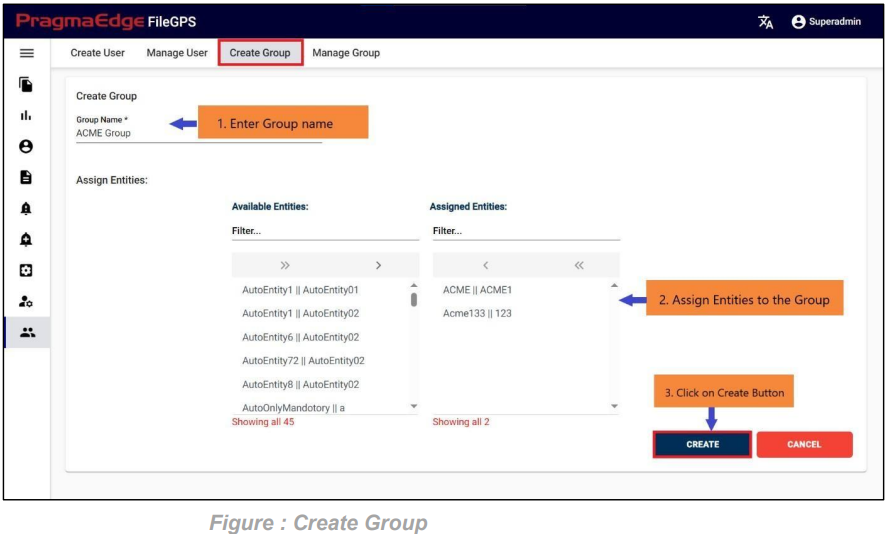
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Name | Name of the group assigned to the partner |
| Assign Partner | Manually add partner to the Entity/User |
| Save Group | Updates the changes |
| Cancel Group | Clear the values of the fields |
On successful group creation, a success message will be displayed as a notification where Group name will be displayed as shown below figure.
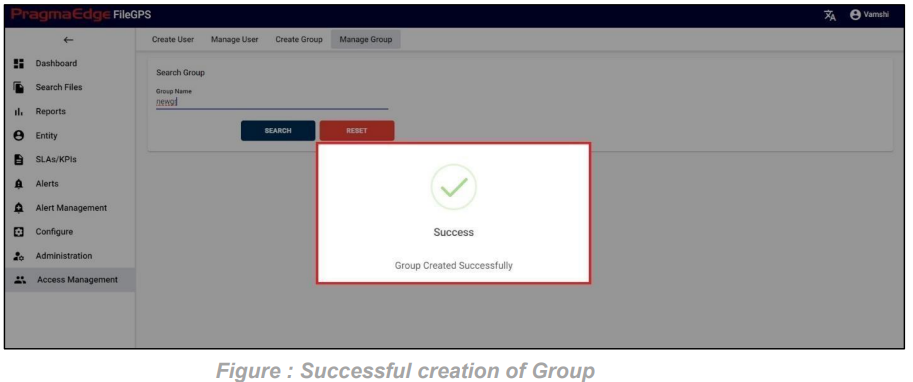
13.4. Manage Group:
In Manage Group screen, users have edit/delete options to perform on Group.
Path:
Login Access Management
Manage Group
Manage group helps in modifying the details after creation of a group and can delete the groups as shown in Figure below.
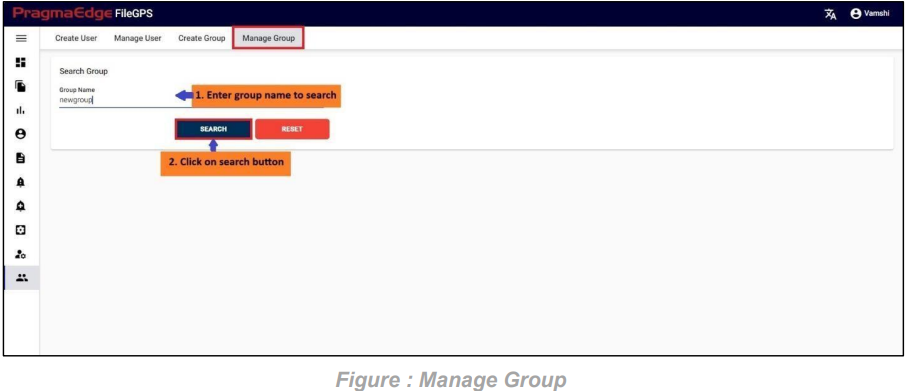
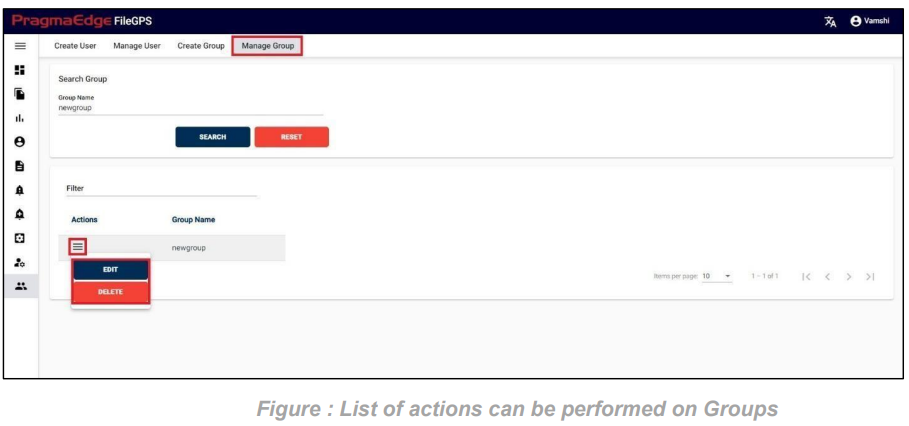
‘EDIT’ option is used to edit the Group details. For example, Group that was created previously could be modified, by clicking on the edit option, consequently the page will be navigated to create page module where user could change details as per requirement as shown in below figure.
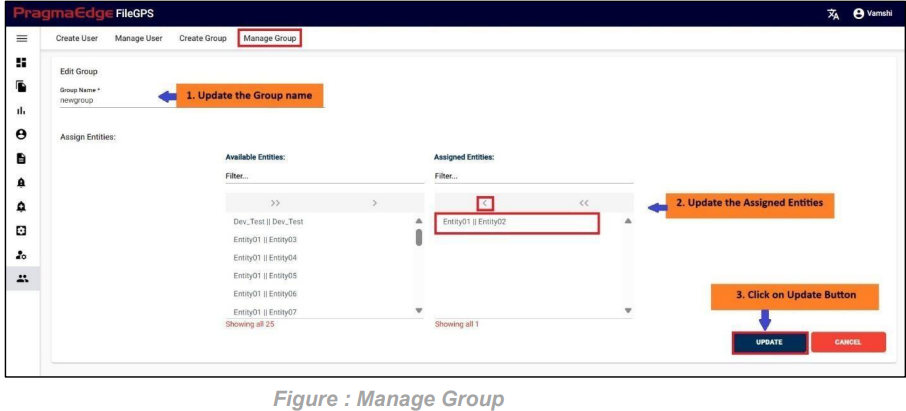
‘UPDATE’ button, after making the required changes, application will update the group details as shown in below figure.
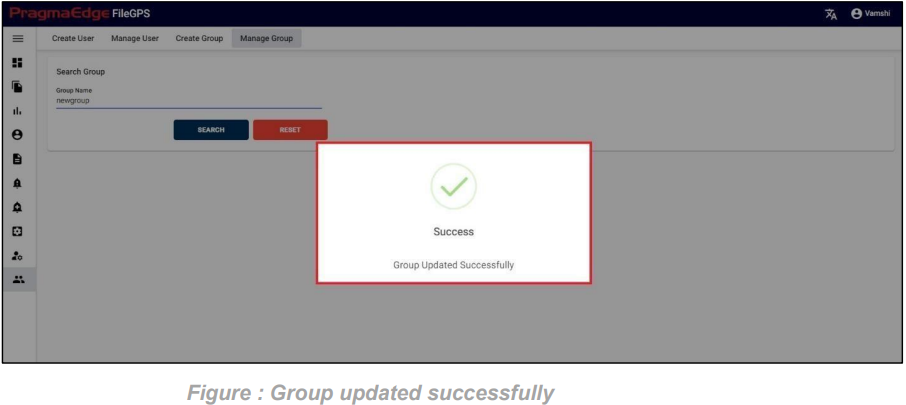
Group record could be permanently deleted with ‘DELETE’ option as shown in below figure.
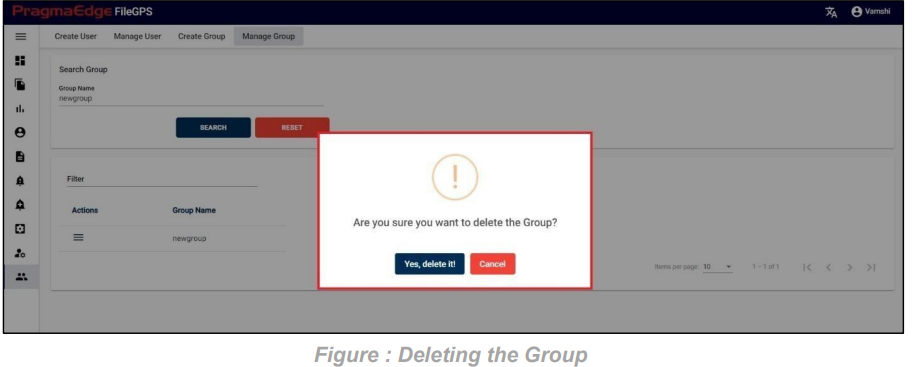
14. Features and Enhancement:
1. Maintenance Window for Alerts
- Allows users to pause active alerts (FNR, TNR, SLA, Subscription, etc.) during scheduled maintenance.
- Prevents unnecessary notifications by temporarily disabling alert checks.
- Ensures smooth operations during planned downtime.
- Retention Policy with Purge Option
- Users can configure Retention Policies to define how long data should be retained in the database.
- New Purge Option: When enabled, data deleted by the retention policy is stored in another table (same DB or another DB) for future reference.
- Provides better control over data lifecycle and compliance.
- File Not Received (FNR) Alert with Count Conditions
- The FNR alert notifies users when expected files are not received.
- New Count Conditions allow more precise alert configurations:
- Less Than – Alert if file count ≥ expected count.
- Less Than or Equal To – Alert if file count > expected count.
- Equal To – Alert if file count ≠ expected count.
- Greater Than – Alert if file count ≤ expected count.
- Greater Than or Equal To – Alert if file count < expected count.
- Enhances flexibility in monitoring file transfers.
- Multi-File Pattern Support for FNR Alerts
- Previously, users could configure only one file pattern per FNR alert.
- Now, users can configure multiple file patterns within a single alert.
- Transaction Not Received (TNR) Alert with Count Conditions
- The TNR alert notifies users when expected transaction count is not met as per configured count.
- New Count Conditions allow more precise alert configurations:
- Less Than – Alert if file count ≥ expected count.
- Less Than or Equal To – Alert if file count > expected count.
- Equal To – Alert if file count ≠ expected count.
- Greater Than – Alert if file count ≤ expected count.
- Greater Than or Equal To – Alert if file count < expected count.
- Rest Consumer changes
- Rest Consumer is a component designed to interact with RESTful web services, enabling efficient communication and data exchange between systems. It acts as a client that sends requests to REST APIs and processes the responses, facilitating integration with various web services.
- Features of Rest Consumer:
- Basic Authentication: Supports basic authentication to ensure secure access to REST APIs, protecting sensitive data during communication.
- SSL Integration: Implements SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt data transmitted between the client and server, enhancing security and preventing unauthorized access.
- Flexible Configuration: Allows customization of request headers, parameters, and payloads to meet specific integration requirements.
- Error Handling: Provides robust error handling mechanisms to manage and respond to various HTTP status codes and exceptions.
- Alert Name Text Limit Changes
- Extended Text Limit: The alert name text limit has been increased from 100 characters to 200 characters.
- Enhanced Flexibility: This change allows for more descriptive and detailed alert names, improving clarity and usability.
- FNR and TNR Window Configuration
- Extended Time Window: The configurable time window for FNR (File Not Received) and TNR (Transaction Not Received) alerts has been extended from 15 minutes to 30 minutes.
- Flexible Configuration: Users can now set the alert window to either 15 minutes or 30 minutes, providing greater flexibility in monitoring and alerting.
- SNOW Integration with FileGPS
- Enhanced Integration: SNOW integration with FileGPS has been improved to support seamless API integration.
- Customizable Alert Parameters: Users can now add SNOW-supported API details directly in the FileGPS alert creation body using the $ symbol followed by key=value.
- Simplified Configuration: This enhancement allows for easier customization of alert parameters, streamlining the integration process.
- FileGPS Alerts Traceability
- We have updated the alerts screen to provide full traceability of API and email alerts. The update includes the addition of the email subject and body, API URL, incident service used, API response code, API response status message, and API payload.